Sanitary standards for summer school health camps. Drinking regimen and its observance in kindergarten, school and camp in the summer
If you want to be healthy, then if you please, observe the drinking regimen. Doctors around the world do not get tired of recommending that we drink as much water as possible, but if an adult is free to dispose of his own body, then children are completely dependent on their elders. Does your child comply with the drinking regimen? And how are things going with it in his kindergarten or summer camp? After all, there you can not look after the child. Should parents worry about such things? And in general, how much water should a child drink per day?
For the little ones
If a baby has recently appeared in your family, then each stage of its development seems insanely important. And this is right, even if fanatical adherence to the precepts of children's doctors is not always reasonable. But the drinking regime is such a moment when it is worth listening to the professionals.
The fact that water is necessary for our body will not become news. The mode of its consumption helps to maintain the water balance at the proper level. A child's body is weaker than an adult, respectively, children are more likely to dehydrate. Because of this, they are at risk of developing many diseases. How younger child the higher the risks. And clean water washes every cell of the body, flushes out toxins. So, at the first request, the crumbs should be given to him to drink. It is better to limit the consumption of food "slag", which includes packaged juices, coffee, soda and sweet yogurts. 
How much do you need?
However, forcibly "shove" water into the child is not worth it. The daily need of a child's organism for life-giving moisture can be calculated based on age and weight. In particular, for a one-year-old baby, the drinking regimen involves the use of about 180 ml of pure water per kilogram of weight. With age, the need decreases slightly. Up to six years, about 120 ml per kilo is required. Schoolchildren already need about 100 ml per kg. It is good when the child has a small bottle with him. clean water. Let there be only 0.5 liters, but this volume will be enough for him until lunch. It is logical that in summer the child will drink more than in winter. Do not forget that drinking while eating is not healthy, as the functions of gastric juice are reduced. Try to teach your child the healthy habit of starting the morning with a glass of water and drinking several glasses in between meals. Such a life hack will help normalize bowel function and minimize the problem of excess weight. 
How to implement?
An adult weighing 70 kg should drink at least two liters of water daily. According to the drinking regime, in the morning you need to drink about 300-400 ml warm water. You can add some lemon juice. Such a volume of liquid replenishes the night loss and activates the metabolism with capillary blood flow in the tissues. Accordingly, the digestive system prepares for breakfast, since the digestive juices are 95% water. It is very useful to drink a glass of warm water 30 minutes before a meal, but after eating for about an hour you need to refrain from taking any liquid so as not to disrupt digestion. The rest of the amount of water should be evenly distributed throughout the day. Parents should teach their children to drink water regularly. So they take care of the health of the younger generation.
It's all about the organization
The organization of the child's drinking regime falls on the shoulders of adults. Instructions and orders will not achieve anything here. It's best to act own example. By the way, the habit of drinking is useful at any age. In the morning, offer your child a glass of water with lemon. Control fluid temperature. It should be moderately warm to gently wake up the digestive system and metabolism. Let the child drink while still in bed, and then slowly get up and do morning hygiene, get dressed. It will be at least half an hour before breakfast. This is enough time to wake up the appetite. The kid definitely will not refuse breakfast. Digestive system is awake, which means you need to give her something substantial. A portion of porridge or scrambled eggs, a glass of milk and a sandwich will do. Before lunch, the child will be full. Give him a bottle of clean water and some fruit with you to school. These are his pre-dinner snacks. Let him drink a few sips of water after each lesson. Explain to the child that this is good for his body, as fluid loss is replenished. Water constantly enters the tissues and supports metabolism. If you drink water at once, then the lion's share will immediately be filtered by the kidneys without participating in metabolism. 
Everything must be done gradually.
If you do something wrong, then the child's body will make itself felt. The lack of fluid intake is manifested by rare urination and a small amount of urine, nervousness, anxiety, tearfulness and rare blinking. In addition, the child may change the color of the urine (it becomes dark), the skin turns pale and dries. By your own example, show your child how important it is to maintain a drinking regimen. Also carry water with you, drink in the morning, refuse or minimize the consumption of soda and other pseudo-thirst quenchers. Boys definitely need to drink more water, athletes who lose moisture abundantly should always drink a lot. But accustom the child to the regime smoothly and do not save on water. Make sure to clean it in a timely manner, and for this, install a filter. Well, or stock up on mineral non-carbonated water. 
Trust but check
Parents can be conditionally divided into two camps depending on their attitude towards children. Some are terribly afraid of losing control over the child and letting him out from under the "wing", while others prefer to talk to him on an equal footing and see him as a person. Accordingly, someone calmly lets the child go to the camp, while someone sees this as another reason for excitement. Drinking regime in kindergarten is regulated by federal laws aimed at improving the well-being of the population. That is, your child is looked after there not only for his comfort, but also for good. To obtain a license, a children's organization must meet a number of requirements. In particular, the use of boiled water is allowed in kindergarten, provided that it is stored for no more than three hours. It is also allowed to drink bottled water, which is used for cooking. The pupils of the garden can always ask for water in any quantity. 
With glamor and brilliance
The drinking regime in kindergarten, where there is a sauna, is slightly different. Such temperature procedures require providing children with tea, juice and mineral water. At the same time, the amount of liquid consumed by a child per day in kindergarten is approximately 70% of the daily volume. So the educator must provide the drinking needs of his wards.
Educational process
If a child spends only the time in the garden when his parents are busy, then he can be at school almost all week. That is why parents are concerned about the drinking regimen at school. In that educational institution also, the rules of the regime are regulated by federal laws, and the responsibility of leaders is no less high. The child is very active at school. Even during the lesson, he does not sit still, and even in physical education classes he does his best. After each lesson, you need to make up for the loss of fluid, but this is often hindered by low quality tap water. So, it is possible to quench your thirst from the school fountain with caution? By no means! The organization of the drinking regime at the school allows you to have free access to drinking water all day long. Sometimes bottled water, special machines, coolers or stationary fountains are used for this. ![]() You can drink water in the dining room, medical office or in any office elementary school. According to the drinking regime, water containers should be replaced in a timely manner, as well as dishes. If a fountain is used, it is hygienic to install a restrictive ring to prevent direct contact with the source. At school, the drinking regime also includes the use of juices, nectars and milk drinks in the canteen. In most cases, this requires an additional fee, but it's worth it because it increases the amount of vitamins your child gets from food.
You can drink water in the dining room, medical office or in any office elementary school. According to the drinking regime, water containers should be replaced in a timely manner, as well as dishes. If a fountain is used, it is hygienic to install a restrictive ring to prevent direct contact with the source. At school, the drinking regime also includes the use of juices, nectars and milk drinks in the canteen. In most cases, this requires an additional fee, but it's worth it because it increases the amount of vitamins your child gets from food.
under personal supervision
Behind academic year parents get used to the fact that the child disappears at school, and the summer holidays can become a stressful situation, but no one has canceled the care of the baby, and you will have to take care of the drinking regime in summer period. What foods do we eat the most in hot weather? Fruits! Fresh vegetables! And soups based on them! It is logical that such nutrition reduces thirst and reduces the need for additional moisture. But if you abuse barbecue, juicy chicken wings on the grill and hamburgers, then there is an additional activation of the thirst center, and the person drinks more water. However, I do not want to deny something to my offspring on summer holidays Oh. So how do you achieve harmony? It is enough to slightly soften the regime of the training months, but in general leave it unchanged. In the morning, the child should drink a glass of water, and have breakfast a little later. No need to drink food. Take with you clean water picnics and walks. Take a couple of sips with your child every hour. This is perceived unobtrusively and reasonably. In the summer, you can not deny your child soda, but still limit its consumption and do not serve it yourself bad example. By the way, do not give your child boiled water at home. In fact, there is nothing useful left in it, since all the bacteria are killed. In addition, she is very tough. Better install a cleaning system. Then you will get rid of impurities in raw water. 
Is it possible to be calm?
If you are sending your child on vacation for the first time, then you will probably be interested in the details of the drinking regime in the children's camp. This is quite understandable, because the summer period is not in vain called wellness. At this time, the child should receive a rationally balanced diet that provides the body with the necessary nutrients and energy. Therefore, attention should be paid not only to the quality of products, but also to storage conditions, as well as to the method of preparation. The diet is developed according to the seasons, and in summer fresh vegetables, fruits and juices are preferred. For prevention in the camp, C-vitaminization of soups and drinks is carried out with the help of ascorbic acid. Children receive compotes and jelly for drinking, but they can also get clean water if they wish. In addition, throughout the territory, the availability of compliance with the drinking regime is ensured. Water must be non-carbonated, packaged in containers or boiled, but the latter is stored for no more than six hours. At the request of the children, water is taken out into the street and poured into disposable dishes.
By all rules
Well, in conclusion, I need to say a few more words about the drinking regime in the garden. Here, too, the use of boiled water is allowed, but on the condition that it is stored for no more than three hours. Children are given warm water poured into ceramic cups. At the same time, a special place is allocated in the garden where the cups are placed upside down on a tray. There is a tray for used dishes. Boil water in the catering unit in a special container. Processing is done daily.
Registration N 32024
In accordance with the Federal Law of March 30, 1999 N 52-FZ "On the sanitary and epidemiological welfare of the population" (Collection of Legislation Russian Federation, 1999, N 14, art. 1650; 2002, N 1 (part 1), Art. 2; 2003, N 2, Art. 167; 2003, N 27 (part 1), Art. 2700; 2004, N 35, Art. 3607; 2005, N19, art. 1752; 2006, N 1, art. ten; 2006, N 52 (part 1), Art. 5498; 2007, N 1 (part 1), art. 21; 2007, N 1 (part 1), art. 29; 2007, N 27, Art. 3213; 2007, N 46, art. 5554; 2007, N 49, art. 6070; 2008, N 24, art. 2801; 2008, N 29 (part 1), art. 3418; 2008, N 30 (part 2), Art. 3616; 2008, N 44, Art. 4984; 2008, N 52 (part 1), Art. 6223; 2009, N 1, art. 17; 2010, N 40, art. 4969; 2011, N 1, art. 6; 07/25/2011, N 30 (part 1), Art. 4563, Art. 4590, Art. 4591, Art. 4596; 12.12.2011, N 50, art. 7359; 06/11/2012, N 24, art. 3069; 06/25/2012, N 26, art. 3446; 2013, N 30 (part 1), art. 4079; No. 48, art. 6165) and Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 24, 2000 N 554 "On Approval of the Regulations on the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Service of the Russian Federation and the Regulations on State Sanitary and Epidemiological Regulation" (Collected Legislation of the Russian Federation, 2000, N 31, Art. 3295; 2004 , N 8, item 663; 2004, N 47, item 4666; 2005, N 39, item 3953) I decide:
1. Approve the sanitary and epidemiological rules and regulations SanPiN 2.4.4.3155-13 Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the device, maintenance and organization of work of stationary organizations for recreation and recreation of children "(Appendix).
2. Consider invalid the sanitary and epidemiological rules and regulations SanPiN 2.4.4.1204-03 "Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the device, maintenance and organization of the working hours of out-of-town stationary institutions for recreation and recreation of children", approved by the decision of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated March 17 2003 N 20 (registered with the Ministry of Justice of Russia on March 21, 2003, registration number 4303).
Acting Chief State Sanitary Doctor
Russian Federation
A. Popova
Appendix
Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the device, maintenance and organization of work of stationary organizations for recreation and rehabilitation of children
Sanitary and epidemiological rules and regulations SanPiN 2.4.4. 3155-13
I. General provisions and scope
1.1. These sanitary and epidemiological rules and regulations (hereinafter referred to as the sanitary rules) establish sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the placement, arrangement, maintenance and organization of the work of stationary organizations for recreation and health improvement of children for summer, seasonal and year-round operation (hereinafter referred to as children's health camps).
Sanitary rules are aimed at the daily routine, improvement and strengthening of the health of children, including children with handicapped health, during their stay in children's health camps.
1.2. These sanitary rules apply to all types of children's health camps, including organizations whose activities are related to the organization children's recreation and rehabilitation of children on the basis of sanatoriums, sanatoriums, rest houses and others.
1.3. These sanitary rules are binding on legal entities and individual entrepreneurs whose activities are related to the design, construction, reconstruction, organization and operation of children's health camps.
The previously built buildings of children's health camps, in terms of architectural and planning solutions, are operated in accordance with the project according to which they were built.
These sanitary rules do not apply to the facilities of children's health camps that are under design, construction, reconstruction and commissioning at the time these sanitary rules come into force.
1.4. When organizing children's health camps of a sanatorium type (or sanatorium shifts), it is necessary to be guided by these sanitary rules and sanitary and epidemiological rules that impose sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the device, maintenance and organization of the work of children's sanatoriums 1 .
1.5. Control over the implementation of these sanitary rules is carried out in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation by bodies authorized to exercise federal state sanitary and epidemiological supervision 2 .
1.6. Legal entities and individual entrepreneurs whose activities are related to the operation of children's health camps, it is necessary, no later than 2 months before the opening of the health season, to notify the authorities exercising the functions of control and supervision in the field of ensuring the sanitary and epidemiological welfare of the population about the planned the timing of the opening of children's health camps, the mode of operation (the dates of the beginning and end of each shift), the planned number of children in each shift, the timing of the deratization, pest control measures and acaricidal (anti-tick) treatments.
1.7. The activities of children's health camps are carried out subject to their compliance with the requirements of these sanitary rules.
1.8. Employees of children's health camps undergo medical examinations in accordance with the established procedure 3 and must be vaccinated in accordance with the national calendar of preventive vaccinations, as well as according to epidemiological indications 4 .
Each employee of the children's health camp must have a personal medical book of the established form, in which the results of medical examinations and laboratory research, information about vaccinations, past infectious diseases, information about the passage of professional hygienic training and certification, admission to work.
Employees of the children's health camp undergo a professional hygiene training and attestation when applying for a job and further with a frequency of at least 1 time per year.
1.9. Children's health camp on the day of arrival of children is completed in groups.
1.10. Admission of children to a children's health camp is carried out if there is a doctor's opinion on the absence of contacts with infectious patients, on the state of health of children and information on available vaccinations.
Admission to a children's health camp for children with disabilities is carried out if there is a doctor's opinion that there are no medical contraindications to sending such children to this organization, as well as if there is a standard medical card and information about available vaccinations.
1.11. The duration of shifts in the children's health camp is:
Sanatorium shift - at least 24 days, for the organization of recreation, rehabilitation, hardening and treatment and prevention procedures;
Improving shift - at least 21 days, for the organization of recreation, rehabilitation and tempering procedures.
It is possible to organize short shifts (20 days or less) to organize recreation and leisure for children.
The duration of shifts during the autumn, winter and spring holidays is recommended for a period of at least 7 days.
When organizing recreation and recreation for children on the basis of other stationary out-of-town organizations, joint accommodation, meals, stay in common places for use by children and adults are not allowed.
1.12. About all cases of group infectious and not infectious diseases, emergencies in the operation of energy and water supply systems, sewerage, technological and refrigeration equipment, as well as other identified violations of sanitary rules that pose a threat of the emergence and spread of infectious diseases and mass poisoning, the head of the children's health camp is obliged to inform the authority within the first two hours authorized to carry out state sanitary and epidemiological supervision, to take measures in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
II. Requirements for a land plot when placing a children's health camp
2.1. Land plot for a children's health camp is located outside industrial facilities and industries, sanitary protection zones of industrial facilities and industries, the first belt of the zone sanitary protection sources of water supply and drinking water pipelines, sanitary breaks from highways, parking lots, facilities railway transport, routes of takeoff and landing of air transport.
When designing a children's health camp, the allocation of sites for construction is carried out taking into account the wind rose and the windward side from sources of noise and air pollution.
2.2. Content harmful substances in atmospheric air, levels electromagnetic radiation, noise, vibration, infrasound, ionizing radiation at the construction site of a children's health camp should not exceed the hygienic standards established for the premises of residential, public buildings and residential areas; soil must be suitable hygiene requirements imposed on the content of substances potentially hazardous to humans in the soil.
2.3. Newly built children's health camps are recommended to be placed in forest, forest and park areas on separate land plots.
2.4. Main lines should not pass through the site of the children's health camp. engineering Communication urban (rural) purposes (water supply, sewerage, heat supply, power supply).
On difficult terrain, it is planned to divert flood and storm water from the site to prevent its flooding and pollution.
III. Requirements for the territory of the children's health camp
3.1. It is recommended to enclose the territory of the children's health camp along the perimeter with a fence and a strip of green spaces or other fencing of natural origin. Landscaping with trees and shrubs is carried out taking into account climatic conditions.
It is not allowed to plant thorny bushes on the territory, as well as green plantings that give small seeds and poisonous fruits.
3.2. The territory of the children's health camp must have outdoor electric lighting. The level of artificial illumination during the stay of children on the territory must be at least 10 lux at ground level at night in the places where children can be located.
3.3. The territory of the children's health camp is planned taking into account the principle functional zoning, with the allocation of the corresponding zones, depending on their functional purpose. The following zones are distinguished on the territory: a zone of residence, a zone of sports and recreational facilities and a zone of economic and technical purpose. Green spaces can be used for zoning the territory.
3.4. In the residential area there are dormitory buildings, a dining room, medical facilities, cultural and administrative facilities, as well as recreation areas and playgrounds.
3.5. The zone of sports and recreational facilities includes areas for physical education, equipped taking into account the age of children.
The surface of sports grounds must be grassy, with compacted soil, dust-free, or made of materials that do not harmful effects per person.
It is allowed to use recreation parks, green areas, swimming pools, sports facilities for organizing sports and recreational activities.
3.6. On the territory of the zone for economic and technical purposes are located: water supply facilities, a boiler room and a pumping station with a water tank (if any), a garage, a parking lot for household vehicles, as well as other economic and technical buildings.
Separate containers with tight-fitting lids are installed on the territory of the economic zone to collect solid household and food waste. They are located on areas with a waterproof hard surface, the dimensions of which exceed the base area of the containers. Distance from containers to residential buildings, recreation areas, playgrounds and sports grounds, water supply facilities should be at least 25 m. The site is equipped on three sides with a windproof fence that exceeds the height of the containers used.
3.7. Entrances and entrances to the territory of the children's health camp, driveways, paths to buildings, outbuildings, container sites for garbage collection are equipped with a flat hard surface.
3.8. For children with disabilities and children with disabilities on the territory of children's health camps under construction and reconstruction, measures are provided to create an accessible (barrier-free) environment.
3.9. Before opening a children's health camp, it is necessary to organize and carry out anti-tick (acaricidal) treatment of its territory and measures to combat rodents in order to prevent tick-borne encephalitis, tick-borne borreliosis and hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome and other infectious diseases. After the treatments, the quality control of the treatments against ticks and rodents should be carried out.
Acaricidal (anti-mite) treatment of the territory of children's health camps is carried out according to the results of an entomological assessment.
The use of the territory of parks and other green areas is possible only after an entomological examination and anti-tick treatment of this territory.
IV. Requirements for buildings, premises and equipment
4.1. When designing children's health camps, buildings for children should have no more than two storeys.
4.2. Entrances to buildings of year-round operation are equipped with vestibules or air-thermal curtains.
4.3. Basement floors are not allowed basements to accommodate children, circle work, placement of medical facilities, sports, dance and assembly halls for children, with the exception of shooting range equipment.
4.4. The area of dormitory rooms is provided at the rate of at least 4 m 2 per child.
In newly built buildings, the capacity of the bedroom should not exceed 5 beds.
4.5. When designing buildings for children's health camps, the height of the living quarters and the ventilation system must provide hygienically reasonable air exchange rates.
4.6. The set and areas of premises for circle classes and sections must comply with sanitary and epidemiological requirements for organizations additional education children.
The areas and equipment of premises where personal computers are used must comply with hygienic requirements for personal electronic computers and the organization of work on them.
4.7. Bedrooms should be separate for boys and girls and equipped with fixed beds.
Furniture must be coated to allow wet cleaning with the use of detergents and disinfectants.
Allowed use bunk beds subject to the norm of area per child and the number of people living in the room.
4.8. Each sleeping place provided with a set of bedding (mattress with mattress topper, pillow, blanket), bed linen(pillowcase, sheet, duvet cover) and 3 towels (for face, feet and bath). The total number of sets of bed linen, mattress covers and towels (for face, feet, bath) must be at least 2 sets per child of a vacationer per shift.
4.9. The windows of the bedrooms are equipped with sun protection devices (such as blinds) or curtains.
4.10. In the premises of the dining room, bedrooms, playrooms, medical purposes, mosquito nets are installed on the windows and swing doors or other measures are taken to prevent the entry of insects into the premises.
4.11. In buildings for children, conditions are provided for drying outerwear and shoes, washing and ironing.
The set of premises of the dormitory building includes: bedrooms; teacher's rooms; premises for day stay of children; washrooms with foot washers; showers with dressing rooms separately for boys and girls; a room for processing and storing cleaning equipment, preparing disinfectant solutions - one per detachment (or residential building); a laundry room equipped with a water supply, a drain, basins for washing things and benches; ironing room; room for drying clothes and shoes; a place for storing shoes, equipped with shelves or racks.
4.12. Premises for sanitary purposes for children are provided separately for boys and girls. Each toilet room is equipped with washbasins and toilet cubicles with doors.
In newly constructed buildings, sanitary facilities are equipped at the rate of: toilets - at least - 2 toilet bowls for 16 girls; 1 toilet and 1 urinal for 16 boys; shower rooms - shower cabins not less than - 1 horn (grid) for 16 people; washrooms - at least 1 washbasin for 5 people and at least 2 foot washers for 16 people; it is recommended to provide girls' personal hygiene rooms.
In newly built buildings, toilets and showers are recommended to be equipped with each sleeping room.
4.13. Toilets are equipped with trash cans, toilet paper holders, soap, electric or paper towels. Soap, toilet paper and towels must be available at all times. Sanitary equipment must be in good working order, free of chips, cracks and other defects. Toilet bowls are equipped with seats that allow their daily wet cleaning with the use of detergents and disinfectants.
4.14. Washing of personal belongings is carried out in laundry or washrooms in basins specially allocated and marked for this purpose. Laundry rooms are equipped with water supply, drains, benches.
4.15. The room for storage and processing of cleaning equipment, preparation of disinfectant solutions is equipped with a pallet and water supply to it, a drain; in the absence of a room, a closet (or place) is allocated for storing cleaning equipment.
Cleaning equipment and disinfectants are kept out of the reach of children.
4.16. When designing medical facilities (medical center), wards for temporary isolation of patients (isolator) are provided.
The medical center provides for the following premises: a doctor's office with an area of at least 10.0 m 2; treatment room with an area of at least 12.0 m 2 ; a nurse's room of at least 10.0 m 2, a room for preparing disinfectant solutions and storing cleaning equipment intended for medical facilities, a toilet with a washbasin.
The isolation ward provides for at least two wards (for drip and intestinal infections), with an area of at least 6 m 2 per 1 bed. The premises of the insulator include: a toilet with a sink for washing hands, as well as a pantry area of at least 6 m 2 with 2 sinks for washing dishes.
4.17. During the construction and operation of the pool, sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the construction, operation and water quality of swimming pools must be observed.
4.18. Ceilings, walls and floors of all rooms must be smooth, without damage, signs of fungus attack and have a finish that allows wet cleaning and disinfection.
Ceilings, walls and floors of industrial and storage premises of the canteen, laundry, ironing, sanitary facilities (showers, toilets, washrooms with foot washers, girls' hygiene rooms, etc.) are made with moisture-resistant materials that allow wet cleaning with the use of detergents and disinfectants.
4.19. In the production and storage rooms of the dining room, laundry, ironing, sanitary facilities (showers, toilets, washrooms with foot washers, girls' hygiene rooms), walls are finished with moisture-resistant materials to a height of at least 1.8 m.
The floors in the industrial premises of the dining room and showers are equipped with drain ladders with slopes to the holes of the ladders.
4.20. The decoration of the premises of the medical center must comply with the sanitary and epidemiological requirements for organizations engaged in medical activities 5 .
4.21. The building and finishing materials used must be harmless to human health. Materials for interior decoration must be resistant to wet cleaning and disinfection.
4.22. During the period of work of the children's health camp, it is not allowed to conduct current and overhaul in places where children are.
4.23. In order to create conditions for the stay of children with disabilities and children with disabilities in children's health camps during construction and reconstruction, measures are envisaged to create an accessible (barrier-free) environment that ensures the free movement of children in buildings and premises.
V. Requirements for water supply and sewerage
5.1. Newly constructed and reconstructed buildings of children's health camps are equipped with centralized systems of domestic and drinking, hot water supply and sewerage in accordance with the requirements for public buildings and structures in terms of domestic and drinking water supply and sanitation.
5.2. Water for household and drinking purposes must meet the hygienic requirements for water quality in terms of safety centralized systems drinking water supply.
5.3. Own source of water supply must meet the sanitary and epidemiological requirements for sources of water supply for drinking purposes.
5.4. Cold and hot water supply is provided for medical facilities, a dining room, toilets, showers, washrooms with foot washers, girls' hygiene rooms, washrooms in front of the dining room, laundry room, rooms for storing cleaning equipment and preparing disinfectant solutions.
5.5. For medical premises, industrial premises of the canteen, showers, washrooms with foot washes, hygiene rooms for girls, washrooms before the dining room, laundry room, rooms for storing cleaning equipment and preparing disinfectant solutions, it is planned to install backup water heaters.
5.6. Domestic, drinking, hot water supply and sewerage systems should be located in good condition.
5.7. The device of household sewerage should be provided in residential buildings, dining rooms, medical facilities, sports and recreation, cultural facilities, service and amenity premises, laundry, shower room, as well as in separate toilets and washrooms.
5.8. Cleaning and disinfection of household Wastewater should be carried out at citywide or local sewage treatment plants.
5.9. Washing and production baths in the dining room are connected to the sewerage system with an air jet break of at least 20 mm from the top of the intake funnel.
5.10. When designing and reconstructing children's health camps in non-sewered areas, buildings are equipped with internal systems sewers with wastewater discharge into local systems sewerage.
5.11. On the territory of children's health camps, it is allowed to use outdoor toilets of a cesspool type, sewered outdoor toilets and stationary dry closets provided with artificial lighting. In the toilet or near the toilet, conditions for washing hands with soap are provided. Soap should be constant.
Outdoor toilets of the cesspool type are equipped with an above-ground part of the building and a waterproof cesspool. The depth of the cesspool from the surface of the earth is calculated depending on the level of standing ground water but not less than 1 meter. It is not allowed to fill the cesspool more than 2/3 of the volume.
Toilets are installed at a distance of at least 25 m from the living area and the dining room and at least 50 m from the bathing area. The device and use of outdoor toilets without a roof (canopy) and screens-partitions is not allowed.
VI. Requirements for heating, ventilation and air-thermal conditions in rooms
6.1. Heating, ventilation and/or air conditioning systems must provide normalized parameters of the microclimate and air environment in the premises of children's health camps.
6.2. Newly constructed children's health camps are provided with centralized or autonomous heating.
When installing fences on heating appliances, the materials used must meet sanitary and epidemiological safety requirements.
Do not use heaters with infrared radiation in rooms for children.
6.3. Optimum temperature air: in sleeping quarters it is +20...+24°С, permissible - not lower than +18°С; in the canteen, recreations, lobby, premises for cultural purposes and for classes +18 ... + 24 ° С; sports halls - +17...+20°С, shower rooms - not less than +25°С.
In medical premises, the microclimate parameters are set in accordance with the sanitary and epidemiological requirements for organizations engaged in medical activities.
In the premises of swimming pools, the microclimate parameters are taken in accordance with the hygienic requirements for the construction and operation of swimming pools.
6.4. In rooms for children, the relative humidity of the air should be 40-60%, the speed of air movement should not exceed 0.1 m / s.
6.5. All rooms must be ventilated daily.
It is not allowed in the presence of children through ventilation of sanitary premises, as well as premises (bedrooms, premises for daytime stay of children, music, sports halls, and others), including their ventilation through toilet rooms.
Ventilation is carried out through transoms and vents. In the rooms of the bedrooms in the cold season, airing is carried out before going to bed. Transoms and vents should function at any time of the year. Wide one-sided aeration of all rooms in the warm season is allowed in the presence of children.
The area of transoms and vents used for ventilation should be at least 1/50 of the floor area.
6.6. Replacing window blocks should not lead to a decrease in natural light rooms and prevent ventilation.
VII. Requirements for natural and artificial lighting and insolation
7.1. The levels of natural and artificial lighting in the premises of children's health camps must comply with the hygienic requirements for natural, artificial and combined lighting of residential and public buildings.
7.2. The design of adjustable sun protection devices on windows in the initial position should not reduce the light-active area of the window opening. Curtains of windows in sleeping quarters are allowed only during the sleep of children, the rest of the time the curtains should be moved apart in order to ensure the insolation of the room.
7.3. As sources of artificial lighting in residential premises, medical facilities, circle activities, canteens, fluorescent lamps or lamps with similar lighting characteristics with light-diffusing fittings; for dining rooms, laundry rooms, showers and baths - with moisture-proof fittings. They are not used in the same room as general lighting at the same time lamps of different types.
Sleeping buildings are additionally provided with emergency (night) lighting.
7.4. For rational use artificial light and uniform illumination of the premises, it is recommended to use finishing materials and paints that create matte surface, light colors.
7.5. Faulty and burned-out fluorescent lamps are collected and stored in a specially designated room and removed in compliance with the requirements for handling mercury-containing waste.
VIII. Requirements for canteen equipment, inventory, utensils
8.1. Arrangement, maintenance and organization of the work of the dining room in terms of space-planning and constructive solutions, sanitary and technical support, requirements for equipment, inventory, utensils and containers, sanitary condition and maintenance of premises, washing dishes, formation sample menu, conditions and technology for preparing dishes, requirements for the prevention of vitamin and microelement deficiencies, compliance with personal hygiene rules and medical examinations by canteen staff, storage and transportation food products, the daily maintenance of mandatory documentation (marriage journals, a health journal, etc.) must comply with the sanitary and epidemiological requirements for catering for students in educational institutions and these sanitary rules.
8.2. Quantity seats in the dining room of the dining room, it is recommended to rely on the simultaneous service of all children (in one shift).
During the construction and reconstruction of the dining room, the number of seats in the dining room is taken at the rate of at least 1.0 m 2 per seat.
In the canteen building, conditions are provided for washing the hands of children near the dining room (or at the entrance to the dining room) and places for undressing children.
During the construction and reconstruction of the dining room next to the dining room, separate toilets for boys and girls are provided, equipped with toilet bowls and sinks for washing hands.
8.3. Sinks for washing hands at the entrance to the dining room are installed taking into account the growth age features children at the rate of at least 1 sink per 25 seats.
Paper towels (napkins) or electric towels may be used to dry hands.
Soap and towels near handwashing sinks should be available at all times.
8.4. The dining room is equipped with the necessary technological, refrigeration and washing equipment. A set of equipment for production, storage facilities is recommended to be taken in accordance with.
All technological and refrigeration equipment must be in good working order.
8.5. Technological equipment, inventory, utensils, containers are made from materials approved for contact with food products.
At work technological equipment the possibility of contact between food raw materials and ready-to-eat food products should be excluded.
production tables, kitchenware, equipment, inventory must be labeled for raw and prepared food products.
8.6. Production equipment, kitchen utensils and utensils must meet the following requirements:
Production tables intended for food processing must be all-metal;
Kitchen utensils, tables, equipment, inventory must be marked and used for their intended purpose (separately for raw and prepared food products);
For cutting raw and finished products, hardwood boards without cracks and mechanical damage are used;
Boards and knives must be marked: "CM" - raw meat, "SK" - raw chickens, "CP" - raw fish, "CO" - raw vegetables, "BM" - boiled meat, "BP" - boiled fish, " VO" - boiled vegetables, "gastronomy", "herring", "X" - bread, "greens";
Kitchen utensils, cutting equipment, containers used for cooking and storing food must be made of materials that are allowed to come into contact with food;
Third dishes (compotes, jelly and others) are prepared in stainless steel dishes;
Separate dishes are used to boil milk;
The number of tableware and cutlery used should correspond to the list of children who eat at the same time;
For the timely replacement and replenishment of broken dishes, a supply of tableware is provided.
8.7. Technological equipment, washing baths for washing tableware and kitchen utensils, which are sources of heat, gases and moisture, are equipped with local exhaust systems ventilation in the zone of maximum contamination.
8.8. Washing baths for washing kitchen utensils, equipment and inventory are provided with cold and hot water supply through mixers.
8.9. For rinsing dishes (kitchen and dining room), washing bathtubs are equipped with flexible hoses with a shower head.
8.10. The room (place) for washing the exchange container is equipped with a washing tub or a ladder with a side.
8.11. In all industrial premises, the dining room toilet, hand-washing sinks with hot and cold water through mixers.
8.12. Kitchen utensils, equipment, inventory are washed separately from tableware.
In washing rooms, instructions are posted on the rules for washing equipment, utensils and inventory, indicating the concentrations and volumes of detergents and disinfectants used.
8.13. Equipment, kitchen utensils and inventory are freed from food debris and washed in a two-section bath in compliance with the following regimen: in the first section - brushing with water at a temperature of at least 40 ° C with the addition of detergents; in the second section - rinsed with running water hot water at a temperature not lower than 65°C using a hose with a shower head and dried upside down on lattice shelves, racks.
Clean equipment, kitchen utensils and inventory are stored on racks installed at a height of at least 0.35 m from the floor.
8.14. Cutting boards and small wooden utensils (shovels, stirrers, etc.) after washing in the first bath with hot water (at a temperature not lower than 40 ° C) with the addition of detergents, they are rinsed with hot water (at a temperature not lower than 65 ° C) in the second bath, doused with hot water (at a temperature of not lower than 90°C), and then dried on lattice racks or shelves.
Cutting boards and knives are stored on special shelves or cassettes; it is allowed to use magnetic holders located in the immediate vicinity of the technological table with the corresponding marking.
8.15. Metal inventory after washing is calcined in the oven; meat grinders, cutting, wiping machines are disassembled after use, metal parts are washed and doused with hot water (at a temperature not lower than 90 ° C), and then dried on lattice racks or shelves.
Tableware and tea utensils must be made of earthenware, porcelain, glass and other materials approved for contact with food.
Cutlery (spoons, forks, knives) must be made of stainless steel and other materials approved for contact with food.
It is not allowed to use dishes with broken edges, cracks, chips, deformed, damaged enamel, plastic and aluminum cutlery.
Disposable tableware is allowed.
8.16. Dinnerware and cutlery are washed in dishwasher or manually in three-section baths.
Tableware and cutlery are washed in the dishwasher in accordance with the instructions for its operation.
8.17. When washing tableware by hand in three-section baths, the following order is observed:
Mechanical removal of food residues;
Washing in water with the addition of detergents in the first section of the bath at a temperature not lower than +45°C;
Washing in the second section of the bath in water with a temperature not lower than +45 ° C and the addition of detergents in an amount 2 times less than in the first section of the bath;
Rinsing dishes in the third section of the bath with hot running water at a temperature not lower than +65 ° C, using metal mesh with handles and flexible hose with shower head;
Drying dishes on grates, shelves, racks (on the edge).
8.18. Cups, glasses, glasses are washed in the first bath with hot water at a temperature not lower than +45 ° C, using detergents; in the second bath, they are rinsed with hot running water at a temperature not lower than +65 ° C, using a metal mesh with handles and a flexible hose with a shower head.
8.19. Cutlery is washed in hot water at a temperature not lower than +45°C, using detergents, followed by rinsing in running water and calcination in ovens (or dry heat) for 10 minutes.
Cassettes for storing cutlery are washed daily with detergents, followed by rinsing and baking in the oven.
8.20. Clean tableware is stored in cupboards or on racks; cutlery - in special boxes-cassettes with the handles up, their storage on trays in bulk is not allowed.
8.21. Disinfection of tableware and equipment is carried out according to epidemiological indications in accordance with the instructions for the use of disinfectants.
For disinfection of tableware disinfectant solution a container with a lid is allocated, with the appropriate marking. The use of a dry oven is allowed.
8.22. Tables in industrial premises and tables in the dining room are washed with hot water after each meal, using detergents, washcloths (brushes), and rags.
Do not use sponges for washing dishes.
At the end of the working day, the production tables for raw products are washed using disinfectants.
Washcloths, brushes for washing dishes, rags for wiping tables after use are washed with detergents, dried and stored in specially marked containers.
Brushes with defects and visible dirt, as well as metal washcloths are not used.
8.23. Food waste is collected in marked buckets or special containers with lids, which are cleaned as they are filled to no more than 2/3 of the volume.
Every day at the end of the day, buckets or special containers, regardless of their filling, are cleaned, washed with a 2% solution of soda ash, and then rinsed with hot water at a temperature of at least 50 ° C and dried.
8.24. Cleaning is carried out daily in the dining room: washing floors, dusting, wiping radiators, window sills.
Wet cleaning of the walls with the use of detergents is carried out weekly and as it gets dirty.
8.25. In the premises of the dining room there should be no insects and rodents, if they are found, measures for disinfestation and deratization are carried out.
8.26. Before the start of each shift, a general cleaning of the dining room, including the dining room, is carried out.
IX. Requirements for the conditions of storage, preparation and sale of food products and culinary products
9.1. Acceptance of food products and food raw materials in children's health camps is carried out in the presence of documents confirming their quality and safety.
For central delivery food products and food raw materials, as well as drinking water packaged in a container (bottled), to confirm the quality and safety of food products, food raw materials and drinking water, the waybill contains information about the number of the certificate of conformity, its validity period, the authority that issued the certificate , or the registration number of the declaration of conformity, its validity period, the name of the manufacturer or manufacturer (supplier) that accepted the declaration, and the body that registered it.
Documentation certifying the quality and safety of products, marking labels (or their copies) are kept until the end of the sale of products.
9.2. The input control of incoming food products is carried out by the responsible person of the children's health camp. The results of the control are recorded in the register of rejection of perishable food products entering the canteen (), which is stored for a year.
Food products with signs of poor quality, as well as products without accompanying documents confirming their quality and safety, and not labeled, are not allowed to be accepted, if the presence of such labeling is provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
9.3. Food products are stored in accordance with the storage conditions and shelf life established by the manufacturer in accordance with the regulatory and technical documentation.
Compliance control temperature regime in refrigeration equipment is carried out daily, the results are recorded in the temperature log in refrigeration equipment (), which is stored for a year.
9.4. If there is one refrigerator compartment food storage areas should be demarcated.
9.5. Warehouses for the storage of dry bulk products are equipped with devices for measuring temperature and air humidity.
9.6. Storing food in refrigerators freezers carried out on racks and pedestals in the container of the manufacturer or in the container of the supplier.
9.7. Milk is stored in the same container in which it was received, or in consumer packaging.
Butter is stored on shelves in factory containers or in bars wrapped in parchment, in trays with lids.
Large cheeses are stored on racks, small cheeses in consumer containers or in trays with lids.
Sour cream, cottage cheese are stored in the same container in which they arrived.
It is not allowed to leave spoons, shoulder blades in a container with sour cream, cottage cheese.
Eggs are stored in boxes on pallets in dry, cool rooms (refrigerators).
Cereals, flour, pasta are stored in a dry room in the original (consumer) packaging on undercarriages or racks at a distance of at least 15 cm from the floor, the distance between the wall and the products must be at least 20 cm.
rye and wheat bread stored separately on racks or in cabinets, with the bottom shelf at least 35 cm from the floor. Doors in cabinets must have ventilation holes. When cleaning the places of storage of bread, the crumbs are swept away with special brushes, the shelves are wiped with a cloth moistened with a 1% solution of table vinegar.
Potatoes and root crops are stored in a dry, dark room; cabbage - on separate racks, in chests; pickled, salted vegetables - in the manufacturer's container with a lid.
Fruits and greens are stored in boxes in a cool place.
9.8. Products that have a specific smell (spices, herring) are stored in a container with a lid and separately from other products that perceive odors (butter, cheese, tea, sugar, salt, and others).
9.9. Sour-milk and other ready-to-eat perishable products are kept in closed consumer packaging before being served to children. room temperature until they reach the implementation temperature of 15 C 2 C, but not more than one hour.
9.10. Milk supplied in cans and flasks must be boiled for at least 2 and no more than 3 minutes before consumption.
9.11. The list of technological equipment must include at least 2 meat grinders (or wiping and cutting machines) for the separate preparation of raw and finished products.
9.12. Catering is carried out on the basis of the principles of "sparing nutrition".
When preparing dishes, sparing technologies must be observed: boiling, baking, poaching, sautéing, stewing, steaming, cooking in a combi steamer. When preparing meals for children, no frying is used.
9.13. When culinary processing of food products, it is necessary to ensure the implementation of the cooking technology set out in the technological map, as well as to comply with sanitary and epidemiological requirements for technological processes cooking.
9.14. Cutlets, minced meat or fish meatballs, fish pieces are baked at a temperature of 250-280 C for 20-25 minutes.
Souffle, casseroles are made from boiled meat (poultry meat); molded products from raw meat (chicken) or minced fish are steamed or baked in sauce; fish (fillet) is boiled in pieces, poached, stewed or baked.
In the manufacture of second courses from boiled meat (poultry, fish), or the release of boiled meat (poultry) for the first courses, portioned boiled meat (poultry) is subjected to secondary heat treatment - boiling in broth for 5-7 minutes and stored in it at a temperature +75°C before serving no more than 1 hour.
Omelettes and casseroles, the recipe of which includes an egg, are cooked in an oven, omelettes - for 8-10 minutes at a temperature of 180-200 ° C, with a layer of no more than 2.5-3 cm; casseroles - 20-30 minutes at a temperature of 220-280 ° C, with a layer of no more than 3-4 cm; storage of egg mass is carried out no more than 30 minutes at a temperature of 4±2°C.
Pancakes, cheesecakes are baked in an oven or oven at a temperature of 180-200 ° C for 8-10 minutes.
The egg is boiled after boiling water for 10 minutes.
Sausage products (sausages, boiled sausages, sausages) are cooked for 5 minutes from the moment the boil starts.
Butter, used for seasoning side dishes and other dishes, is preliminarily subjected to heat treatment (melted and brought to a boil).
Rice and pasta side dishes are cooked in a large volume of water (in a ratio of at least 1:6) without subsequent rinsing.
9.15. In the manufacture of potato (vegetable) puree, a vegetable mashing machine is used.
When mixing the ingredients that make up the dishes, you must use kitchen utensils without touching the product with your hands or use gloves.
9.16. Treatment raw eggs is carried out in a specially designated place of the meat and fish workshop, using marked baths and (or) containers for these purposes. It is possible to use perforated containers, provided that the eggs are completely immersed in the solution in the following order: I - treatment in a 1 - 2% warm solution of soda ash; II - processing in disinfectants approved for this purpose; III - rinsing with running water for at least 5 minutes, followed by laying out in a clean, marked dish.
It is allowed to use other detergents or disinfectants, in accordance with the instructions for their use.
9.17. Groats should not contain foreign impurities. Before use, the cereals are washed with running water.
9.18. Consumer packaging of canned foods is washed with running water and wiped before opening.
9.19. Hot dishes (soups, sauces, hot drinks, main courses and side dishes) should be served at a temperature of +60...+65°С; cold appetizers, salads, drinks - not lower than +15°C.
From the moment of preparation to the holiday, the first and second courses can be on a hot stove for no more than 2 hours. Reheating food is not allowed.
9.20. When processing vegetables and fruits, the following requirements must be met:
9.20.1. Vegetables and fruits are sorted and washed.
Fruits and peeled vegetables are washed in a cold shop (zone) or a secondary vegetable processing shop (zone).
Peeled vegetables are washed again in running water in small batches using colanders and nets.
Vegetables must not be pre-soaked.
Peeled potatoes, root crops and other vegetables are stored in cold water for no more than 2 hours.
9.20.2. Vegetables harvested last year (cabbage, onion, root crops) in the period after March 1 is allowed to be used only after heat treatment.
9.20.3. When culinary processing of vegetables are observed following rules: vegetables are cleaned immediately before cooking and put only in boiling water.
9.20.4. Vegetables intended for the preparation of vinaigrettes and salads are boiled in their skins and cooled. Boiled vegetables are peeled and cut in the cold shop for finished products or in the hot shop on the table for boiled products.
9.20.5. Cooking vegetables on the eve of the cooking day is not allowed.
9.20.6. Vegetables boiled for salads are stored in the refrigerator for no more than 6 hours at a temperature of plus 4 ± 2 ° C.
9.20.7. leafy vegetables and greens intended for the preparation of cold appetizers without subsequent heat treatment should be thoroughly washed with running water and kept in a 3% solution of acetic acid or a 10% solution table salt for 10 minutes, followed by rinsing with running water and drying.
9.21. Salads are prepared and dressed immediately before distribution.
Not seasoned salads are allowed to be stored for no more than 2 hours at a temperature of plus 4 ± 2 ° C. Salads are dressed just before serving.
Vegetable oil is used as a salad dressing. The use of sour cream and mayonnaise for dressing salads is not allowed.
Dressed salads can be stored for no more than 30 minutes at a temperature of 4±2°C.
9.22. Kefir, fermented baked milk, curdled milk and other fermented milk products are portioned into cups (glasses) from bags or bottles immediately before they are distributed.
9.24. In order to prevent micronutrient deficiencies (vitamins and minerals) in the nutrition of children, food products enriched with micronutrients are used.
Fortification of dishes is carried out taking into account the state of health of children, under the supervision of a medical worker.
The technology for preparing fortified drinks must comply with the technology specified by the manufacturer in accordance with the instructions and certificate of state registration. Vitaminized drinks are prepared immediately before distribution.
In the absence of fortified drinks in the diet, artificial C-vitaminization is carried out at the rate of 20.0 mg per serving.
Vitamin preparations are introduced into the third dish (compote or jelly) after it has been cooled to a temperature of 15°C (for compote) and 35°C (for jelly) immediately before distribution. Vitaminized dishes are not heated.
Fortification of dishes is carried out under the supervision of a medical worker (in his absence, another responsible person).
Data on the fortification of dishes are entered by a medical worker in the journal of fortification of dishes (), which is stored for one year.
9.25. extradition prepared food allowed only after the inspection by the marriage commission consisting of at least 3 people. The control results are recorded in the finished culinary product rejection log (), which is stored for one year.
The mass of portioned dishes must correspond to the output of the dish indicated in the menu. In case of violation of the cooking technology, as well as in case of unpreparedness, the dish is allowed to be served only after the identified culinary shortcomings have been eliminated and brought to readiness.
9.26. Immediately after cooking, a daily sample of finished products (all cooked dishes) is taken. The daily sample is taken in volume: portioned dishes - in in full; cold appetizers, first courses, side dishes and drinks (third courses) - in an amount of at least 100 g; portioned second courses, meatballs, meatballs, sausage and others are selected individually, as a whole (in the amount of one serving).
Samples are taken with sterile or boiled spoons into sterile or boiled dishes (jars, containers) with tight-fitting lids. Each sample of the dish is placed in separate dishes and stored for at least 48 hours at a temperature of +2 - +6°C. Dishes with samples are marked with the name of the meal and the date of sampling. Control over the correctness of the selection and storage of the daily sample is carried out by the responsible person.
9.27. To prevent the occurrence and spread of infectious and mass non-infectious diseases (poisoning), it is not allowed:
The use of food products specified in;
Production of cottage cheese and other fermented milk products in the canteen, as well as pancakes with meat or with cottage cheese, naval pasta, pasta with chopped egg, brawn, fried eggs, cold drinks and fruit drinks from fruit and berry raw materials (without heat treatment), forshmaks from herring, jellies, pastes, jellied dishes (meat and fish); okroshka and cold soups;
Using leftover food from a previous meal and food prepared the day before; food products with expired shelf life and obvious signs of poor quality (spoilage); vegetables and fruits with mold and signs of rot.
X. Requirements for catering for children
10.1. Nutrition should meet the physiological needs of children for essential nutrients and energy and be less values indicated in table 1.
10.2. Meals should be organized in accordance with an approximate menu approved by the head of the children's health camp, designed for at least 2 weeks, taking into account the physiological needs for energy and nutrients for children of all age groups and recommended daily food packages for children's nutrition (). In year-round children's health camps, a seasonal menu is being developed.
10.3. Based on the approved sample menu, a layout menu is compiled daily indicating the output of dishes for children different ages. Approximate volume ready meals depending on the age of the children is taken in accordance with.
10.4. An example menu should contain information in accordance with. References to the recipes of the dishes and culinary products used in accordance with the collections of recipes must be provided. The names of dishes and culinary products indicated in the sample menu must correspond to their names indicated in the recipe books used. The repetition of the same dishes or culinary products on the same day or the next two days is not allowed.
The actual diet should correspond to the approved sample menu.
10.5. When compiling an exemplary menu, one should be guided by the distribution of the energy value (calorie content) of the daily ration for individual meals, taking into account table 2.
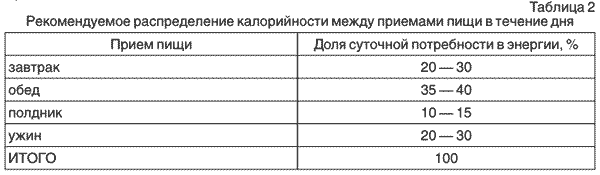
Deviations from the caloric content norms for individual meals during the day are allowed within 5%, provided that the average percentage of caloric intake per shift meets the above requirements.
10.6. The production of ready-made meals and culinary products is carried out in accordance with technological maps, which should reflect the recipe and technology for their preparation. Technological cards must be formatted in accordance with .
10.7. Breakfast should consist of a hot dish, a sandwich and a hot drink. Lunch should include an appetizer (salad or portioned vegetables, herring with onions), a first main course, a second main course, and a drink. The afternoon snack includes a drink (milk, sour-milk drinks, juices, tea) with bakery or confectionery products without cream, fruits; it is allowed to issue cottage cheese or cereal casseroles and dishes. Dinner may include fish, meat, vegetable and cottage cheese dishes, salads, vinaigrettes and hot drinks. The second dinner includes a fermented milk drink (can be supplemented with a confectionery product (cookies, waffles, etc.).
10.8. The sample menu provides for the daily use in the diet of children: milk, sour-milk drinks, meat, potatoes, vegetables, fruits, bread, cereals, butter and vegetable oil, sugar, salt. Other products (cottage cheese, sour cream, poultry, fish, cheese, eggs, juices and others) are included at least 2 times a week.
When compiling the menu, national and territorial peculiarities of the nutrition of the population and the state of health of children are taken into account.
10.9. In the absence of any products, in order to ensure a complete balanced diet, it is allowed to replace them with products of equal composition in accordance with the table for replacing products for proteins and carbohydrates ().
With absence fresh vegetables and fruits, it is possible to replace them in the menu with juices, quick-frozen vegetables and fruits.
10.10. For children, a drinking regimen should be organized around the clock. Water must meet the safety requirements for drinking water.
The drinking regime is organized in the following forms: stationary drinking fountains; water industrial production, packaged in containers (bottled) non-carbonated; boiled water (boil for at least 5 minutes from the moment of boiling).
Boiled water is changed every 3 hours. Before changing the water, the container is completely freed from water residues and rinsed thoroughly.
When using installations with metered bottling of potable water packaged in containers, the container is replaced as necessary, but not less than the shelf life of the opened container specified by the manufacturer.
10.11. When organizing the drinking regime, a sufficient amount of clean dishes allowed for contact with food products, as well as separate labeled trays for clean and used dishes, should be provided; containers - for collecting used disposable tableware.
10.12. When conducting trips, the organization of nutrition for children must meet the sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the arrangement, maintenance and organization of the working hours of children's tent-type camps during the summer holidays.
10.13. Storage of food products in residential areas for children is not allowed.
10.14. An approximate set of food products allowed for transfer to children by visitors, including parents and legal representatives of children, is established by the head of the children's health camp. An approximate set of products should not contain food products that are not allowed to be used in children's nutrition (Appendix N 6).
XI. Daily routine requirements
11.1. The daily regimen should include: the duration of night sleep is at least 9 hours (for children from 7 to 10 years old, at least 10 hours), daytime sleep (rest) - at least 1.5 hours, meals for children at least 5 times (breakfast, lunch, afternoon tea, dinner, second dinner), morning exercises, sports and cultural mass events, hygienic, health-improving and hardening (water, air) procedures, as well as rest and free time. Morning rise of children is carried out not earlier than 8 hours.
For children 15 years of age and older, it is allowed to replace daytime sleep with reading books and board games.
11.3. Physical culture and sports events are organized taking into account the age, physical fitness and health of children.
11.4. In the daily regimen of the day, hardening procedures should be carried out. Hardening should include exercises, physical education, water, air and solar procedures. When organizing hardening, the basic hygienic principles should be implemented - gradual, systematic, comprehensive and accounting individual features child.
11.5. Morning exercises are carried out daily on outdoors. In rainy weather, morning exercises are recommended to be carried out in well-ventilated areas.
The duration of morning exercises is at least 15 minutes.
11.6. It is recommended to bathe children in open water on sunny and calm days, at an air temperature of at least +23°C and a water temperature of at least +20°C. The recommended duration of continuous stay in the water in the first days is 2-5 minutes with a gradual increase to 10-15 minutes. Bathing immediately after a meal (less than 30 minutes) is not recommended.
When organizing bathing for children, the presence of a medical worker is mandatory.
11.7. The use of surface water bodies for bathing children is allowed only if there is a document confirming its compliance with sanitary rules that impose hygienic requirements for protection surface water and (or) imposing sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the protection of coastal waters of the seas from pollution in places of water use of the population, issued by bodies exercising the functions of control and supervision in the field of ensuring sanitary and epidemiological welfare of the population.
11.8. Bathing of children is carried out in specially designated and equipped places. Sheds from the sun are equipped on the shore and cabins for changing clothes and toilets are installed.
11.9. Taking into account the educational and health-improving orientation of children's health camps, in accordance with their age, it is possible to organize the following types of work. For children 7-13 years old, it is allowed to make beds, pick berries and medicinal herbs under the supervision of a teacher; for children over 14 years old - cleaning of bedrooms, dining room duty (serving dining tables, cleaning dirty dishes cleaning the dining room).
11.10. It is not allowed to involve children in work associated with heavy physical exertion (carrying and moving heavy loads, sawing firewood, washing bed linen, etc.), with a danger to life (washing windows, wiping lamps, etc.), cleaning places common use: landings, flights and corridors, washing floors with the use of detergents and disinfectants; performing epidemiologically dangerous types of work (cleaning bathrooms, washrooms, cleaning and removal of waste and sewage, processing the pool bowl and others).
11.11. When on duty in the dining room, children are not allowed to prepare food, peel boiled vegetables, distribute prepared food in the kitchen, cut bread, wash dishes, serve hot food. Children are not allowed to enter directly into industrial premises dining room.
11.12. The duty of children in the dining room and territory in the children's health camp should be no more than once every 7 days.
11.13. Meetings of children with visitors, including with legal representatives of children, are held in accordance with the daily routine established by the head of the children's health camp.
It is not allowed to stay on the territory of the children's health camp of visitors, including legal representatives of children outside specially designated places.
XII. Requirements for the sanitary maintenance of premises and territory of children's health camps
12.1. spring-cleaning territory and all premises is carried out before the start of each shift with the use of detergents and disinfectants.
12.2. In all rooms where children stay, 2 times a day, the technical staff of the children's health camp carries out wet cleaning with the use of detergents.
Carpets are cleaned daily using a vacuum cleaner.
Window panes are washed as they become dirty, but at least once per shift.
12.3. In washrooms, showers, laundry rooms, girls' hygiene rooms and toilets, daily doorknobs, washbasin taps, toilet bowl and urinal cisterns, toilet seats are washed with hot water using detergents and disinfectants.
Cleaning of toilets with the use of disinfectants should be carried out as they get dirty, but at least 2 times a day. Toilet bowls are washed with ruffs and brushes with hot water using detergents and disinfectants.
12.4. Cleaning equipment must be labeled depending on the purpose of the premises and types of cleaning work and stored in a room for cleaning equipment or in a specially equipped cabinet. Cleaning equipment for the toilet (rags, buckets, brushes) is marked and stored in the toilet room in a special closet or in a designated place.
Cleaning equipment (brushes, rags, ruffs) is washed, disinfected, rinsed and dried.
Detergents and disinfectants are stored in the manufacturer's containers or in labeled containers.
12.5. Bath days for children are held at least 1 time in 7 days.
In the bath and showers, you must use individual accessories: shoes, towels, soap, washcloths.
The possibility of washing children in the shower should be provided daily.
12.6. Bedding (mattresses, pillows, blankets, sleeping bags) should be knocked out once before the summer season, aired, air dried or dry cleaned.
According to epidemiological indications, bedding should be subjected to chamber disinfection in specialized organizations.
12.7. Bed linen and towels are changed as they get dirty, but at least once a week.
12.8. Dirty linen in the sleeping quarters is folded into special bags, which are delivered to the laundry.
In the absence of a laundry in a children's health camp, it is possible to organize a centralized washing of bed linen in other laundries. A special room is provided for the collection and storage of dirty linen.
12.9. In the premises of the children's health camp there should be no insects and rodents. On the territory and in the premises of the children's health camp, deratization and pest control measures should be carried out.
12.10. The territory of the children's health camp must be kept clean. Cleaning of the territory is carried out at least once a day.
Garbage is collected in metal waste bins with lockable lids. Waste bins are cleaned when they are 2/3 full. After emptying, the waste bins are disinfected with the means allowed for this purpose.
12.11. Cleaning of medical premises and processing of medical products are carried out in accordance with sanitary and epidemiological requirements for organizations engaged in medical activities 6 .
Class B medical waste (epidemiologically hazardous waste) is disinfected in accordance with the sanitary and epidemiological requirements for medical waste management.
XIII. Requirements for the implementation of sanitary rules and the organization of the work of medical personnel
13.1. The head of the children's health camp is responsible for the implementation of these sanitary rules, including ensuring:
Availability of the text of these sanitary rules, familiarization with them and their implementation by the personnel of the children's health camp;
Necessary conditions for compliance with sanitary rules;
Employment of persons with a permit for health reasons, who have undergone professional hygienic training and certification;
Availability of personal medical books for each employee and timely passage of preliminary and periodic medical examinations;
Organization of measures for disinfection, disinfestation and deratization, anti-mite (acaricidal) treatments (according to indications).
13.2. Medical personnel carry out daily monitoring of compliance with:
Requirements of these sanitary rules;
Personal hygiene rules for children and staff;
Implementation of the daily routine;
Catering organizations (quality of incoming products, conditions for its storage, compliance with the terms of implementation, technology of preparation and quality of finished food; sanitary condition and maintenance of the canteen; quality of washing dishes);
Fulfillment of daily norms and diet, daily sampling, organization of the drinking regime.
Medical personnel provide:
Daily examination of the staff of the dining room and children on duty in the kitchen for the presence of pustular skin diseases, catarrhal phenomena of the upper respiratory tract, a survey for the presence of dysfunction of the gastrointestinal system. The results of the examination are recorded in the health journal ();
Timely isolation of infectious patients;
Notification of territorial medical organizations and departments of Rospotrebnadzor about cases of infectious diseases within the first two hours;
Organization and implementation of sanitary and anti-epidemic measures.
13.3. First aid and medical assistance are provided in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
___________________________________
1 Decree of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation of March 18, 2011 N 21 "On approval of SanPiN 2.4.2.2843-11" Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the device, maintenance and organization of the work of children's sanatoriums "(registered by the Ministry of Justice of Russia on March 24, 2011, registration N 20279) .
2 Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 05.06.2013 N 476 "On issues state control(supervision) and invalidation of certain acts of the Government of the Russian Federation" (Sobraniye zakonodatelstva Rossiyskoy Federatsii, 2013, N 24, art. 2999).
3 Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated April 12, 2011 N 302n "On approval of lists of harmful and (or) dangerous production factors and work, during the performance of which mandatory preliminary and periodic medical examinations (examinations) are carried out, and the Procedure for conducting mandatory preliminary and periodic medical examinations (examinations) of workers engaged in heavy work and in work with harmful and (or) hazardous conditions labor" (registered by the Ministry of Justice of Russia on 21.10.2011, registration N 22111) as amended by the order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated 15.05.2013 N 296n (registered by the Ministry of Justice of Russia on 03.07.2013, registration N 28970).
4 Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated January 31, 2011 N 51n "On approval of the national calendar of preventive vaccinations and the calendar of preventive vaccinations for epidemic indications" (recognized as not requiring state registration by a letter of the Ministry of Justice of Russia dated February 17, 2011, registration N 01 / 8577-DK).
APPROVE
Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation G. G. Onishchenko
^ 2.4.4. CHILDREN'S OUT OF SCHOOL INSTITUTIONS, SUMMER HEALTH INSTITUTIONS
Hygienic requirements for the device, maintenance and organization of the regime in health-improving institutions with daytime stay of children during the holidays
Sanitary and epidemiological rules SP 2.4.4.969-00
^ 1. General provisions and scope
1.1. These sanitary and epidemiological rules (hereinafter referred to as the sanitary rules) determine the hygienic requirements for the placement, arrangement, maintenance and organization of the regime in health-improving institutions with daytime stay of children, aimed at improving the health of children and adolescents during the holidays.
1.2. Sanitary rules apply to all (except tent) recreational facilities with day stay of children and adolescents, regardless of their subordination and form of ownership.
1.3. Health-improving institutions with day stay of children are organized for students of grades I-IX educational institutions all types of property during the summer, autumn, winter and spring holidays. The capacity of the health facility is no more than 250 people. Health-improving institutions are recruited from among the students of one or more nearby schools, divided into units (groups) of no more than 25 people for students of grades I-IV and no more than 30 people for students of grades V-IX. Specialized institutions for young technicians, sailors, tourists, naturalists, athletes and others can be created, uniting children of interest.
1.4. Health-improving institutions with day stay for children are organized on the basis of educational institutions, institutions of additional education for children, sports facilities and others in the presence of a sanitary and epidemiological conclusion on compliance with their sanitary rules.
It is allowed to organize recreational institutions with daytime stay for children under the age of 10 on the basis of temporarily non-functioning preschool educational institutions (DOE).
Specialized shifts (groups) can be organized on the basis of health-improving institutions with daytime stay of children in compliance with the requirements of these sanitary rules and in agreement with the territorial centers of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision (hereinafter referred to as the TsGSEN).
Recreational institutions with day stay are divided into:
Institutions with the stay of children until 2.30 pm and the organization of 2 meals a day;
Institutions with children staying until 18.00 and organizing 3 meals a day, as well as organizing daytime sleep for children under 10 years old.
Institutions are not used for the rehabilitation of children:
Relating to the level of sanitary and epidemiological well-being to the 3rd group;
located in sanitary protection zone industrial organizations.
1.5. The duration of a shift in a health-improving institution is determined by the duration of the holidays and is at least 21 days during the summer holidays; autumn, winter and spring for at least 7 days.
The break between shifts in the summer for general cleaning and sanitization of the institution is at least 2 days.
1.6. Acceptance of a health institution is carried out by a commission 3-5 days before its opening, which includes representatives of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision, with the subsequent execution of an act. 1.7. The opening of a health-improving institution is carried out in the presence of a sanitary-epidemiological conclusion on compliance with its sanitary rules before the start of each health-improving shift.
1.8. The head of a health-improving institution must immediately inform the territorial center of state sanitary and epidemiological supervision about cases of group infectious diseases, about emergency situations in the operation of water supply, sewerage, technological and refrigeration equipment.
^ 2. Requirements for the site
2.1. The site of the health institution should be landscaped, landscaped, have convenient access roads, and be divided into zones (sports and recreation, administrative and economic, for recreation), equipped with playgrounds for recreation, sports, children's games.
On the territory of the site of the health facility, means of protection from the sun are provided.
2.2. For the improvement of children, it is advisable to use parks of culture and recreation, green areas, sports facilities, swimming pools, natural reservoirs.
2.3. used sports and play equipment must be safe, serviceable, secure, stable and appropriate for the height and age of children.
^ 3. Requirements for the building
3.1. The health facility should be located no higher than the third floor.
The set of premises of a health-improving institution should include: game rooms, rooms for classes, bedrooms for children's daytime rest, a medical office, a gym, a catering unit, a locker room for outerwear, a pantry for sports equipment, games and club equipment, a library, a sanitary room, bathrooms and wash basins.
Depending on climatic and geographical conditions, it is necessary to provide a room for drying clothes and shoes.
The areas, equipment and decoration of the premises must comply with the hygienic requirements for children's health institutions.
3.2. Placement of children in bedrooms is carried out at the rate of at least 3 m 2 per 1 person, but not more than 15 people in one room. Sleeping quarters for boys and girls are arranged separately, regardless of age.
3.3. Game rooms (at the rate of at least 1 m 2 per 1 person) and circle rooms (at the rate of 1 room with an area of at least 36 m 2 per 50 people) are located in rooms whose area and configuration can ensure the correct arrangement of furniture, favorable conditions for visual work .
3.4. In circle rooms, the possibility of hitting children should be completely excluded. electric shock, chemicals, explosives and other harmful and damaging factors.
Work in metalwork, carpentry, sculpture, art workshops is carried out by children only in overalls.
3.5. The walls and floors of the premises of health-improving institutions must be smooth, allowing them to be cleaned with a wet method.
Floor coverings for games, circles, bedrooms, medical, sports facilities, corridor and other premises for the stay of children, plank, parquet or linoleum and other materials permitted for use in the prescribed manner are allowed.
Floors in the premises of the catering unit, showers and sanitary facilities lined with ceramic or mosaic polished tiles.
^ 4. Requirements for air-thermal conditions
4.1. Transoms and vents should function at any time of the year. The presence of a grid on the windows, transoms in the summer is mandatory.
4.2. The windows of the premises, except for those oriented to the northern rhumbs of the horizon, are equipped with sun protection devices or curtains in order to avoid overheating.
4.3. In game rooms, rooms of circles, bedrooms, the ventilation regime should be observed. Through ventilation is carried out in the absence of children, one-sided - in the presence of children. The duration of ventilation depends on the season, outdoor temperature and indoor temperature.
The air temperature in sleeping, playing, club rooms should not be lower than +18°C (with tape glazing +20°C); in the gym - not lower than +17 ° С.
In the main premises of the health institution, the relative humidity of the air should be in the range of 40-60%.
4.4. Bathrooms are equipped with a channel exhaust ventilation with mechanical motivation.
^ 5. Requirements for natural and artificial lighting
5.1. All main premises of health-improving institutions should have natural lighting.
5.2. Artificial lighting should provide the following levels of illumination, depending on the purpose of the premises:
| Name of the room | Illumination (vlk) | The surface to which the lighting standards apply |
|
| at lum. lamps | with incandescent lamps |
||
| circle (game) rooms | 300 | 150 | on the working surface of the table |
| sleeping rooms | 75 | 30 | at the level of 0.5 m from the floor |
| gym | 200 | 100 | floor |
| recreation | 150 | 75 | floor |
5.3. For general lighting of circle and other rooms, fluorescent lamps of the LB type are recommended ( white color) and LE (natural color).
When using incandescent lamps as light sources, the presence of ceiling lamps is mandatory. Closed ceiling lamps are allowed in sleeping quarters.
5.4. Luminaires must be cleaned before the start of the health facility. Children and teenagers are not involved in this work.
Faulty fluorescent lamps are collected and stored until delivery in places inaccessible to children.
^ 6. Requirements for sanitary equipment
6.1. The building of the health institution must be equipped with plumbing, hot water supply and sewerage.
In case of their absence, the choice of a source of water supply and methods for removing sewage and waste are subject to agreement with the territorial center of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision.
Provides for the availability of backup sources of hot water in the catering unit.
6.2. Health facilities are provided with good quality drinking water in accordance with the hygienic requirements for water quality of centralized drinking water supply systems.
6.3. Buildings of health institutions should be equipped only with systems central heating and ventilation. Furnace and gas heating not used.
6.4. Depending on weather conditions, radiators, tubular heating elements embedded in concrete panels. Heating appliances should be protected with removable wooden grates, except for those made of particle boards, as well as other materials, when heated, the emission of harmful substances into the indoor air may occur.
6.5. In front of the dining room, washbasins (with hot and cold water supply) are equipped at the rate of 1 washbasin for 20 seats. Each washbasin is provided with soap, electric towels or paper rolls, or individual towels.
6.6. The sanitary room (for washing feet before going to bed) is equipped with benches, a container for warm water, basins, ladles, wooden grates.
6.7. Sanitary units are organized separately for boys and girls at the rate of 1 point for 15-20 people.
^ 7. Requirements for the equipment of the premises
7.1. Bedrooms are equipped with stationary single-tiered beds or hard-surface folding beds.
When organizing sleeping quarters on the basis of a preschool educational institution (in accordance with clause 1.3 of this document), it is allowed to use built-in 2-tier beds.
Stationary 2nd and 3rd bunk beds are not used.
7.2. Each bed is provided with a set of bedding (a mattress with a mattress topper, a pillow, a flannelette or woolen blanket) and at least 1 set of bed linen (a pillowcase, a sheet, a duvet cover, 2 towels).
7.3. Bed linen is changed as it gets dirty, but at least once every 7 days. In agreement with the territorial Central State Sanitary and Epidemiological Service, washing of bed linen can be carried out individually by the parents of children staying in a health facility.
7.4. Dressing rooms are equipped with hangers or cabinets for outerwear for children and staff.
7.5. Rooms for group work and playrooms are equipped with tables and chairs, taking into account the types of activities in accordance with the growth data of children.
Stools, benches, benches are not used instead of chairs.
7.6. To watch TV programs, you can install in game room TV set with rows of chairs. The distance from the TV screen to the first rows of chairs must be at least 2 meters.
^ 8. Hygienic requirements for daily routine
8.1. The regime of the day in a recreational institution with a day stay is developed in accordance with the hygienic requirements for regimens for children of various age groups, and provides for their maximum stay in the fresh air, holding health-improving, physical culture, cultural events, organizing excursions, hiking, games; regular 3 meals a day (break between meals no more than 3.5-4.0 hours) and afternoon (daytime) sleep for children under 10 years old (in accordance with clause 1.3 of this document).
The daily routine is developed taking into account the state of health of children and is adjusted depending on the season of the year.
8.2. In recreational institutions with a day stay for children, the following daily routine is recommended:
| Elements of the daily routine | Time spending |
|
| stay until 14.30 | stay until 18.00 |
|
| Collection of children, exercises | 8.30-9.00 | 8.30-9.00 |
| morning ruler | 9.00-9.15 | 9.00-9.15 |
| Breakfast | 9.15-10.00 | 9.15-10.00 |
| Work according to the plan of detachments, socially useful work, the work of circles and sections | 10.00-12.00 | 10.00-12.00 |
| Wellness treatments | 12.00-13.00 | 12.00-13.00 |
| Free time | 13.00-13.30 | 13.00-13.30 |
| Dinner | 13.30-14.30 | 13.30-14.30 |
| leaving home | 14.30 | |
| Afternoon (afternoon) nap | 14.30-15.30 |
|
| afternoon tea | 15.30-16.00 |
|
| Cultural and sports events, work of circles and sections | 16.00-18.00 |
|
| Evening line, going home | 18.00 |
|
8.3. All circle, sectional, club, excursion, gaming, communicative and educational, physical culture and health and sports activities, if possible, should be carried out outdoors, using awnings, awnings, verandas in inclement weather.
8.4. A visit by one child to more than 2 circles (sections) of different profiles is not recommended. In the case of a child attending 2 circles, it is preferable to combine sports and non-sports profiles. The frequency of attending classes is no more than 2 times a week in one circle.
8.5. The duration of classes and sports sections is allowed no more than 35 minutes for children 7 years old and no more than 45 minutes for children over 7 years old.
For certain types of circles (tourism, young naturalists, local history, etc.), the duration of classes is up to 1.5 hours.
8.6. The optimal occupancy of groups in the organization of circle, sectional, club, etc. work is no more than 15 people, the allowable one is 20 people (with the exception of choral, dance, orchestral and others).
8.7. After circle activities with limited physical activity (graphic activity, modeling, chess, needlework, etc.), it is necessary to provide for active rest, physical exercises, outdoor sports entertainment.
8.8. The organization of classes using computer technology is carried out in accordance with the hygienic requirements for video display terminals and personal electronic computers.
8.9. The total duration of TV viewing per day is recommended no more than 1.5 hours for students of grades I-IV and no more than 2.5 hours for students of grades V-IX.
8.10. Children and adolescents are not involved in cleaning sanitary facilities, common areas (stairwells, flights and corridors), washing windows, wiping lamps.
8.11. Taking into account the peculiarities of the work of a health-improving institution, changes can be made to the daily routine in agreement with the territorial center of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision.
^ 9. Hygienic requirements for the organization of physical education and recreational activities
9.1. Physical education activities are organized in accordance with the age of children, their state of health, the level of physical development and physical fitness.
9.2. Physical culture and health-improving work is coordinated with a medical worker and provides for the following activities:
Morning exercises;
Physical education classes in circles, sections, swimming training;
All-camp and detachment walks, excursions and hikes with games on the ground;
Sports competitions and holidays;
Training on simulators.
9.3. Sports and recreational activities can be held on the basis of the stadium and gym of the school or boarding school, sports facilities of district, local or city significance, sports schools and other facilities allocated for a health institution.
9.4. The distribution into medical groups for physical education is carried out by a medical worker. Children of the main medical group are allowed to participate in all sports and recreational and sports events without restrictions.
With the children of the preparatory medical group, physical culture and recreation activities are carried out, taking into account the state of health and individual tolerance.
9.5. For the purposeful improvement of the functions and development of muscle groups, it is necessary to introduce simulators and training devices into the practice of physical education in children's health institutions.
In addition to the premises, simulators can be installed on open playgrounds and sports grounds, health zones.
^ 10. Requirements for catering
10.1. Nutrition for children and adolescents is organized on the basis of a canteen that works on raw materials, canteen-preparation, or canteen-distribution of a functioning institution, as well as nearby facilities Catering if there is a sanitary-epidemiological conclusion on compliance with their sanitary rules, with the allocation of a separate room, inventory and utensils for children and determining the schedule for eating.
10.2. Constant control over the quality of incoming products, the period of their implementation and storage conditions is carried out by a medical worker or his substitute, who has completed a course of hygienic training.
Periodic control is carried out by the territorial center of state sanitary and epidemiological supervision SP 2.4.4.969-00
10.3. When catering for children, one should be guided by an exemplary menu for country health camps if there is a sanitary and epidemiological conclusion on compliance with its sanitary rules.
When compiling the menu, dishes and side dishes of the same name are not included within one day; dishes and side dishes of the same name for two days in a row. The layout menu is compiled taking into account nutritional standards.
10.4. Based on the indicative menu, other dietary options can be developed and agreed upon for specific conditions and food availability.
10.5. In order to preserve nutritional value products and warnings food poisoning should be respected the right technology cooking.
10.6. Products are bookmarked by weight according to the menu layout in the presence of a medical worker. In the manufacture of piece dishes (cutlets, cheesecakes, buns, pies, etc.), they are weighed by the cook before heat treatment. Casserole, scrambled eggs, roll cut into ready-made weight indicated in the menu layout. Liquid dishes are distributed by volume, and side dishes by weight.
10.7. C-vitaminization of third courses is carried out daily at the rate of
Vitaminization of compotes should be carried out after they have been cooled to a temperature of +12 to +15 °C before sale.
Vitaminization of ready-made meals is carried out under the supervision of a medical worker and is recorded in a special journal.
10.8. The issuance of prepared food is carried out only after the sample is taken by a medical worker. The assessment of the quality of dishes is carried out according to organoleptic indicators (the sample is taken directly from the containers in which food is cooked). In the marriage journal, it is necessary to note the bookmark of the main products, taste, readiness of the dish and permission to issue.
10.9. Daily left daily test prepared food. The selection and storage of daily samples is carried out under the supervision of a medical worker. The sample should be taken in the amount of a serving in a sterile jar with a lid (garnishes are taken in a separate container) and stored in a specially designated place in the refrigerator at a temperature of +2 to +6 °C.
10.10. If there is a pre-cooking canteen or a raw canteen in the health facility, the health worker must keep a marriage log perishable products, which indicates the name of the received product, its quantity, invoice number, the sales period for the invoice and the actual sales period for the product, the balance and its implementation.
10.11. In order to prevent the emergence and spread of infectious diseases and mass poisoning in the diet of children:
A) are not used:
Leftover food from a previous meal, as well as food prepared the day before;
Flask, barrel, unpasteurized milk without heat treatment (boiling);
cottage cheese, sour cream, green pea in its natural form without heat treatment (boiling);
Fish without heat treatment (stroganina, vobla, etc.);
Sour milk "samokvas";
Drinks, fruit drinks, etc. own cooking, kvass;
Meat products, waste sausage shops, pork chops, diaphragms, blood, brains, head meat rolls, blood and liver sausages;
Meat that has not passed veterinary supervision;
Egg and meat of waterfowl;
Canned homemade products;
Canned food in tomato sauce;
Powders of unknown composition as dough leavening agents, dry concentrates for preparing side dishes.
B) are not manufactured:
Cheese mass, cottage cheese;
pasta with minced meat(“in a naval way”), pancakes with meat, jellies, brawns, okroshka, pates, minced herring, jellied dishes (meat and fish);
Macaroni with chopped egg, fried eggs;
creams, confectionery with cream;
Fried products.
B) not included: spicy sauces, mustard, horseradish, pepper, vinegar. natural coffee, juices and drinks in the form of dry concentrates.
D) meat of 2-3 categories is not accepted; gutted chickens;
substandard products; soaked products in soft containers (flour, cereals, sugar, etc.); canned food with a violation of tightness (bombing, crackers); vegetables, fruits, berries with signs of spoilage;
products damaged by rodents, as well as contaminated with their excrement.
Depending on the epidemic situation, by decision of the territorial center of state sanitary and epidemiological supervision, the list of products and ready-made meals that are not used in a recreational institution with daytime stay for children can be expanded.
10.12. Sour cream, yogurt and cottage cheese, produced by milk processing organizations in small packages, do not require special heat treatment.
10.13. Canned meat and fish in oil own juice can be used several times during a health-improving shift (including in the absence of natural meat and fish) if there is a sanitary and epidemiological conclusion on their compliance with sanitary rules.
10.14. Storage and sale of food products is carried out in accordance with the current regulatory and technical documentation at the appropriate temperature and humidity parameters.
10.15. Unpeeled boiled vegetables can be stored for no more than 6 hours at a temperature of +2-+6 ° C, peeled boiled vegetables - no more than 2 hours. Dressing salads is made immediately before their issuance.
10.16. Bread is stored in trays on racks. Doors in cabinets for bread must have holes for ventilation; cleaning in the cabinet is carried out 1 hour before each load of bread with a 1% solution of table vinegar.
10.17. The deck for chopping meat is made of hardwood, mounted on metal stand, painted on the outside oil paint in 2 layers. At the end of the work, the work surface is cleaned with a knife and sprinkled with salt (the container with salt for processing the deck is stored in meat shop), the side part is washed with hot water. When deep notches appear, the cutting surface is cut off.
10.18. Cutting boards and knives are marked: C (herring), PC (raw fish), KS (raw chicken), MS (raw meat), OS (raw vegetables), PB (boiled fish), 0B (boiled vegetables), MB (meat boiled), KB (boiled chickens), X (bread), G (gastronomy). Boards are made from hardwood.
Make sure you have an adequate supply of cutting boards and knives. Cutting boards are cleaned with a knife, washed with hot water with the addition of detergents, scalded with boiling water and stored on edge directly at the workplace or in a suspended state.
10.19. The number of sets of dishes should be at least 2 according to the number of children per shift. The dishes are not washed during the meal.
Aluminum, duralumin utensils can only be used for cooking and short-term storage of food.
It is allowed to use tableware made of faience, porcelain, cupronickel, enameled, stainless steel.
Do not use dishes with cracks and broken edges, as well as enamelware with damaged enamel.
AT field conditions it is allowed to use plastic utensils that are approved for use in the prescribed manner.
10.20. Dishwashing is carried out after each meal using detergents and disinfectants approved in the established order for use for these purposes. Dishwashing is carried out in stages: washing tea utensils;
washing tableware; washing cutlery; washing kitchen utensils.
For washing dishes are not used: washing powder, washcloths, sponges. It is allowed to use metal and plastic ruffs (brushes) for these purposes.
10.21. Metal brushes for washing dishes, rags for wiping tables are boiled for 15 minutes or soaked in a 0.5% clarified solution of bleach, or soaked for 30 minutes in a 1% solution of chloramine, dried and stored in a specially designated place. Rags, detergents, disinfectants (used according to epidemiological indications) are stored in labeled containers. In the washing departments, instructions are posted on the rules for washing dishes and equipment.
10.22. Transportation of food products is carried out by special vehicles with a sanitary passport.
^ 11. Requirements for sanitary condition and maintenance
health institution
11.1. The territory of the health facility is kept clean; in summer it is watered, in winter it is cleared of snow and ice.
The equipment of the site (tables, benches, physical education equipment), in order to avoid injuries, must be in good condition and securely fastened.
Garbage bins are cleaned daily when filling no more than 2/3 of the volume.
11.2. All premises of the health institution are subject to daily wet cleaning using detergents, wiping window sills, cabinets, tables, etc. When cleaning, it is recommended to use vacuum cleaners. Room cleaning is carried out open windows and transoms in the summer and open windows and transoms in other seasons.
11.3. It is recommended to clean the premises: sleeping quarters - after a day's sleep; dining room - after each meal; gym - after each lesson; other rooms - as needed and at the end of the day.
11.4. In washrooms and sanitary facilities, cleaning is carried out as they become dirty, but at least 2 times a day with hot water using detergents and disinfectants. Toilet bowls are treated with kvachas (brushes) using the Sanitary preparation or a 2% hydrochloric acid solution, followed by copious washing with water. Wash toilet seats daily with warm soapy water.
Bathrooms are cleaned with specially allocated equipment (rags, buckets, brushes), which has a signal marking of red or orange color and is stored separately from the rest of the cleaning equipment in the toilet room in a special closet.
11.5. All cleaning equipment should be washed with hot water and detergent after use.
Detergents and disinfectants are stored in specially designated areas that are not accessible to children; disinfectants are stored in a dark place, in a dark container with a tightly closed lid.
11.6. General cleaning of all premises is carried out before and after the end of each shift.
11.7. Repair work during the functioning of the health institution is not carried out.
11.8. When conducting repair work during the preparatory period, it is allowed to use finishing materials(varnishes, paints, mastics, linoleum, finishing tiles and other synthetic finishing materials) allowed in the prescribed manner.
^ 12. Hygiene requirements for preventive medical examinations and personal hygiene of personnel
12.1. All employees of health-improving institutions undergo preliminary medical examinations upon admission to work and periodic preventive medical examinations in accordance with the procedure determined by federal body executive power for health care.
12.2. Only employees vaccinated against diphtheria are allowed to work with children in health-improving institutions.
12.3. Employees of health-improving institutions undergo hygienic training in accordance with the established procedure.
12.4. The staff of the health institution must observe the rules of personal hygiene: come to work in clean clothes and shoes; leave outerwear, headgear and personal items in the dressing room; cut nails short; Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water after each visit to the toilet.
Before starting work, medical personnel and catering workers should thoroughly wash their hands with soap and water, put on overalls and put their hair under a cap.
The staff of the catering unit should not wear rings, earrings, stab overalls with pins, varnish their nails, eat, smoke at the workplace during work.
All catering workers are daily examined by a health worker for the presence of pustular diseases and catarrhal phenomena. Persons with pustular skin diseases, as well as patients, are suspended from work. The results of the inspection are recorded in the journal of the established form.
^ 13. The main activities carried out by medical personnel in a health institution
13.1. Medical workers in day-care health-improving institutions carry out:
Preliminary examination of children upon admission to a health institution (including examination for pediculosis);
Preliminary inspection and verification of readiness for receiving children of premises, places of physical education and sports;
Medical cabinet set up medicines and medical equipment;
Verification of medical documents of employees and children of the health camp (extract from " Individual card development of the child” indicating the diagnosis, the medical group for physical education, the results of studies on diphtheria);
Carrying out a medical examination of children on the first day of the health institution (or on the eve of the opening) in order to identify patients;
Systematic monitoring of the health of children, especially children with health problems;
Distribution of children into medical groups for physical education;
Informing the head of the health institution, educators and physical education teacher about the state of health of children, the recommended regimen for children with health problems;
Daily outpatient appointment to provide medical care (if necessary), active identification of sick children; their timely isolation, first aid in case of accidents; transportation to the hospital;
Immediate notification to the territorial institutions of health care and state sanitary and epidemiological supervision about cases of infectious diseases among children of a health-improving institution;
Control over: the organization of nutrition for children, the quality of incoming products, the conditions for their storage, compliance with the terms of implementation, cooking technology, the quality of prepared food, the sanitary condition and maintenance of the catering department, washing dishes, fortifying food, daily examinations of catering staff and children on duty for pustular diseases, taking a daily sample, monitoring the implementation of nutritional standards;
Systematic monitoring of the sanitary condition and maintenance of all premises and territory of the institution, compliance with the rules of personal hygiene by children and staff;
Organization and implementation of sanitary and anti-epidemic measures;
Carrying out work on the formation healthy lifestyle life with staff and children. Organization of "Health Days", games, quizzes on a medical theme;
Medical control over the organization of physical education, over the condition and maintenance of places for physical education, monitoring proper conduct physical culture activities depending on gender, age and health status of children.
^ 14. Requirements for compliance with sanitary rules
14.1. The head of the health-improving institution ensures the implementation of these sanitary rules.
14.2. The medical staff of the health-improving institution exercises daily control over the observance of sanitary rules.
14.3. Supervision over the implementation of these sanitary rules is carried out by the territorial centers of the state sanitary and epidemiological supervision.
14.4. For violation health legislation the head of the health-improving institution is responsible in the manner prescribed by federal law"On the sanitary and epidemiological well-being of the population" No. 52-FZ * dated 30.03.99.
Nutritional norms
Children and teenagers in health-improving institutions with children's day stay
| Name of products | Norms per child per day (grams per day) |
|
| up to 10 years | over 10 years old |
|
| Dairy products: milk | 375 | 500 |
| semi-fat cottage cheese | 30 | 40 |
| sour cream | 7,5 | 10 |
| cf | 7,5 | 10 |
| meat, sausages | 120 | 160 |
| fish | 45 | 60 |
| egg | 1 PC. | 1 PC. |
| Rye bread | 75 | 100 |
| wheat bread | 188 | 250 |
| wheat flour | 7,5 | 10 |
| pasta, cereals, legumes | 56 | 75 |
| sugar, confectionery | 60 | 80 |
| potato flour | 6 | 8 |
| yeast | 1,5 | 2 |
| butter | 34 | 45 |
| vegetable oil | 12 | 15 |
| potato | 263 | 350 |
| vegetables, greens | 300 | 400 |
| fresh fruits | 150 | 200 |
| dried fruits | 12 | 15 |
| tea | 0,75 | 1 |
| coffee, coffee drink | 2 | 2,5 |
| salt | 6 | 8 |
| spices | 0,75 | 1,0 |
Note: during the summer period, the norms should be increased by 10-15%.
^ 1.6 Main directions of recreational activities
at the children's health camp
Health-improving work in summer health-improving institutions is carried out in the following areas, which determine the use of specific forms and methods:
schedule;
nutrition;
psychological sparing in Everyday life;
tempering activities;
use of traditional (based on folk traditions) methods;
assessment of the effectiveness of recreational work.
^ Physical education becomes an effective means of strengthening and maintaining health only if it is methodically correct and adequate. physical abilities child. So effective use means of physical culture for health promotion, improvement of physical development and adaptive abilities is impossible without properly organized medical control.
^ medical control for physical education in a summer health camp is a wide range of activities, which includes:
Medical examination of children;
Implementation of sanitary and hygienic control over the places and conditions for hardening activities, physical culture and sports, adherence to the daily routine and measures to prevent injuries during classes exercise and labor activity;
Organization and control over all forms of physical education and sports;
Organization and control of hardening activities;
Medical support for all physical culture and health and sports events;
Sanitary and educational work with vacationing children and camp staff;
Maintaining medical records in order to record and control the physical education and rehabilitation of children;
Evaluation of the effectiveness of recreational activities and the choice of methods to improve their quality.
morning exercises;
hardening procedures;
Outdoor games and activities various types physical training;
Sports, physiotherapy exercises, swimming training;
Walks, excursions and hikes;
Sports competitions and holidays.
In the first days of the work of a health-improving institution, an in-depth medical examination of children is carried out, on the basis of which the type and intensity of hardening effects and physical activity are selected depending on the age, health status of children and their physical fitness, belonging to one or another health group and medical group is determined by physical education.
To main medical group include children who do not have deviations in the state of health, are well physically developed and tolerant to physical activity. They are shown all forms of physical education and sports, participation in sports competitions, passing sports normative complexes, all types of tempering procedures (after the adaptation period).
To preparatory medical group include children with minor deviations in the state of health (often of a functional nature) or in physical development with a satisfactory response to physical activity. They are shown classes aimed at general physical training, subject to the gradual development of a set of physical exercises. Hardening procedures are prescribed depending on the state of health and on the previous hardening of the child.
To special medical group include children in whose health status there are pronounced deviations of a permanent or temporary nature that do not interfere with their normal life, but require limitation of physical activity due to the unsatisfactory adaptability of the body to them. Such children are shown physical education classes with limited motor activity and the use of hardening procedures of low impact.
Together with the health group and the physical culture group, the doctor determines motor mode, on the basis of which the intensity of recreational activities, the amount of physical activity in the camp for each child is regulated. There are two modes in the health camp: sparing and training. This also takes into account the period of stay in a health institution (adaptation and main).
sparing mode is assigned:
Children who have had intercurrent (acute) diseases;
For the entire period, children who are contraindicated in increasing physical activity for health reasons (assigned to a special medical group, exempted from physical education); all children for the period of adaptation, (duration from 1 to 5 days). As an adaptogen, morning and evening walks are shown with a gradual increase in distance from 500 to 1000 m, close excursions of an introductory nature (lasting no more than an hour), board and other sedentary outdoor games with a gradual increase in physical activity (from 30 to 60 minutes), additional rest in climate pavilions or in places equated to them, music and aromatherapy. With a prolonged period of adaptation, it is possible to use medications(apilak, etc.) and phytoadaptogens ( chinese lemongrass, eleutherococcus, etc.), acupressure, psychotherapy. With exacerbation of foci of chronic infection, treatment should be carried out according to indications.
At the end of the adaptation period in the camp coaching the mode is assigned to children who satisfactorily cope with the physical activity provided for by the program of physical education general education schools. This mode involves the use of all forms of physical activity in full. At the same time, it is allowed to carry out the entire range of recreational activities: morning hygienic gymnastics, daily walks and games in the air, sun and air baths, swimming in reservoirs, dosed running, hiking, excursions, training on simulators, in sports and sports-applied circles and sections, groups of choreography, therapeutic gymnastics, etc.
In the first days of the shift, the medical staff introduces the camp staff (the head of the institution, educators, physical education instructors) to children of the "risk group" who need a sparing regimen, special attention and individual approach. The involvement of these children in outdoor games, their participation in sports events, walking tours, swimming in the pool and open water must be coordinated with medical workers. It is better for them to organize physical culture classes separately (physiotherapy exercises are effective), to classes in sports sections and they are not allowed to compete. They must be involved in the preparation of social events (including sports) without coercion. When choosing games, activities, it is necessary to proceed from the interests of the child (from the standpoint of psychological sparing).
^ Admission to classes in sports sections and sports and applied circles. For children who want to learn and improve in certain types sports, sports sections are organized in the camp. They can be attended by children assigned to the main or preparatory group in physical education (provided that for health reasons this sport is not contraindicated for them). In the classroom, the physical fitness and fitness of children should be taken into account. Lessons are held less often 3 times a week and should be directed, first of all, to general physical training. Back to classes children are allowed who do not have contraindications to them for health reasons, about which the camp health worker makes an individual mark in the list of those wishing to study. In addition to sports sections, in the summer health camp there can be sports and applied circles, classes in which are associated with physical activity (“young fireman”, “young naturalist”, tourist circle, radio sports circle, etc.). Children should also be allowed to participate in such circles based on their state of health. In order to avoid excessive load on the body, each child is recommended to engage in no more than one sports (sports and applied) section and 2 circles of a different orientation at the same time.
^ Current medical control during the shift includes:
Systematic monitoring of the health status of children, especially those with deviations in it, active identification of the diseased;
Correction of the regimen and loads for children with health problems;
Daily outpatient reception of children and employees, hospitalization for medical reasons of children in a medical and preventive institution assigned to the camp, accompanying the child;
Assembling and regularly checking the availability of first aid kits medical care in places of physical culture, bathing, hardening, during hiking trips;
Control over the state of places for physical education, hardening, participation in the preparation and conduct of hiking trips;
Control over the implementation of the daily routine, all forms of organization of physical education and sports, hardening of children; access to sports and mass events, trips and competitions;
Medical support for all sports events, the presence of children in the river, swimming pool during bathing;
Carrying out work on the formation of a healthy lifestyle and the prevention of injuries with staff and children, the organization of "days of health", games, quizzes on a medical theme;
Maintaining medical records.
Current monitoring of the health status of children, correction of the regimen and loads for children with health problems are carried out throughout their stay in a health institution. The control consists in a systematic assessment of the tolerance of health-improving and tempering procedures, assessment of well-being during physical exertion, walks and excursions. Expansion of the motor regime and an increase in the intensity and duration of recreational activities are allowed subject to individual tolerance of loads. Sometimes it becomes necessary to limit physical activity. Children who have had acute illnesses during their holidays or shortly before arriving at the camp are exempted from physical education and sports: with tonsillitis, acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, bronchitis - for 1-2 weeks, with acute otitis media - for 2-4 weeks.
If necessary, medical consultations are held in order to issue individual recommendations for practicing various sports and recreational physical education. If there are complaints related to poor tolerance of physical culture and recreational activities, the doctor decides on the correspondence of physical activity to the functional capabilities of the body (including using functional tests given in the section "Evaluation of the effectiveness of recreational activities").
portability information physical activity and its adequacy to the state of health can be obtained directly in the places of physical exercise in the course of medical and pedagogical (medical and pedagogical) observations of physical education. For this, the following methods are used:
a survey about how you feel during the lesson, after the lesson;
monitoring signs of fatigue (table 1);
registration of changes in heart rate and blood pressure during the session.
Based on the results of the observation, a hygienic assessment of the lesson is carried out, medical, pedagogical and psychological methods are developed to improve the quality of classes in order to obtain the maximum healing effect. During the medical and pedagogical observation, a protocol is filled out, where the comments and recommendations of the doctor are entered.
Medical and pedagogical observations are carried out over all forms of organization of physical education in a summer recreational institution: morning exercises, classes in sports sections and various types of physical training, outdoor games, physical therapy classes, swimming and bathing training, etc.
Morning hygienic gymnastics is performed daily by all children, regardless of the physical culture group and motor regimen (sparing, training), in the open air, in rainy weather on the veranda or in a room of sufficient size with open windows. The purpose of the morning exercises in the camp is to bring the body into a state of wakefulness more quickly, hardening the body, improving physical health. Morning hygienic exercises have an organizing and disciplining value. During morning exercises and subsequent water procedures, the activity of skin and muscle receptors, the vestibular apparatus is activated, the excitability of the central nervous system increases, breathing, blood circulation and metabolism improve, coordination in the activity of the neuromuscular apparatus improves.
The duration of morning exercises is at least 15 minutes * (* SanPIN 2.4.4.1204-03). Exercises should be performed in light and loose clothing, sports shoes. Morning hygienic gymnastics is combined with hardening ( air baths in lightweight clothing). Short-sleeved clothing is chosen at an air temperature above +20 degrees, with a long sleeve - at a temperature of +15 to +20 degrees, in a woolen suit at a temperature of +10 to +15 degrees.
The complex is compiled by the sports leader of the camp and consists of 8-12 exercises of a dynamic nature. Exercises should be easy, familiar. Static exercises that cause strong tension and breath holding are not applicable. Movements should be free, at a calm pace, with a gradually increasing amplitude, with the involvement of small muscles first, and then larger muscle groups. Special attention focus on correct breathing and posture. The complex of exercises is adjusted during the shift 1 time in 7-10 days in the direction of a gradual increase in load (by increasing the number of repetitions, complicating the starting positions, introducing other exercises). After the completion of gymnastics, water procedures(washing, rubbing).
If the physical fitness of the children is approximately at the same level, a single dosage is suggested, i.e. the same number of repetitions for all children. An exception is made for children who are weakened and recovering from illness.
The following grouping of children by age is recommended when conducting sports and recreational activities, including morning exercises: 6-9 years old, 10-11 years old, 12-13 years old, 14-15 years old, 16 years old and older. It is allowed to conduct morning exercises for all children at the same time, and in order. It should be remembered that conducting a lesson in a group of 30 or more children of different ages increases the risk of injury and does not allow monitoring the dosage of physical activity for weakened children.
Gymnastics after daytime sleep should also be done daily for all children, especially in those cases when, in a health institution with daytime stay of children, daytime sleep - rest is organized on folding beds. Gymnastics is performed immediately after waking up in a sleeping room in lightweight clothing (panties, T-shirt). The complex includes 4-5 exercises of a general tonic and respiratory nature with a small number of repetitions, which can be performed in the initial position lying and sitting (on the bed) and standing (by the bed). Before the start of the lesson, the children put the blankets at their feet (there are no pillows). Lying, sips are performed, then the shoulder girdle, torso, legs are kneaded, and in conclusion, a breathing exercise is done. Then the children get up and walk barefoot on special exercise equipment, rugs, etc. to prevent flat feet. gymnastic sticks, pencils, napkins, etc. are used for the same purposes. It is useful to include in the complex elements of acupressure self-massage, reflex irritation of the feet. This type of health-improving gymnastics goes well with hardening procedures (walking barefoot on wet paths, wet rubdowns, extended washing). All this takes no more than 8-15 minutes.
The purpose of gymnastics after daytime sleep, as well as morning, is to improve the state of health and performance, hardening, switching the attention of children to active joint activities. It is possible to replace this form of motor activity with outdoor activities of the “motor hour” type immediately after daytime sleep under the guidance of a physical education instructor or educator.
^ Game exercises, outdoor games and relay races. Games and relay races should be conducted with maximum use of the open sports ground. To do this, a daily “Sport hour” is provided in the daily regime. The organizational part of the lesson under the guidance of an adult should be 25-30% of the time, and in the remaining time, children can study independently under the supervision of a teacher. The total duration of a sports hour should not exceed 45 minutes. To participate in games and relay races, you can involve all children at the same time (if the group is small) or conduct them separately by age. It is advisable to form teams in groups with approximately equal motor capabilities, this approach is preferable for children of a special medical group for physical education, who are on a sparing regimen.
^ 1.7 Organization of walks, excursions and hikes
Considering that almost all out-of-town recreational institutions in the Altai Territory are located in endemic areas along tick-borne encephalitis, it must be remembered that in the first season, exits from the territory of the ZOU are prohibited. Subsequently, all walks, walking tours and hiking trips and routes must be coordinated with the Rospotrebnadzor service.
Walks and walking tours can be up to 5 km long for children 6 - 11 years old (special group with doctor's permission - up to 3 km); for children over 11 years old: the main group - up to 10 km, preparatory - up to 8 km, special - up to 6 km. The pace of movement is 2 - 2.5 km / h, every 35 - 40 minutes. walk should be arranged for 10 minutes. rest stop. During the rest, you can organize calm games, training in tourist skills. Headwear is required. It is necessary to take boiled (bottled) drinking water for children.
Tourist trips are carried out 1-2 weeks after the arrival of children, no more than 2 times per shift for each child. The administration of the health institution should be familiar with the route of the hike; to conduct a trip, you must obtain permission from the local territorial department of Rospotrebnadzor (taking into account the sanitary and epidemiological well-being of the area in relation to infectious diseases, the state of water supply sources, the quality of drinking water, places for swimming, etc.). The doctor 1 - 2 days before departure on a hike, after prior agreement with Rospotrebnadzor, signs the route sheet.
Children 7 - 9 years old are allowed to participate in one-day trips, 10 - 13 years old - in one-, two-day trips, from 14 years old - in two-, three-day trips.
All participants in the hike must undergo a medical examination and obtain permission from a doctor.
To participate in the campaign, groups of 6 to 15 people of the same age are formed (the allowable difference is 1.5 years) and two leaders.
The length of the trip for junior schoolchildren(7 - 11 years old) - no more than 5 km, for older people - from 8 to 10 km per day. The speed of movement is not more than 3 km / h. Every 45 - 50 minutes of walking should make stops for 10 - 15 minutes.
The weight of a backpack for younger students should not exceed 2 kg, for older students making a 2 - 3-day hike - 8 - 9 kg ( sleeping bag- 2 kg, backpack - 0.5 - 1 kg, heat-insulating mat - 0.1 kg, personal belongings - 3 kg, food - up to 1 kg per day, personal first aid kit and repair kit - 0.2 kg, group equipment - 1 kg).
Before the trip, you should check the set and quality of food packaging, the availability of a sufficient amount of disposable tableware, as well as the equipment, the condition of the shoes and clothes of the participants.
An approximate set of products in grams per day per participant in the trip: black and white bread, crackers, cookies, crispbread - 500 g, cereals, pasta, ready-made cereal concentrates - 100 - 200 g, soup concentrates in bags - 50 g, butter melted cream - 50 - 60 g, stewed meat - 150 g, sugar, confectionery - 80 - 100 g, canned sausages in jars - 50 g, canned fish in natural juice, oil for cooking first courses - 50 g, fresh vegetables - 100 g, dry, freeze-dried vegetables - 50 g, dry milk, dry cream - 25 - 30 g, condensed milk - 50 g, cheese, processed cheese - 20 - 40 g, fresh fruits - 100 g, various dried fruits - 30 g, unnatural coffee - 3 g, cocoa powder - 10 g, tea - 4 g, Bay leaf, onion, garlic - 30 - 40 g, vitamins, salt - 10 - 12 g.
For drinking on a hike, only boiled water is used, prepared from water from drinking water sources (artesian wells, water supply networks, wells), the quality of which must meet the hygienic requirements for drinking water.
Contraindications for participation in hiking are:
all acute febrile conditions;
the period of convalescence after somatic and infectious diseases;
lag in physical development;
scoliosis of the 3rd degree, clubfoot, various osteoarticular deformities;
organic heart disease, rheumatism;
decrease in vision over 6 diopters;
toothache;
the presence of abrasions, scuffs on the legs, pronounced phenomena of epidermophytosis of the feet;
inguinal-scrotal hernia;
menstruation;
mental retardation in children requiring special supervision;
residual effects of paresis, paralysis; cerebral palsy phenomena, cicatricial changes that limit the movements of the limbs
^ 1.8 Physical Culture at the children's health camp
Physiotherapy exercises in a summer recreational institution, they are carried out by an exercise therapy instructor in a group method. Groups are formed from children with similar diseases. A set of exercises is selected depending on the nature of the disease and age characteristics of children. Hall physiotherapy exercises should be set up in a bright, well-ventilated room in which required humidity air and corresponding temperature. It is desirable that one of the walls of the hall be equipped with mirrors.
The area of the training room is at least 20 sq. m (at the rate of 4 sq. m per person). The discrepancy between the area of the room and the number of people involved sharply increases the risk of injury and limits the choice of exercises. The office (hall) of exercise therapy should be equipped with small equipment, at least 15 of each item. The presence of a sports uniform and individual mats for performing exercises lying down and sitting is mandatory. Classes should begin 1-1.5 hours after eating. The number of children involved at the same time should not exceed 10-15 people.
^ Mass physical culture and sports and health-improving events in the summer recreation facility are organized (physical and sports holidays outdoors, relay races, team games, visiting the pool, intra-camp and inter-camp competitions, sports games on rough terrain), and spontaneous forms of physical activity (individual and small-group ball games, tennis, badminton, jumping rope, etc.). When planning and conducting physical culture and sports events, teachers need to use information about the physical culture group of children and exercises that are contraindicated for them for health reasons. When holding any mass physical culture and sports event, it is mandatory to have at the venue first aid kits.
^ Sports holidays in the camp are held in the form of various complex competitions, including no more than 2-3 components. For young children, sports activities and competitions are held in the form of a game. The duration of such activities for students in grades 1-4 is 3 hours, for grades 5-7 - 4 hours. Before the start of the competition, the medical worker of the camp gives permission to participate in them in the form of an application sheet.
To participate in competitions not allowed:
children exempted from physical education and assigned to a special medical group;
children assigned to the preparatory physical culture group, if the exercises used in the declared type of competitive activity are contraindicated for them;
children with malaise and poor health (as well as girls during menstruation);
children who have not recovered from traumatic injuries, convalescents after acute and exacerbations chronic diseases;
untrained children who do not have appropriate sports training .
Before the start of the competition, a warm-up is required.
^ health care mass sports events both within the camp and between teams of neighboring camps are carried out by the medical service of the camp where the competitions are held. A doctor or a nurse serving the competitions is a member of the panel of judges as a deputy chief referee for the medical part. The decision of a medical worker concerning his competence is binding on the panel of judges.
The scope of duties of a person serving a physical education event includes:
control for correct design medical documentation (application sheets);
control over the sanitary and hygienic condition of the competition venues;
condition control sports equipment, equipment, sportswear, footwear of participants of competitions;
monitoring the conditions of the competition and taking appropriate measures (up to the termination of the competition) in cases where the situation threatens the health and safety of the participants (for example, a sharp deterioration in weather, other unforeseen circumstances);
monitoring the health of athletes and resolving questions about the possibility of continuing to participate in competitions after an injury or illness;
organization and provision of first aid to participants and spectators.





