Safety requirements before starting work, safety requirements during work, safety requirements at the end of work - safety precautions when working as a mechanic for instrumentation and automation. Work safety requirements
All documents presented in the catalog are not their official publication and are intended for informational purposes only. Electronic copies of these documents can be distributed without any restrictions. You can post information from this site on any other site.
Model instruction No. 1 on labor protection for car drivers
Approved by order of the Department of Motor Transport of the Ministry of Transport of Russia dated February 27, 1996 No. 16
Developed by the State Research Institute of Road Transport.
Approved by order of the Department of Road Transport of the Ministry of Transport Russian Federation dated February 27, 1996 No. 16.
Agreed by the Central Committee of the Trade Union of Road Transport and Road Workers on August 7, 1995.
The standard instruction was developed in accordance with the requirements of the Regulations on the procedure for the development and approval of rules and instructions for labor protection and Guidelines on the development of rules and instructions for labor protection, approved by the Ministry of Labor of Russia on July 16, 1993 No. 159, and on the basis of the Rules for labor protection for road transport, POT R O-200-01-95 .
The standard instruction is intended for managers and specialists of motor transport organizations in their work on the development of labor protection instructions for their subordinate employees.
Donchenko V.V., Samoilova L.G., Kuznetsov Yu.M., Manusadzhyants Zh..G. took part in the development of the Instruction. (NIIAT), Ipatov G.V. (Department of Road Transport), Obukhov V.I. (Trade Union of Road Transport and Road Workers).
1. INTRODUCTION
1.1. This Instruction regulates the basic safety requirements for the work of a car driver (hereinafter referred to as the driver).
1.2. The driver must comply with the requirements of the instructions developed on the basis of this one, and the instructions developed taking into account the requirements set forth in the standard labor protection instructions:
When hanging the car and working under it (Instruction No. 17);
When removing and installing car wheels (Instruction No. 18);
When towing, coupling, uncoupling cars or a car, trailer, semi-trailer (Instruction No. 19);
When moving around the territory and industrial premises of a motor transport enterprise (Instruction No. 20);
On the prevention of fires and the prevention of burns (Instruction No. 23).
Having noticed a violation of safety requirements by any employee, the driver must warn him of the need to comply with them.
The driver must also follow the instructions of the representative of the joint committee (commission) for labor protection or the authorized (trusted) person for labor protection of the trade union committee.
The driver must know and be able to provide first aid to the victim in accordance with the Model Instruction No. 22 on the provision of first aid in case of accidents.
The driver should not start performing one-time work that is not related to direct duties in the specialty, without receiving targeted instruction on labor protection.
2. GENERAL SAFETY REQUIREMENTS
2.1. Driving a car is allowed to persons who have an appropriate driver's license, who have passed induction training and primary briefing at the workplace on labor protection.
2.2. Driver not passing on time re-briefing on labor protection (at least 1 time in 3 months) and an annual test of knowledge on labor safety, should not start work.
2.3. The driver must comply with the internal labor regulations adopted at the enterprise.
2.4. The duration of the driver's working time should not exceed 40 hours per week.
Duration daily work(shift) is determined by the rules of the internal work schedule or shift schedules approved by the employer in agreement with the trade union committee.
2.5. The driver must be aware that the most dangerous factors that may affect him in the process of performing work are:
Posted car or its units;
Hot water and steam;
flammable substances;
Gases and other toxic substances;
leaded gasoline;
Equipment, tools, fixtures;
The fall of the driver as a result of his careless actions when leaving the cab and moving around the territory.
2.5.1. A car suspended only by a lifting mechanism is a great danger, as it may fall and crush the driver.
2.5.2. Hot coolant, water and steam cause burns if it comes into contact with the skin.
2.5.3. Flammable substances (vapours, gases), in the process of handling of which the safety rules are violated, can cause a fire and explosion.
2.5.4. Gases and other toxic substances (butane, nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, ethyl mercaptan and others), entering the human body through the respiratory system, lead to severe poisoning.
2.5.5. Leaded gasoline has a toxic effect on the body when its vapors are inhaled, the body is contaminated with it, it enters the body with food or drinking water.
2.5.6. Equipment, tools and accessories, if used incorrectly or malfunctioning, lead to injury.
2.6. It is forbidden to use tools, devices, equipment, with which the driver is not trained and instructed.
2.7. In accordance with the standard industry standards for the free issue of special clothing, special footwear and other means to workers and employees personal protection issued:
2.7.1. Drivers trucks, special vehicles, truck cranes and tractors:
Cotton overalls;
Mittens combined two-fingered.
In winter in special and IV additional belts:
Cotton jacket with insulating lining;
Cotton trousers with insulating lining;
Felt boots.
2.7.2. bus drivers and cars:
Cotton gloves.
2.7.3. Drivers of all vehicles running on leaded gasoline, when working on the line, additionally:
Rubber apron with bib;
Rubber gloves;
Sleeves are PVC.
2.7.4. in winter in areas assigned to II, III, IV and special climatic zones, drivers engaged in outdoor work, in addition to warm overalls, are given a heating kit of the "Penguin" type.
2.8. The driver must comply with fire safety regulations. Smoking is allowed only in designated areas.
2.9. Vehicle malfunctions noticed while working on the line, as well as violations in the packaging or securing of cargo, the driver should try to correct on their own, and if it is impossible - inform the company and call for technical assistance.
2.10. When sending two or more people to work together, the driver must follow the orders and instructions of the senior appointed by the employer responsible for compliance with safety requirements.
2.11. Gas-balloon (gas-diesel) vehicles can enter the maintenance and repair posts only after the engine has been switched to work on gasoline (diesel fuel).
Before entering, it is necessary to check the gas supply system for leaks at a special post. It is forbidden to enter premises with a non-hermetic disposable power supply system.
When switching the engine to liquid fuel, it is necessary to close the supply valves and completely exhaust gas from the power system (until the carburetor engine stops completely), then close the main valve, turn on the liquid fuel supply and start the engine.
2.12. The driver must observe the rules of personal hygiene. Before eating and smoking, wash your hands with soap and water, and after working with components and parts of a car running on leaded gasoline, wash your hands with kerosene beforehand.
2.13. For failure to comply with the requirements of the instructions developed on the basis of this and specified in, the driver is liable in accordance with applicable law.
3. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS BEFORE STARTING WORK
3.1. Before leaving the line, the driver must:
3.1.1. Pass a pre-trip medical examination.
3.1.2. Get from the dispatcher waybill and briefing on the working conditions on the line and the features of the cargo being transported.
3.13. Together with the gearbox mechanic, check the technical serviceability and completeness of the car and get the appropriate mark on the waybill. On examination Special attention pay to:
Serviceability of the battery, starter, brakes, steering, lighting, alarm, cab doors, interior, heating device, side locks, muffler and tightness of its connections, etc.;
No leakage of fuel, oil, coolant;
Air pressure in tires and their serviceability;
Proper completeness of the car with the necessary tools, fixtures, inventory and their serviceability.
3.1.4. Cars running on gas fuel must be inspected daily to check the tightness and serviceability of gas equipment. The tightness of all connections is checked using special devices (leak detectors), by ear or by soap emulsion.
Malfunctions of gas equipment (leaks) are eliminated only at the posts for the repair and adjustment of gas equipment or in a specialized workshop.
3.2. Before starting the engine, the driver must:
Disconnect and disconnect heating elements;
Slow down the car with a parking brake;
Put the gearshift lever (controller) in the neutral position;
Check the tightness of the power supply system;
Ventilate the engine compartment (on vehicles running on gas fuel).
3.3. The driver may use the starting handle only in the event of a temporary failure of the starter or when starting the engine after a repair.
3.4. When starting the engine with the starting handle, the driver must comply with the following safety requirements:
Do not take the handle in a girth;
Turn the starting handle from the bottom up;
When manually adjusting the ignition timing, set the ignition later;
Do not use any levers acting on the starting handle.
3.5. The driver is prohibited from:
Start the engine by towing;
Warm up the engine, gearbox, crankcases of drive axles with open fire;
Release compressed natural gas or drain liquefied petroleum gas while the engine is running or the ignition is on;
Leave the flow valves in an intermediate state: they must be fully open or closed;
Use additional levers to close or open supply, main and filling valves;
Hit gas equipment and fittings under pressure;
Stop a gas-balloon car closer than 5 m from places of work with open fire, as well as use open fire closer than 5 m from the car;
Check the tightness of the connections of gas pipelines, gas equipment and fittings by fire;
Operate vehicles with the air filter removed.
4. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS DURING WORK
4.1 When working on the line, the driver must:
4.1.1. Start moving the car only after making sure that there are no obstacles in the way of movement. On a tipper vehicle, additionally only when the body is lowered.
4.1.2. Before leaving the cab, turn off the ignition or cut off the fuel supply, brake the car with a parking brake, make sure that there is no danger associated with movement Vehicle both in the same direction and in the opposite direction. Do not jump from the cab, car body.
4.1.3. After exiting the cab, if the car is stopped on a road section with a slope (even a slight one), place wheel chocks (shoes) under the wheels.
4.1.4. Clean dirt, snow and ice off the footboards in a timely manner. Avoid contact with oil and fuel.
4.1.5. Rest in the cab of the vehicle only when the engine is not running, as otherwise it may lead to poisoning by carbon monoxide contained in the exhaust gases of the vehicle.
4.1.6. Before reversing the vehicle, make sure that this maneuver will not create a hazard and that there are no people nearby.
4.1.7. Before driving in reverse in conditions of insufficient rear visibility (due to cargo in the body, when leaving the gate, etc.), require the allocation of a person to organize the movement of the car.
4.1.8. When driving a tanker vehicle, the capacity of which is filled by less than 3/4, to ensure the stability of the vehicle when cornering, reduce the speed.
4.1.9. Open the radiator cap on a hot engine in a mitten or cover it with a rag (rag). Open the cork carefully, avoiding the intense exit of the peer in the direction of the opening.
4.1.10. Refuel the car with fuel in accordance with the safety rules established for gas stations.
4.1.11. To overflow gasoline, use a special device. It is forbidden to suck gasoline by mouth through the hose.
4.1.12. IN winter time to prevent cases of frostbite when troubleshooting on the way, work only in gloves. It is forbidden to touch metal objects, parts and tools with hands without gloves.
4.1.13. When refueling a car in winter, use refueling nozzles only with gloves on, do not allow dousing and getting fuel on the skin of hands and body.
4.1.14. To open and close the sides of the truck, seek the assistance of another person.
4.1.15. Receive additional instruction from the employer when sent to work away from the main base, on ice roads, crossing water bodies and off-road in accordance with the current Rules for labor protection in road transport.
4.1.16. Before being sent to work in a quarry, receive additional instruction in accordance with the Uniform Safety Rules for the Development of Mineral Deposits open way with an entry in the instruction log.
4.1.17. When stopping the movement of a gas-balloon (gas-diesel) car for parking for more than 10 minutes, close the main valve, and less than 10 minutes - it is allowed to leave the main valve open.
4.1.18. Before refueling the vehicle with LPG, stop the engine and close the supply valves.
4.1.19. After filling the cylinders with gas, first close the valve on the filling station, and then the filling valve on the car and disconnect the gas filling hose.
If the gas filling hose is accidentally depressurized during refueling, immediately close the outlet valve on the gas filling station and then the filling valve on the vehicle.
4.1.20. If, when starting at a gas station, the engine starts to pop, the driver must immediately turn off the engine and tow the car to a safe place for troubleshooting.
4.1.21. Fulfill the requirements specified in -
4.1.22. Instruct passengers before boarding a truck intended for transporting people about the procedure for boarding and disembarking, warning them that it is prohibited to stand in the back and sit on the sides of a moving vehicle.
4.1.23. Do not allow persons accompanying the cargo to travel in the back of a truck if it does not provide seating located at least 15 cm below the level of the side.
4.1.24. Check the compliance of the stowage and reliability of fastening of cargo and awnings on the rolling stock with the safety requirements and ensuring the safety of cargo, and in case of detection of violations in the stowage and fastening of cargo and awnings, require the person responsible for loading operations to eliminate them.
4.1.25. Transport glass containers with liquids only in special packaging, and they must be installed vertically (cap up).
4.1.26. When loading the car body with bulk cargo, make sure that it does not rise above the sides of the body (standard or extended) and is evenly distributed over the entire area of the body.
4.1.27. Make sure that piece loads that rise above the sides of the body are tied with strong, serviceable rigging (ropes, ropes). It is forbidden to use metal rope and wire.
4.1.28. Make sure that box, roll-drum and other piece cargo is packed tightly, without gaps, strengthened or tied so that during movement (sharp braking, starting off and sharp turns) it cannot move along the floor of the body. If there are gaps between the places of the load, wooden spacers and spacers should be inserted.
4.1.29. Make sure that the liquid cargo drums are installed with the cap up. Each row of barrels laid on its side should be wedged on the outer rows. It is forbidden to use other objects instead of wooden wedges.
4.1.30. Transport dusty goods in rolling stock (open bodies) equipped with canopies and seals.
It is forbidden to transport hot goods in wooden bodies.
4.1.31. Carry goods that exceed the dimensions of the body in length, width and height, in accordance with the requirements of the Rules of the Road.
4.1.32. Cargoes exceeding the dimensions of the rolling stock in length by 2 m or more (long-length cargoes) must be transported on vehicles with trailers-dissolutions, to which the cargoes must be securely fastened.
When transporting long loads of different lengths at the same time, ensure that shorter loads are placed on top.
4.1.33. Make sure that when loading long loads (pipes, rails, logs, etc.) on a car with a trailer-dissolution, a gap is left between the shield installed behind the car cab and the ends of the load so that when turning and turning, the load does not cling to shield. To prevent the load from moving forward during braking and downhill driving, the load must be securely fastened.
4.1.34. Accept and transport dangerous goods and empty containers from under them in accordance with the Rules for Ensuring the Safety of the Transportation of Dangerous Goods by Road.
4.1.35. Ensure that all packages containing hazardous substances have labels indicating the type of hazard of the cargo, the top of the package, the presence of fragile vessels in the package.
4.1.36. Loading and unloading of tank trucks is carried out by gravity or using pumps through serviceable hoses or pipes.
4.1.37. At automatic system pouring flammable liquids be at the control panel emergency stop filling, and when pouring ammonia water into tanks - be on the windward side.
4.1.38. Before loading dangerous goods onto a vehicle and unloading them from a vehicle, turn off the engine (with the exception of loading oil products into a tank truck, as well as loading performed using a pump installed on a vehicle and driven by the vehicle engine. In this case, the driver must be at the pump control panel ).
4.1.39. Clean the car body before delivery to the place of loading from foreign objects, as well as from snow, ice, debris, etc.
4.1.40. Inspect the loaded containers in order to determine the correct loading and reliability of container fastening on specialized semi-trailers or universal vehicles (road trains).
4.1.41. Do not allow people to pass in the back of the car where the containers are installed, and in the containers themselves.
4.1.42. When transporting containers, observe the following precautions:
Do not brake sharply;
Reduce speed on curves, curves and bumps in the road;
Pay attention to the height of gates, overpasses, contact networks, trees, etc., sufficient for passage.
4.1.43. In the absence of a wheel of a breaking bar at the places of unloading, require instructions from the consignee on minimum distance from a slope or cliff, on which he can drive up for unloading.
4.1.44. Ensure that before starting loading and unloading operations, a trestle is installed under the frame of the panel hauler trailer to prevent it from tipping over (when loading - from the loading side, when unloading - from the opposite side).
4.1.45. Park your car no closer than 1 m from the car in front and at least 1.5 m from the car standing on the side under loading or unloading.
When placing a car for loading or unloading, observe an interval of at least 0.5 m between the building and the car and at least 1 m between the pile of cargo and the car.
When loading or unloading cargo using overpasses, platforms, ramps with a height equal to the floor level of the body, move the car close to them.
4.1.47. In the event that violations of the rules and norms of labor protection are detected while working at the facility of the consignor or consignee, which can lead to an accident or an accident, demand their elimination from the consignor or consignee.
4.1.48. When stopping and parking on unlit sections of the road at night or in conditions of insufficient visibility, turn on the marker or parking lights of the car.
4.1.49. When the car is forced to stop on the side of the road or on the carriageway for repairs, place an emergency stop sign or a flashing red light behind the car.
4.1.50. When working under a vehicle, position yourself so that your feet are not on the roadway.
4.1.51. If it is necessary to perform work under the raised body of a dump truck, install inventory devices for fixing the body (stops, clamps, rods).
4.1.52. When inflating or inflating tires removed from the car on the road, install a safety fork of the appropriate length and strength into the holes of the wheel disc or place the wheel with the lock ring down.
4.1.53. Before starting work, a truck crane, a car with a mounting hoist, etc. install on a horizontal platform with the obligatory installation of extended supports. Special wooden linings should be placed under the shoes of the supports. It is forbidden:
Install truck cranes, assembly hoists, etc. at the edge of a ditch, ditch, cliff, etc., where soil slippage is possible;
Work with non-extended and unlocked supports;
Use random items as linings;
Move the car with people lifted in the cradle or a lifted load;
Sit on the sides of the raised carrycot;
Install truck cranes, dump trucks, vehicles with assembly lifts, etc. near power lines without special permission;
Perform work at night without adequate lighting.
4.2. The driver is prohibited from:
Perform any work on maintenance and repair of the vehicle at a distance closer than 5 m from the area of operation of loading and unloading mechanisms;
Use an open fire and smoke at a filling station, carry out repair and adjustment work, refuel while the engine is running, allow fuel to overflow, allow passengers to be in the cabin, cabin or body;
Allow the engine to run on a mixture of two fuels - gasoline and gas (with the exception of gas-diesel);
Use the tail lift of the vehicle to lift or lower people;
Smoking in the cab of a gas-balloon (gas-diesel) vehicle;
Smoking and using open fire when loading, unloading and transporting explosive cargo;
Carry goods with ends protruding beyond the side dimensions of the vehicle;
Block the cabin doors with cargo;
Load long loads above the bunk racks;
During the loading of containers onto a vehicle (unloading), be in the cab, body, and also at a distance of less than 5 m from the area of action of the lifting mechanism (with the exception of the driver of the self-loader vehicle);
Carry passengers in the back of an unequipped truck;
Transport children in the back of a truck, even equipped for transporting people;
Transport people on flatbed platforms, on cargo placed at or above the side of the body, on long-length cargo and next to it, on tanks, trailers and semi-trailers of all types, in the back of a dump truck and a specialized truck (refrigerator, etc.), in the back of a car with containers;
Carry more people in the cab, body and cabin than indicated in the manufacturer's passport;
Transport people on the steps, fenders, bumpers and sides, standing in the back of an equipped truck, as well as with the doors of the rolling stock open;
Transport in the cold season of passengers, loaders and persons accompanying goods in an open body;
Carry dangerous substances together and food products or feed cargo;
Submit the car to the loading and unloading overpass if it does not have a fence;
Place a dump truck for unloading under power lines without the permission of the owner of the power line;
When refueling with gas fuel, stand near the gas filling hose and cylinders;
Tighten connection nuts gas system under pressure, and knock on them with metal objects;
Work without gloves when refueling with gas fuel;
Fill cylinders in case of detection of depressurization of the power supply system;
Fill gas cylinders, the period of examination of which has expired;
Allow unauthorized persons, including passengers and loaders, to repair the car.
5. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS IN EMERGENCIES
5.1. The driver must:
5.1.1. Immediately inform the employer about the accident that happened to him or through his fault, as well as about any accident involving other employees of the enterprise, of which he was a witness.
5.1.2. Provide the victim in an accident with first aid (Model Instruction No. 22), help deliver him to a health center or the nearest medical institution or, if necessary, call medical personnel to the scene.
5.13. In the event of a malfunction of the gas supply system, immediately close the supply and main valves, and then ventilate the engine compartment and other compartments where the gas pipeline passes.
5.1.4. If a gas leak is detected from the cylinder fittings, release or drain the gas in compliance with safety measures. Compressed release or drain liquefied gas in the conditions of a motor transport enterprise, it should be carried out only at specially equipped posts.
5.1.5. Open main and supply gas valves slowly to avoid water hammer.
5.1.6. When releasing compressed natural gas or draining liquefied petroleum gas, do not smoke or use open flames, do not carry out work that is not related to releasing or draining gas.
5.1.7. If a gas leak from the power system is detected on the line, with the exception of the cylinder fittings, immediately stop, close the flow valves, exhaust gas from the system until the engine stops, then close the main valve and, if possible, take measures to eliminate the malfunction or inform the company.
5.1.8. In the event of a gas leak from the cylinder fittings, drive the car to a safe place for others and release or drain the gas from the cylinder.
5.2. It is forbidden to release compressed natural gas and drain liquefied petroleum gas while the engine is running or the ignition is on, as well as in the immediate vicinity of parking lots of other vehicles or near sources of fire and where people are located.
6. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS AFTER WORK COMPLETION
6.1. Upon completion of work, the driver must:
6.1.1. Comply with the safety requirements set out in ,
6.1.2. After putting the car on a night or long-term parking, close the supply valves (for compressed gas) or the main valve (for liquefied gas), exhaust gas from the power system, then turn off the ignition and turn off the ground.
6.1.3. Before parking the vehicle in a heated parking space, make sure there is no fuel leakage.
6.1.4. Wash your hands with soap, and after working with the components and parts of a car running on leaded gasoline, you must first wash your hands with kerosene.
6.1.5. Notify your immediate supervisor of any deficiencies discovered during work.
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR MOTOR TRANSPORT ENTERPRISES ON THE APPLICATION OF STANDARD INSTRUCTIONS ON LABOR SAFETY
The presented standard instructions on labor protection for the main professions and types of work, along with the Rules for labor protection in road transport, approved in December 1995, and other regulatory and methodological documents are intended to create an information and methodological base on labor protection for managers and specialists of motor transport enterprises.
On the basis of standard instructions, each motor transport enterprise, taking into account the specifics of its working conditions, develops and approves instructions for certain occupations of workers, as well as for some of the most traumatic types of work. Responsibility for the timely and high-quality development of labor protection instructions at each motor transport enterprise rests with its head. The development of instructions must be carried out by the heads of workshops (sections), mechanics, foremen, since they know the working conditions of their subordinate workers best. To provide methodological assistance in the development of instructions and their coordination, employees of the labor protection service of the enterprise should be involved.
The design of the covers of the first and last pages of the instruction for employees must comply with appendices 1,2,3 *.
* Not shown - Note. Ed.
The revision of labor protection instructions is carried out at least once every five years, and for professions and types of work (operations) for which additional (increased) safety requirements are imposed, at least once every three years.
In addition, instructions are revised when changing technological process, working conditions, the use of new equipment and in a number of other cases. The revised instructions are approved in due course.
Each manager at his site, in order to ensure high-quality briefings and better assimilation by workers of the basic methods of safe work, must have appropriate instructions on labor protection. He is also obliged to daily monitor the fulfillment by the workers of the requirements of these instructions in the course of their work.
For more effective assimilation by workers of safe methods of work, the formation of stable and correct stereotypes of behavior in them in hazardous production situations, it is advisable to draw up and bring to the attention of workers the main provisions of the instructions in the form of appropriate memos, posters, filmstrips, etc.
The results of the research show that when performing a production task, a worker, as a rule, focuses on solving only one task - how to quickly complete the assigned work in compliance with established requirements to its quality (useful activity). At the same time, another, no less important task - how to avoid an accident when performing assigned work (protective activity) - is either not taken into account by the worker, or is considered by him as secondary.
In this regard, the main tasks during the briefing of workers are: drawing the attention of the instructed to the most typical traumatic situations that may arise when performing certain types of work, operations, actions; fixing in their memory the conditions for the emergence and development of these situations. At the same time, it is desirable that the instructor conducts the analysis of the material on real examples taken either from the life of your enterprise, or from information and teaching materials, with a detailed story about the tragic consequences of a particular accident and methods that allow you to correctly and safely perform a particular job.
Model instructions for professions consist of 6 sections:
General provisions;
Safety requirements before starting work;
Safety requirements during work;
Safety requirements in an emergency;
Safety requirements at the end of work.
The second section contains the norms for the free issuance of special clothing, special footwear and other personal protective equipment (PPE).
It should be borne in mind that the standard instructions contain the norms for issuing overalls, which are a mandatory minimum for the administration of the enterprise. Labor collectives have the right to make decisions on additional free distribution of overalls and special footwear (except for tarpaulin, fur and sheepskin coats) at the expense of the fund social development(Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the USSR and the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions of August 20, 1988 No. 1032). In this regard, in the instructions for employees, each enterprise enters the overalls, safety shoes and PPE that it will issue to employees.
In the third section, along with safety requirements before starting work, it is necessary to indicate the necessary dermatological ointments and creams (based on local conditions) that the worker should use to protect the skin of the hands.
Along with standard instructions for professions, a number of instructions for performing certain types of work are also presented, in which, as practice shows, violations of the rules and norms of labor protection are most often observed and, therefore, accidents most often occur. Instructions for these types of work are singled out as independent ones, since in a motor transport enterprise they can be carried out by workers of different professions.
All presented standard instructions cover only the main professions and types of work in motor transport enterprises. As for instructions for other professions, in particular for personnel servicing electrical installations, boiler rooms, hoisting mechanisms, pressure vessels, and other equipment, as well as for workers through professions, they should be developed on the basis of relevant industry rules and regulations. documents.
TO laboratory work allowed students who have passed briefing on labor protection and studied the guidelines.
In laboratory work, instruments and devices powered by a 220 V mains are used. : stand simulating premises, noise meter VShV-003-M2. dangerous places are current-carrying parts, socket housings, plug plugs. Voltage 220 V applied to instruments and devices represents danger to life!
Safety requirements before starting work
Make sure that the stand, VShV-003-M2 device, connecting wires are in good condition by external inspection and trial inclusions.
Familiarize yourself with the location and purpose of the switches on the laboratory stand and on the front panel of the VShV-003-M2 measuring device.
Safety requirements during work
After complete assimilation of theoretical information and the procedure for performing the work, proceed to the laboratory work.
The measuring instrument is not fixed on the laboratory bench. Be careful not to drop the appliance on the floor.
If any malfunctions of the device or laboratory bench are found, disconnect them from the power supply and inform the teacher.
When power off take only for a fork and not by the cord.
PROHIBITED connect devices to the electrical network with wet hands!
Attention! Turn on the noise source only for the duration of noise level measurements.
Safety requirements in emergency situations
Electrical appliances (device, stand) disable immediately :
when a person gets under voltage;
when smoke, fire or a specific smell occurs when the insulation is heated;
with strong heating of instrument and equipment cases;
upon detection of a dangerous situation on other laboratory benches.
In the event of damage to electrical components (plugs, sockets, insulation of electrical wires) suspend work and notify the teacher leading the lesson.
When a person is injured electric shock necessary:
release the victim from the action of electric current, for which disconnect the electrical wiring (cord with plug, switch, knife switch) or release him from contact with live parts in other ways (pull the victim by dry clothes).
Call immediately: emergency medical service by phone 03 - urban communications, 112 - unified rescue service - mobile communications.
If the victim has no pulse and breathing, it is necessary to immediately perform artificial respiration, alternating it with an indirect heart massage.
If the heartbeat is preserved, but there is no breathing, perform only artificial respiration.
If both the heartbeat and breathing were preserved, the victim should be laid on a hard, smooth surface (table, bench), unbuttoning the tight parts of the clothing.
When evacuating, remain calm, act quickly, but without panic.
Safety requirements at the end of work
Disconnect electrical appliances and the stand from the network.
Put in order workplace.
Report the end of the work to the teacher.
At the end of the work, the locksmith must:
6.1.1 Disconnect electrical equipment from the mains, turn off local ventilation.
6.1.2 Tidy up the workplace. Remove fixtures and tools in the place provided for them.
6.1.3 If the car remains on special supports (traguses), check the reliability of its installation. It is forbidden to leave the car, the unit hung out only with a lifting mechanism.
6.1.4 Remove personal protective equipment and put them in the place intended for them. Timely hand over special clothing and other personal protective equipment for dry cleaning (washing) and repair.
6.1.5 Wash your hands with soap, and after working with parts and assemblies of an engine running on leaded gasoline, you must first wash your hands with kerosene.
6.1.6 Notify your immediate supervisor of all shortcomings found during work.
According to the fire hazard class, the room belongs to category B.
Possible fire classes B2 (combustion of liquid substances soluble in water) and C (combustion of gaseous substances).
The degree of fire resistance of section II according to SNiP 21-01-97.
The room where maintenance takes place with increased danger, because there is the possibility of a person simultaneously touching the metal structures of buildings connected to the ground, technological devices, mechanisms, etc., on the one hand, and to metal cases electrical equipment - on the other (PUE (6th ed.) section 1.1.13). Electrical network 380 V 50 Hz. According to the degree of danger of electric shock, the room belongs to class 2, i.e. networks with U< 1000 В с глухозаземленной нейтралью .
The main causes of fire are:
Failure to comply with fire safety standards by the personnel of the enterprise.
Violation of the technological process (welding, use of electrical equipment), which leads to a fire.
Use of faulty equipment in the course of work at the enterprise.
The building is not equipped with the necessary fire equipment: equipped fire cabinets, shields, and fire extinguishers.
Fire safety provided by the fire prevention system and the fire protection. Requirements for these systems are defined by GOST, PPB.
Fire-fighting equipment. Premises for maintenance, checks technical condition, repair of automatic telephone exchanges and their units, as well as storage of automatic telephone exchanges is equipped with fire extinguishing means and automatic fire alarms.
Type selection and required amount of primary fire extinguishing equipment at the maintenance site was produced depending on their fire extinguishing ability, taking into account the category of the room, the maximum extinguishing area, the class of fire of combustible substances and materials in the room.
The number of primary fire extinguishing equipment at the maintenance site is taken taking into account the standards:
foam fire extinguishers with a capacity of 10 l (OVP-10) - 1 pc.;
powder fire extinguishers OP-1 - 2 pcs.;
a box with sand with a capacity of 0.5 m 3 and a shovel - 1 pc.;
felt, asbestos cloth or felt mat 2x2 m - 2 pcs.
Once every 10 days, it is necessary to carry out an external inspection and clean the fire extinguishers from contamination. On boxes with sand it is necessary to put the inscription: "Sand in case of fire!"
An evacuation plan has been developed at the site in case of fire, which indicates evacuation routes, evacuation and emergency exits, established rules for the behavior of people, the procedure and sequence of actions in conditions emergency(clause 3.14 GOST R 12.2.143-2002).
On the evacuation plan symbols evacuation routes, evacuation and emergency exits, locations of fire-fighting equipment, emergency telephones, means of first aid are indicated. medical care and additional means of rescue.
The solid green arrows show the main recommended escape routes and the dotted arrows show the emergency escape routes.
Explosion and fire safety of the site is ensured by organizational and technical measures and fire protection measures.
The premise of the site has fireproof walls, partitions and coatings with a fire resistance limit of 0.75-1 hour.
Security and fire alarm in the aggregate area is carried out using telephone and electrical fire alarm(EPS) automatic action.
As heat detectors of maximum action, a TPT-3 sensor is used, which is triggered when the temperature of the air around them reaches a temperature above a critically set one, for example, 60, 80 or 200 degrees. FROM.
6. 3 Protection environment
The main source of air pollution during the operation of motor vehicles are internal combustion engines, which pollute the atmosphere with harmful substances emitted with exhaust gases, crankcase gases and fuel vapors.
Pollution Wastewater occurs mainly when washing cars, assemblies, assemblies and parts during their repair, charging batteries, restoration of chrome and nickel coatings, repair of the cooling system, machining of metals and other materials.
To the most typical species wastewater pollution includes oil products, acids, alkalis, cutting fluids, antifreeze, galvanic and mud discharges, metal particles.
Soil pollution during work service center maybe:
1. Garbage, emissions. This group includes mixed pollutants of various nature, including both solid and liquid substances, which are not too harmful to the human body, but clog the surface of the soil, making it difficult for plants to grow in this area.
2. Heavy metals. This type of pollution already poses a significant danger to humans and other living organisms, since heavy metals often have high toxicity and the ability to accumulate in the body. The most common automotive fuel - gasoline - contains a very toxic compound - tetraethyl lead, which contains the heavy metal lead, which enters the soil. Other heavy metals whose compounds pollute the soil include Cd (cadmium), Cu (copper), Cr (chromium), Ni (nickel), Co (cobalt), Hg (mercury), As (arsenic), Mn (manganese). ).
To clean the air from paint aerosols and unpleasantly smelling substances, a local ventilation from necessary set filters. To clean the air from dust, a dust collection chamber is installed in the floor, which, like the filter, is periodically cleaned. The removed air is released into the atmosphere at a level of 1 meter from the highest point of the building with a dust content not exceeding the norm.
STO wastewater is divided into domestic, storm, industrial, as well as water from car washing.
Household sewage is sent to the city sewerage and there it is disposed of at special enterprises.
For cleaning storm drains, it is necessary to provide treatment facilities, consisting of mud settlers, filters and oil separators, as well as a mechanized device for removing oil products and sediment.
Polluted industrial effluents, except mechanical cleaning, are subjected to flotation, neutralization and chemical cleaning.
For the treatment of industrial wastewater from oil products and suspended solids, we will provide a treatment plant "Crystal", which allows for the repeated use of purified water for the technical needs of the SC.
Oil waste is subjected to regeneration, sludge is sent for processing.
On the territory of the SC, sites and garbage cans for storage and further disposal of industrial waste should be provided.
If the content harmful substances in the air working area exceeds the maximum allowable concentration, it is necessary to take special measures to prevent poisoning. These include restrictions on the use of toxic substances in production processes, sealing equipment and communications, automatic control of the air environment, the use of natural and artificial ventilation, special protective clothing and shoes, neutralizing ointments and other protective equipment.
6 Design section
Hydraulic presses are designed for pressing, pressing out, straightening and bending parts. Used to work with small, medium and large parts. Models used with small and medium parts can work in any spatial position.
The hydraulic press consists of two communicating hydraulic cylinders (with pistons) of different diameters. Cylinder filling hydraulic fluid, water, oil or other suitable liquid. According to the laws of the French philosopher and scientist Pascal, pressure (that is, the force acting per unit area) in any place of a liquid (or gas) at rest is the same in all directions and is equally transmitted throughout the volume. Pascal's law is the most important law of hydrostatics. All hydraulic press factories in their production are based on the law of hydrostatics. In essence, a hydraulic press can be compared to the effect of a lever, where a liquid is used as a force-transmitting object, and the force depends on the ratio of the areas of the working surfaces.
Oil change equipment can be the most diverse
When choosing oil change equipment for your car repair shop, you should be careful. You need to understand that not all manufacturers offer their customers quality products. After all, everything related to vehicle maintenance should be on highest level so that you can be sure that customers will be satisfied with the services provided and will contact you again. Although, it seems to some that oil change equipment, the price of which is quite high, can be purchased, even if it is not the most good quality. But in fact, all this is not so. Quality should always come first and there is no doubt about that.
So, if you are faced with the need to choose equipment for oil change, then you should carefully consider this process. Because, those products that seem too simple, in fact, are not. Sometimes, in order to make the right decision, it is worth contacting professional consultants so that they can tell you something and explain how one device differs from another. Also, it is important to understand what influences pricing and what functional characteristics on such equipment.
Studying all the offers in the catalog, you can pay attention to the fact that oil drain equipment can be very diverse. In this regard, it is far from always possible to focus on what exactly is needed for your service. After all, everyone has their own requirements and it’s worth counting everything based on how many clients you are going to accept, most importantly, evaluate everything realistically so that you don’t suffer from your illusions later. Situations can be the most unpredictable, and therefore, it is better not to take risks before deciding to purchase equipment, carefully consider everything.
Engine stands
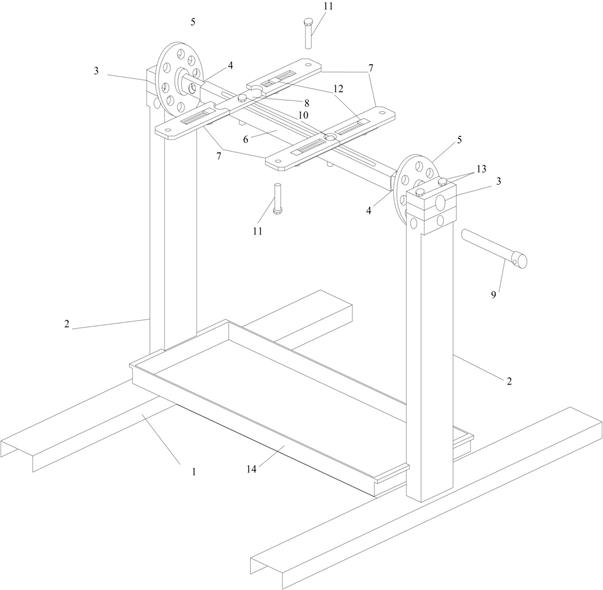
Specifications
In some situations, when repairing a car or servicing it, it is necessary to inspect the engine from all sides, but this is not so easy to do without special equipment. As a rule, in order to get full access to the motor, a tilter is used. A special stand for the engine is designed for transporting the engine indoors. Also one of its functions is to rotate the engine around the axis. As practice shows, such a device is very popular, but not everyone is familiar with some aspects of working with it.
Problems with this kind of device occur quite rarely and only if the rules of use are not followed. As a rule, the engine tilter can withstand high weight loads, however, you should not exceed the limit set in the instructions, as a breakdown may occur and the motor may fall. The engine disassembly stand must always be on a stable surface, since all the load is transferred to the base of the stand itself .
At correct location load, in our case, the engine, on the tilter stand, you can absolutely calmly do any work, be it disassembly and subsequent repair or ordinary cleaning. For a more secure fixation of the motor, you can use a locking pin that locks rotary mechanism. This will give the structure a stable position and reduce vibration during operation.
If you use a stand tilter, then make sure that safety precautions are observed, since if it is used incorrectly, damage can be caused to both equipment and people.
All stands for dismantling the engine, as a rule, are evaluated according to two criteria. The first of them is the versatility in operation, which directly indicates the capabilities of the equipment when correct use. The second criterion is ease of use, which indicates how convenient it is for the worker to use it in work.
In order to make it easier for you to choose a stand tilter, a catalog has been created that presents all the available models today. To place an order, you can contact our managers, as well as ask them all your questions.
Conclusion
I was given the task of designing a service station for the repair of engines of trucks in Cheboksary
As a result of the work done, the following results have been achieved:
1. An analysis of the state of the technical and technological support HUNDRED.
2. The performed calculations made it possible to determine the necessary data for the design of service stations to meet the needs of the Kalininsky district of Cheboksary. In general, the calculated indicators of the car service station are close to the reference values.
3. The technology of maintenance and repair of vehicles was analyzed, a list of works to be performed by personnel was determined.
4. To organize the reconstruction of the site, a selection and justification was made technological equipment and rigging.
5. Technological planning of the location of equipment in the site was carried out and the requirements for the organization of work at the workplace were considered.
6. Proposals for labor protection and sanitary hygiene of production have been developed.
7. Considered requirements environmental safety in the maintenance and repair of automotive equipment.
8. The economic calculation carried out showed that when using the proposed equipment and tooling, with a slight increase in the cost of the services provided, the quality of work will improve and the time for their implementation will be reduced, which will lead to the intensification of the technological process. The payback period for the proposed activities is 6 months.
The goal of the graduation project was achieved.
Bibliography
1. Car service: car service stations: Textbook / Gribut I.Z., Artyushenko V.M., Mazaeva N.P. and others / Ed. V.S. Shuplyakova, Yu.P. Sviridenko. - M.: Alfa-M: INFRA-M, 2008. - 480 p.
2. Afanasiev L.L., Kolyasinsky B.S. Maslov A.A. Garages and car service stations. -M.: Transport, 1980 - 210 p.
3. Buraev Yu.V. Life safety in transport: textbook. For students of higher educational institutions/ Yu.V. Buraev - M.: Academy 2004.-288s.
4. Buyanov V.V. Method for determining the rational number of posts of car service stations owned by citizens. - In kN: Economics and organization of road transport and road construction. - Omsk: Omskhi im. Kirova, 1992, p. 39-45 (Proceedings of MADI, issue 50)
5. VSN 01-89 "Car maintenance enterprises" (approved by order of the Ministry of Autotransport of the RSFSR dated January 12, 1990 N VA-15/10 - M .: Standards Publishing House, 1990. - 17 p.
6. GOST 16350-80 Zoning and statistical parameters climatic factors for technical circuits. - M .: Publishing house of standards, 1981. - 113 p.
7. GOST 18332-78. The system of maintenance and repair of equipment. Terms and Definitions.
8. Karagodin V.I. Repair of cars and engines: Proc. for stud. avg. prof. textbook institutions / V.I. Karagodin, N.N. Mitrokhin. - 2nd ed., erased. - -M.: Publishing center "Academy", 2003. - 496 p.
9. Kovalev V.P. Fire-fighting measures at the enterprise: Organization and implementation: Production and practical guide. - M .: Alfa-Press, 2008. - 336 p.
10. Kuznetsov Yu. M. Occupational safety at the enterprises of road transport: textbook / Yu.M. Kuznetsov. - M.: Transport, 1990. - 288.
11. Markov O. D. Vehicle maintenance stations. - K.: Kondor, 2008. - 536 p.
12. Masuev M.A. Design of road transport enterprises: textbook - M.: Academy, 2007. - 224 p.
13. Intersectoral rules for labor protection in road transport POT RM-027-2003. - M.: NTSENAS, 2004. - 168s.
14. Napolsky G.M. Technological design motor transport enterprises and Service Stations: Textbook for High Schools. - 2nd ed., revised. And extra. - M.: Transport, 1993.- 271s.
15. ONTP-01-91. All-Union norms of technological design of road transport enterprises - M .: Giproavtotrans, 1991. - 184 p.
16. Pavlova E.I. Ecology of transport Textbook for universities. - M.: Transport, 2000. - 248 p.
17. Regulations on the maintenance and repair of rolling stock of road transport / M-vo automob.transp. RSFSR. - M.: Transport, 1986. - 73 p.
18. Rabinovich E.Kh. Technical operation of cars (section "Organization of maintenance and repair of cars): Lecture notes. - Kharkov: KHNADU, 2004 - 60 p.
19. RD 46448970-1041-99. The list of the main technological equipment recommended for equipping enterprises performing services (works) for maintenance and repair vehicles. - M.: FTOLA-NAMI, 1999, 32 s
20. The sheet of technological equipment and specialized tools for car service stations. - M.: NIINAvtoprom, 1980. - 78 p.
21. Maintenance and repair of vehicles: a textbook for students of institutions environments. prof. education / V. M. Vlasov [and others]; ed. V.M. Vlasov. - M.: Publishing Center "Academy", 2003. - 480 p.
22. Turevsky I.S. Maintenance and repair of motor vehicles. Tutorial. - M.: ID "FORUM": INFRA-M, 2011. - 192 p.
23. Turevsky I.S. Industry economics. Road transport - M .: Publishing House "FORUM"; INFRA-M, 2011, - 288s.
24. Khasanov R.Kh. Basics technical operation Cars: Textbook. - Orenburg: GOU OGU, 2003. - 193 p.
1. Volgin, V.V. Car service: structure and personnel: A practical guide / V.V. Volgin. - M.: Publishing and Trade Corporation "Dashkov and Co", 2010. - 711 p.
2. Turevsky, I.S. Diploma design of motor transport enterprises: study guide / I.S. Turevsky. - M.: Publishing House "Forum": INFRA-M, 2010. - 240 p.: ill. - (Professional education).
3. Kartashov, V.P. Organization of maintenance and repair of automobiles / V.P. Kartashov, V.M. Maltsev. - M.: Transport, 2011. - 234 p.
4. Kolesnik, P.A. Maintenance and repair of cars: Textbook for universities. - 2nd ed., revised. and additional / P.A. Kolesnik, V.A. Sheinin. - M.: Transport, 2011. - 325 p.
5. Lakhtin Yu.V. Designing an automobile transport enterprise (safety and environmental friendliness of design solutions) / Yu.V. Lakhtin, M.L. Bykhovsky. – M.: MGOU, 2012. – 135 p.
6. Napolsky, G.M. Technological calculation and planning of car service stations. Tutorial for course design by discipline / G.M. Napolsky, A.A. Solntsev. – M.: MADI (GTU). - 2009. - 53 p.
7. Turevsky, I.S. Diploma design of car service stations: textbook. Allowance / I.S. Turevsky, B.D. Golubev. - M.: Publishing House "Forum": INFRA-M, 2010. - 240 p.
8. Efremova O.S. Checking knowledge of labor protection requirements: a practical guide 2nd ed. / O.S. Efremov. - M.: Publishing house - "Alfa-Press", 2012. - 168 p.
Additional literature:
1. Napolsky, G.M. Technological design of motor transport enterprises and service stations. Textbook for universities, 2nd ed. revised and additional / G.M. Napolsky. - M.: Transport, 1985. - 271 p.
2. Napolsky, G.M. Technological calculation and planning of car service stations. Textbook for course design in the discipline / G.M. Napolsky, A.A. Solntsev. – M.: MADI (GTU). - 1996. - 53 p.
3. Ulitskaya, I. M. Nagaeva I. D. Organization and wages in road transport. - M.: Transport, 1989.
4. Cherednikov A. A. Buses: Device, maintenance, operation. - M.: Transport, 1999. - 216 p.
5. Shakhles M. M. Equipment for car repair. Transport Publishing House, 1981, pp. 1-424.
Standard instruction on labor protection for a fitter
TOI R-218-35-94
Approved
Federal Highway Department
General safety requirements
1. Persons at least 18 years of age, recognized as fit for this work by a medical commission, who have undergone special training, are allowed to perform reinforcing work. safe methods and methods of production of works and having a qualification certificate.
2. Newly hired fitter is allowed to work only after he has passed an introductory briefing on labor safety, environmental requirements and initial briefing at the workplace, which must be recorded in the relevant journals with the obligatory signature of the instructed and instructing.
3. Periodic testing of knowledge of the fitter on labor safety should be carried out once every 12 months.
4. The fitter must be re-instructed at least once every 3 months.
5. When changing safety requirements or working conditions (changing the technological process, replacing equipment, fixtures and tools, changing other factors affecting labor safety), in case of violation of labor safety requirements that have led or may lead to injury, accident or fire, according to at the request of the supervisory authorities, as well as during breaks in work for more than 60 calendar days, the fitter must undergo an unscheduled briefing. When registering an unscheduled briefing, the reason for its conduct is indicated.
6. The fitter is obliged:
Follow the rules of the internal labor schedule and the daily instructions of the master (foreman);
Remember personal responsibility for compliance with safety requirements in the course of work and for the safety of workmates;
Use the issued overalls, special footwear and safety devices; while on the construction site, use a protective helmet;
Do not allow unauthorized persons to be present at the workplace;
Perform only the work for which he has been instructed and approved by the foreman (foreman);
Do not follow orders if they contradict safety requirements, inform the superior manager about it;
Know the rules for the technical operation of the equipment and tools used and safe ways to connect and disconnect them, as well as the main causes of malfunctions and safe ways to eliminate them;
Know the location of the power switch.
7. Workplaces must be provided with tested inventory fences, protective and safety devices, devices (scaffolding, scaffolding, step-ladders, bridges, etc.).
8. The fitter must keep the workplace in order and cleanliness throughout the working day, not clutter it and the passages with materials and structures.
9. It is forbidden to carry out reinforcing work at unenclosed workplaces located at a height of more than 1.3 m above the ground or ceiling, in unlit or dark places.
10. It is forbidden to carry out external reinforcing work on scaffolding during thunderstorms, ice, fog, with a wind speed of 15 m/s or more.
11. In case of inexpediency of scaffolding or scaffolding, the fitter, when working at height, is obliged to use a tested safety belt.
The places for fastening the carabiner of the safety belt must be indicated by the master (foreman).
12. Reinforcing steel at the construction site should be placed on racks with a height of no more than 1.5 m, rolled metals (corner, section steel) - in stacks with a height of no more than 1.5 m with linings and gaskets, reinforcing steel in coils, coils - in stacks no more than 1.5 m high.
13. Slinging of stored materials with lifting mechanisms can be carried out by a trained and certified fitter.
14. Vertical transportation of reinforcing steel and finished fittings should be carried out using proven lifting devices.
15. Wooden handles of tools (hammer, sledgehammer, etc.) must be smoothly processed, fitted and securely fastened.
16. Wrenches should be selected according to the size of nuts, bolts.
Wrenches are not allowed large sizes with a lining of metal plates between the faces of the nut and the key, as well as extend the wrenches with another key or pipe.
17. It is forbidden to use a hand tool that has potholes, chipped working ends, burrs and sharp ribs in places of clamping by hand, cracks and chips on the back of the head, overheating, knocked down chips on the working surface.
18. In the area of reinforcement bending, a place for scale collection and local suction with connection to exhaust ventilation should be provided.
19. For non-compliance with the requirements of the labor protection instruction developed on the basis of this standard instruction, the fitter is liable in accordance with the internal labor regulations and current legislation on labor protection.
Safety requirements before starting work
20. Before starting work on the procurement and processing of reinforcement, it is necessary:
Check the serviceability of the machine, workbench; their reliable fastening to the floor (foundation); reliability of fastening of machine knives; availability and serviceability of fences, grounding and protective devices;
Check the starting and braking devices of the machine, winches;
Lubricate all rubbing parts of the machine, starting it at idle, make sure it is in good condition;
When tensioning the reinforcing steel, check the serviceability of the hydraulic pumps or jacks, as well as the fixings of the clamping plates and grippers. Make sure that there are no undercuts, breaks or other defects in the reinforcement.
21. In the absence of current, turn off the machine.
It is forbidden to leave unattended machines and electrical equipment without supervision.
22. If any malfunctions are found, immediately stop the machine, the winch and inform the master (mechanic) about this. It is forbidden to start work until the malfunctions are eliminated.
Safety requirements during work
23. Mechanized operations for the procurement and processing of reinforcement (cutting, bending, etc.) must be performed in a separate specially designated, equipped or fenced area (polygon).
Driveways and passages in this area should not be cluttered with materials, parts and finished products.
24. Machines for cutting and straightening reinforcing steel must be equipped with local metal dust exhausts.
The place from the installation of the turntables to the machine must have a fence that allows observation of the unwinding of the straightening reinforcement. Entry beyond this guard is allowed only after the machine has stopped.
25. All workbenches for the preparation of rebar must be firmly attached to the floor, and double-sided workbenches, in addition, are separated by a longitudinal metal mesh with cells size 50´ 50 mm, 1 m high above the workbench.
26. When straightening reinforcing steel on automatic machines, the following safety requirements must be met:
Fill the ends of the fittings into the drum only when the electric motor of the machine is turned off;
Close the drum before starting the machine with a protective cover;
Check the presence of a fence for the transition of reinforcing steel from the turntable to the drum; the turntable for stacking coils of steel should be installed at a distance of 1.5 m from the machine and at a height of 0.5 and from the floor and fenced. Between the turntable and straightening machine a metal case is installed to restrict the movement of the unwound wire rod.
27. When cutting reinforcing steel on a machine with a mechanical drive, you must:
Before starting the machine, check the presence of protective covers, make sure that the braking and starting devices are in good condition, that the cutting parts of the shears are securely bolted; the gap between the planes of the movable and fixed knives is allowed no more than 1 mm;
Feed reinforcing steel for cutting only after the flywheel of the machine has developed a sufficient rotational speed;
In case of breakage or dullness of the knives, stop work and notify the mechanic about the need to replace the knives;
On machines for cutting and bending reinforcement or near them, there must be plates indicating the maximum allowable diameters and steel grade of the processed reinforcement according to passport data;
When cutting steel on the machine, do not keep your hands closer than 0.2 m from the cutting. It is forbidden to cut pieces of reinforcing steel with a length of less than 0.3 m on driven machines without a device that protects against injury.
29. When cutting reinforcing steel with a circular saw, the fitter must:
Carry out cutting in protective glasses;
Hold the reinforcing steel at right angles to the saw blade.
If a crack, dent or other defect is found in the saw blade, stop work and inform the mechanic about it.
29. Laying reinforcing steel on the driven bending machine is allowed only when the disk is stopped.
It is forbidden to change the stops and bending fingers of the machine during the operation of the machine.
When cutting high-strength wire with a circular saw, the latter must be protected in the upper part by a solid casing.
Adjustment of the counterweight of the saw blade must ensure that the saw is brought into working condition only when the force of the fitter is applied to its handle, and the withdrawal to the non-working state is automatic after the removal of the force.
30. When cutting and bending reinforcing steel on manual machine fitter must:
Make sure that the machine is firmly attached to the workbench;
Do not extend the lever (handle) with pipes or any object.
31. When bending several rods, the fitter must ensure that all the rods are in the same vertical plane; for this, special holders are used.
32. Extraction of fittings should be carried out using a remote-controlled winch.
Extraction of fittings by means of vehicles is prohibited.
33. It is forbidden to straighten the coils of wire rod reinforcement when unwinding the coil and tensioned bundles of reinforcement.
34. When the winch is operating, the fitter must ensure that the rope is wound on the drum with the correct turns.
35. It is forbidden to be near a tense rope, a bundle of reinforcement and correct incorrect winding of the rope on the drum during winch operation.
36. When tensioning reinforcing steel mechanically the following precautions must be observed:
Install protective fences (mesh) with a height of at least 1.8 m.
It is forbidden for workers to pass in the reinforcement tension zone.
37. With the electrothermal method of tensioning reinforcing bars, in order to avoid electric shock, as well as burns and injuries, the following precautions should be taken:
Place the rods on the contacts and remove them only when relieved stress. The voltage in the heated rods should not exceed 42 V;
Put on protective covers on the ends of reinforcing bars with anchor stops;
Take the heated rods by the protruding cold ends;
The service personnel should be on the sides of the form containing the reinforcement, in order to avoid accidents in case of possible breaks in the anchor heads and breaks in the stressed rods;
Use rubber dielectric gloves, galoshes and a rug during maintenance of the installation for electrothermal tension of live fittings.
38. In the event of a failure of the device that provides control of the tension of the reeled reinforcement, an electrical blocking of the machines for shutdown should be provided.
39. Fitters who have undergone special training, passed tests and received appropriate certificates may be allowed to work on electric arc and resistance welding of fittings.
40. During the installation and assembly of the reinforcing cage of foundation structures, it is necessary:
Reinforcing bars should be lowered into pits and trenches along special trays; dropping them from above is prohibited;
When descending into the pits, use ladders, and when descending into narrow trenches, use ladders; it is forbidden to descend into the trenches along the struts of the fasteners.
41. Reinforcing cages should be assembled outside the formwork in special conductors, tested for strength and stability.
42. Reinforcing cages and meshes weighing more than 50 kg should be lifted and moved using mechanisms and devices.
43. Reinforcing cages with a length of more than 10 m must be fixed in the formwork at least at three points.
44. In the absence of data on the position of the center of gravity of reinforcing cages and meshes, their center of gravity must be established by a trial lift to a height of not more than 10 cm.
45. When assembling the reinforcement of columns and other high vertical structures it is necessary to arrange a flooring with railings with railings and side boards every 2 m in height. The raised reinforcement of the columns before its final installation should be temporarily unfastened with stretch marks and props, conductors.
It is forbidden to climb on the reinforcing cages until they are finally installed or until they are temporarily securely fastened.
46. Work from scaffolding and scaffolding is allowed to be performed only after they have been checked by the foreman (foreman). It is forbidden to work from unchecked scaffolding and scaffolding, as well as from flooring laid on supports made of random objects (bricks, barrels).
47. When working from scaffolding, scaffolding, it is forbidden to overload them with fittings and other materials.
While doing welding work from scaffolding, scaffolding and cradles, to protect the flooring from fire, it is necessary to cover them with sheet iron or asbestos.
It is forbidden to drop tools, metal scraps and any objects from a height.
48. When cleaning the formwork (before installing reinforcement in it) with compressed air, the worker must wear goggles.
It is allowed to walk on the laid reinforcement only on special bridges with a width of at least 0.6 m, arranged on trestles installed on the formwork.
During the tension of the reinforcement at the stands, the red signal light should be lit.
49. A fitter may be allowed to work as a steeplejack at a height, as well as to sling lifted frames, nets, blocks and other loads only after he has undergone special training and receives an appropriate certificate for the right to perform these works.
50. Before lifting the frames of meshes of reinforcement-formwork blocks by cranes and mechanisms, it is necessary:
Inspect the area for lifting and moving goods and make sure that there are no people in this area;
Make sure that there are no foreign objects on the lifted load;
To eliminate rocking, use braces. It is forbidden to leave the lifted armature on weight.
51. Uncoupling of cables, load-handling devices to be carried out after reliable fastening of the frames and blocks to be installed.
52. It is forbidden for the fitter to be during the lifting and installation of reinforced structures under scaffolding and scaffolding.
53. It is forbidden to install fittings near electrical wires and electrical equipment.
54. When working in rooms with increased danger, it is allowed to use portable electric lamps with a voltage of not more than 42 V, and in especially hazardous conditions not higher than 12 V.
It is forbidden to use stationary lamps as hand-held portable lamps.
Safety requirements in emergency situations
55. Immediately inform the foreman (foreman) about the identified violations of labor protection requirements and cases of injuries.
56. In order to avoid electric shock, it is forbidden to touch open current-carrying parts of electrical equipment, bare wires, make corrections or connections on your own, install or replace electric lamps under voltage.
57. The fitter must be able to provide first aid to the victim at work, take measures to eliminate violations of safety requirements.
Safety requirements at the end of work
58. Upon completion of work, the fitter is obliged:
Disconnect machines, winches from the mains;
Clean the instrument and deposit it;
Tidy up the workplace construction garbage and foreign objects from the aisles;
Wipe and lubricate the rubbing parts of machines and mechanisms;
Collect all rigging devices, clean steel ropes, slings, chains from dirt and lubricate them, put them in storage.
Ropes should be cleaned in gloves with a steel brush; it is forbidden to do this with rags or rags.
59. Wash hands and face with warm soapy water or take a shower.
60. The fitter must inform the master (foreman) about all the problems noticed.
Agreed:
Central Committee of the Trade Union of Workers
road transport and road economy
January 1994





