Transport accidents. Road accidents and their causes
It is clear in itself that accidents, in fact, arise due to violations of the Rules by drivers. traffic. Autoinstructors will try to figure out more specifically what can lead to a traffic accident.
Violation of traffic rules
For example, violation of the maximum speed limit. Probably, all of us have seen that in a city where the speed limit is 60 km/h, some motorists do not even fit into the limit of 90 km/h.
It is not uncommon for violations of such rules as: driving at a prohibiting traffic light, overtaking in prohibited places, non-compliance with priority rules.
However, traffic rules are violated not only by motorists, but also by pedestrians themselves who cross the road, completely ignoring prohibition signs and traffic lights. Even cyclists are no exception, they ride without paying any attention to other road users. And, of course, one of the most common causes of accidents is driving while intoxicated. Accidents also happen due to excessive driver fatigue, for example, after a long journey.
Statistical information for 2011 is shown in the picture:
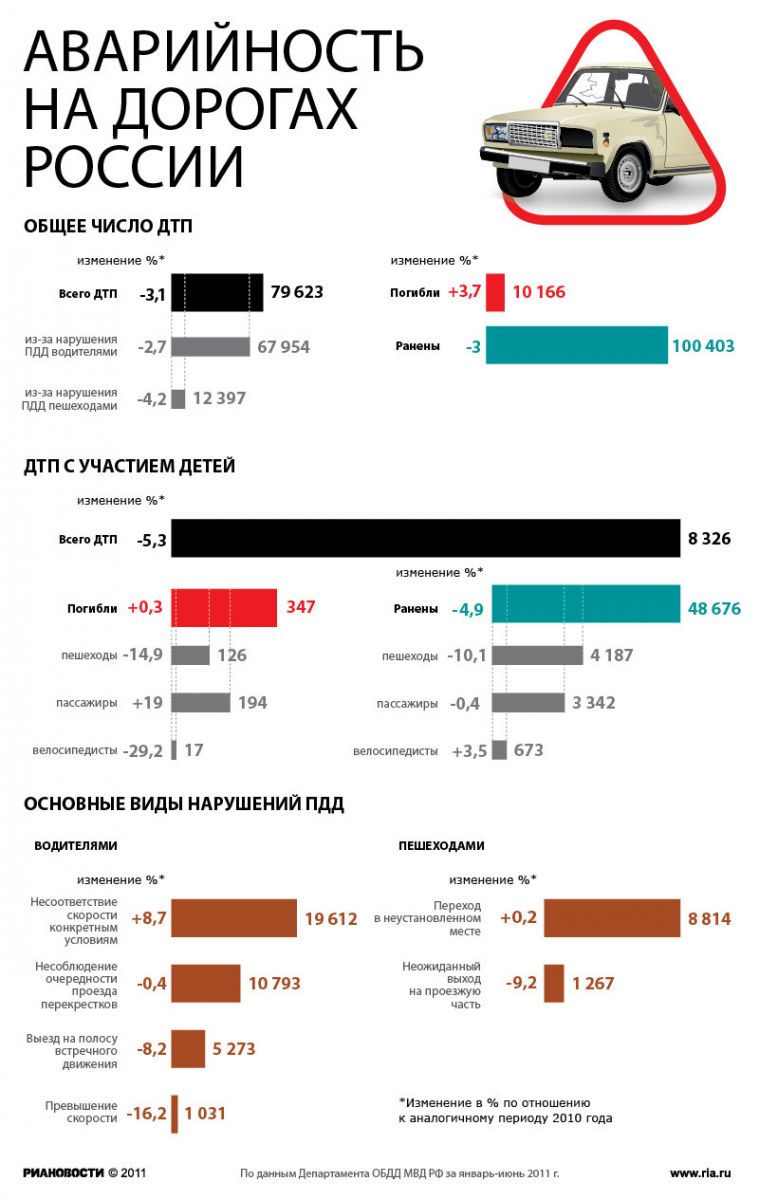
Vehicle malfunctions
A common cause of accidents is a technical malfunction of cars. For example, according to the legislation of the Russian Federation, with technical malfunctions, subsequent movement is prohibited, as well as further operation of the vehicle in general. In the second case, you have the right to bring the car, at least to a car repair shop, and in the first case, only a tow truck or towing will help.
So, for example, if your headlight burns out, then you can get to the place of parking or repair, but if the brakes fail, then that’s all - it’s forbidden to move on your own.
Failure to follow these rules is the main cause of accidents.
Contempt
Accidents also occur because all participants in the movement, from pedestrians to drivers, are not attentive to each other. It often happens that the driver, without even violating traffic rules , just doesn't have time to react. Due to dulled attention, drivers do not notice the brake lights of the car in front, direction indicators, which subsequently leads to an accident.
Roads
An old topic of conversation is the poor condition of the roads. After all, we all have encountered urgent potholes, pits and ruts. But this often becomes a dangerous factor in the spontaneous departure of the car into the oncoming lane. And the road services, for some reason, do not bear responsibility. It is not uncommon that the cause of an accident is a technical malfunction of traffic organizers, for example, traffic lights. If the green light is on all the traffic lights at once, then in the event of an accident in this case, the traffic participants will not be punished at all, and the road services and the traffic police will be guilty of this, but who is pleased to be a participant in the accident, even if not through their own fault.
The right decision when detecting a malfunctioning traffic light, of course, will either turn around and go the other way, or call the traffic controller by phone, but this will take you some time.
Poor preparation
Another cause of accidents is insufficient training of new drivers in theory, but mostly in practice. And this is the real violation of the law, i.e. a crime for which, in theory, there should be a serious punishment. After all, such people become potential killers, exposing everyone around them to great danger. It also happens that people just learn to be right “so that they are”, and they start driving only after a few years, in this case everything learned is simply forgotten, so in order to drive and not create emergency situations on the road, it is enough to periodically practice on deserted roads.
Be careful and good luck on the road!
The article used an image from the site www.lenta.ru and www.ria.ru
Currently, any type of transport poses a potential threat to human health and life. Technological progress, along with comfort and speed of movement, has also brought a significant degree of threat. Depending on the type of transport accident, it is possible to receive multiple injuries and burns that are life-threatening.
Transport accident is a vehicle accident that resulted in the death of people or the infliction of severe bodily harm to the victims, the destruction and damage to transport structures and facilities, or damage to the environment.
Transport disaster is a major accident with significant loss of life. Transport accidents are divided according to the type of transport on which they occurred, and (or) the damaging factor of dangerous goods.
Road traffic accident (RTA) is a traffic accident that occurred in the process of road traffic involving a vehicle and caused the death of people or causing them severe bodily harm, damage to vehicles, roads, structures, cargo or other material damage.
Emergencies caused by traffic accidents, causes, possible consequences and actions of the population in the event of a threat or emergency
The modern period is characterized by the development of transport and as a result of movement more than 50% of accidents and disasters occur on various types transport. The safest mode of transport for passengers is a city bus, and the most dangerous is a car and a motorcycle. Therefore, as a result of traffic accidents, a large number of citizens die and are injured and injured, many become disabled.
The most common types of accidents are collisions of vehicles or their overturning, collisions with pedestrians, collisions with obstacles.
The main causes of traffic accidents are:
Low professional level of individual drivers,
Drunk driving;
Violation of traffic rules;
Vehicle malfunctions;
Poor condition of the road surface;
Unfavorable weather conditions;
Influence on the mental, physiological state of drivers, pedestrians, dangerous and harmful factors.
Security measures
When boarding a car and driving, it is advisable for a passenger to sit in the middle of the rear seat, or at least in the back seat, if you are in the front seat, be sure to fasten your seat belt; during the movement, do not distract the driver and constantly monitor traffic; sitting on the seat sideways in the direction of travel is dangerous, with sudden braking, injury is possible; it is dangerous to get into a car with a drunk driver; do not allow children to kneel and look out the rear window, when braking, a blow to the head may occur.
In the event of an accident, the driver passenger car must: avoid a head-on collision with a car without exposing his side to another car; it is advisable not to collide with another car in the place where it has a gas tank; in the event of a collision, to mitigate the impact force, it is advisable to crash with the right or left edge of the hood; in case of an inevitable head-on collision, rest your hands on the steering wheel, with your left foot on the casing of the left wheel, with your right foot on the brake pedal; if the car catches fire, immediately evacuate passengers to a safe distance.
In the event of a car accident, the passenger must: tighten the muscles and not relax until they come to a complete stop; in a frontal collision, if you are sitting in the back, put your hands and feet on the front seat, press your head to your hands; if sitting in front, rest against the front reading, but not against the glass; in the event of a car overturning, press against the seat and hold on to it with your hands, remembering that the main thing is to protect your head from injury; do not try to leave the car while driving in a frontal collision; if the car is in the water, wait for the cabin to fill with water, do not panic, inhale the remaining air and get out;
Actions of a passenger in a bus, trolleybus, tram in case of an accident: at the time of the impact, while sitting on the seat, rest your feet and hands on the front seat, and if you are standing, grab the handrail, in case of a fall, do not hit your head; maintain muscle tension until the transport stops completely; after an accident or catastrophe, immediately leave the vehicle without creating panic, through an emergency window, emergency exit, through a window or through the upper ventilation hatches; in the event of a fire in the cabin, use a handkerchief or other part of the fabric to protect the respiratory system; use a fire extinguisher or sand if possible; in case of a short circuit, flash in the passenger compartment of a tram or trolleybus, leave the vehicle when it stops and the electrical circuit is disconnected.
If the bus with passengers is in the water, stay where you are until the passenger compartment is filled with water, without creating panic among the passengers; remember that the main danger is not water, but other passengers. Get out through the window, the upper ventilation hatches until the bus cabin is filled with water, breathe deeper and more often to saturate the body with oxygen.
When traveling in public transport, the passenger must: remember that the middle of the passenger compartment is the safest place; in case of sudden braking, it is better to sit with your back forward; hold the back of the front seat with your hands when sitting facing forward; it is safer to sit on the starboard side than on the port side; if you are standing, then place the support points so that their projection onto the floor forms a triangle of a larger area; when braking hard, pay attention to where you will fall and who will fall on you.
Major incidents on railway transport- train wrecks, railway accidents and catastrophes.
train wreck- this is a collision of passenger or freight trains, the result of which is the death or injury of people, the destruction of the locomotive or wagons.
Railway accident- accident on railway, resulting in damage to one or more units of rolling stock of railways to the extent of overhaul and (or) the death of one or more people, causing bodily harm to the injured.
Train disaster- a railway accident, as a rule, with human casualties.
The main causes of accidents and crashes: malfunction of the track, rolling stock and technical means management; errors of employees responsible for the safety of train traffic; violation of the rules for crossing railways by road; the erroneous actions of the railway workers.
Among the catastrophes, train wrecks and accidents, there are: derailment of rolling stock, collisions, collisions with obstacles at crossings, fires and explosions on rolling stock, collision of trains with each other.
The consequences of accidents and catastrophes at stations and stages are: explosions of dangerous goods, leading to the destruction of the track, rolling stock, structures; spill or release into the atmosphere of aggressive or toxic substances; fires of rolling stock, station buildings and other structures; defeat of railway workers, passengers by fire, explosions, poisonous liquids and gases; destruction of transported goods.
Depending on the number of victims, there are 5 categories of railway accidents and disasters:
Security measures
When using railway transport services, it is necessary: to be located in the middle of the train; do not put heavy and bulky things on the upper shelves of the car; leave passages at night free; do not forget the location of personal belongings (documents, money, valuables); foreign objects (bottles, food) should not be on the table.
In the event of a train crash or emergency braking: grab onto the handrails and rest your feet on something; it must be remembered that after the first blow there may be others, continue to hold; after the blows stop, leave the car, otherwise a fire may occur, in case of its absence, try to provide first aid to the injured, calm the passengers without causing panic; when the doors are blocked by a crowd of people, use windows - emergency exits, as well as through the window of any compartment, but due to its strength when broken, injury is possible; when leaving the car, take documents, money and necessary clothes; Help the other passengers to get out as well by breaking the windows of the carriages from the outside.
In the event of a fire in the carriage, the passenger must: in the event of smoke or fire, urgently use a scarf, any cloth soaked with liquid to protect the respiratory system; a long stay in a compartment is dangerous, because. the temperature in an enclosed space rises quickly and it is possible to burn the lungs with one breath and lose consciousness from the dangerous toxic gas released during combustion; get out of the car through the vestibule when it is filled with people, use the emergency exit; strictly follow the instructions of the conductor; leaving the car, engage in rescue operations, observing safety measures (risk of stride voltage with broken wires, passing oncoming trains, spilled fuel, etc.).
Accidents and disasters in air transport
In civil aviation, cases of complete or partial destruction of an aircraft with passengers on board are called aviation accidents.
plane crash- a dangerous incident on an aircraft, in flight or in the process of evacuation, which led to the death or disappearance of people, causing bodily harm to the injured, destruction or damage to the aircraft and material assets carried on it.
The main causes of accidents can be grouped into the following groups: human factor - 50-60%, equipment failure - 15-30%, environmental impact - 10-20%, others - 5-10%. More than half of air accidents occur at airfields and adjacent areas.
Security measures
After boarding the aircraft, the passenger must: be in outerwear, in case of fire it will save from burns; is in shoes - it will save you from all kinds of fragments; remove tie, scarf, glasses, hairpins and other sharp objects; fasten your seat belt, check the location of the oxygen mask.
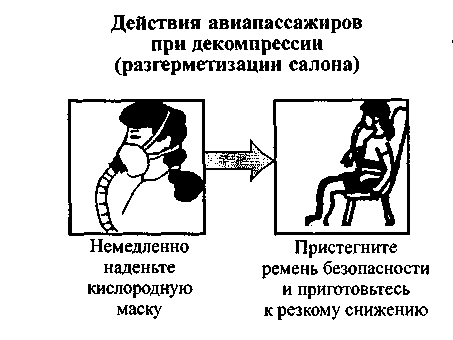
In case of decompression (rarefied air in the cabin): whistling, pain, noise and ringing in the ears, warming and tingling of the skin, deafening roar - immediately put on an oxygen mask and move less, if possible help other people put them on.
When takeoff and landing accidents the crew of the aircraft manages to notify the passengers about the accident. Before an accident, the passenger must: take a fixed position (bend, tightly clasp his hands under his knees, tilting his head as much as possible or rest his hands on the front seat, put his head on his hands, and rest his feet on the floor).
At the moment of impact, strain as much as possible. After the plane stops, you must leave through the nearest exit route.
At emergency exit from the plane you should: open the emergency hatch, use the rescue rope, throwing it out, observing the exit rules (first the legs, then the head); remove high-heeled shoes and synthetic stockings; stretch the fabric chute, sit on the threshold of the inflatable ladder and go down; do not hold on to the onboard edged cord - burns are possible.
At aircraft cabin fire to protect skin burns, and respiratory organs from poisonous gases, use outerwear; movement is possible to the exit when the aircraft is completely stopped; if there is a lot of smoke, move on all fours (crouching), the main danger is smoke, not fire; if there is a crowd at the exit, look for other exits; if there is fire and smoke outside, do not open emergency hatches in this place; upon exiting the salon, refuse hand luggage; fight panic and apathy, because lose precious time, it could cost you your life. The plane must be left in 5 minutes and move away from it at a distance of 1.5 km, before the explosion of fuel.
Accidents and disasters in water and pipeline transport
Accidents on water transport are classified:
-- shipwreck- loss of the ship or its complete destruction;
-- accident- damage to the ship or its being aground for at least 40 hours (passenger - 12 hours);
-- accident- a dangerous incident on a river vessel that led to the release of hazardous chemical, biological, radioactive substances, ionizing radiation, oil spills.
Pipeline accident- this is an accident on the pipeline route associated with the release or outflow under pressure of hazardous chemical or fire-explosive substances, leading to a man-made emergency.
Depending on the type of transported product, accidents on main pipelines can pose one or another danger - from possible loss of life to damage to the economy and environmental disasters.
Damaging fire factors are: open fire and sparks; increased temperature of air and surrounding objects; toxic combustion products; reduced oxygen concentration; destruction or damage to buildings, structures, installations, the possibility of an explosion.
Damage factors of the explosion: shock wave; flame and fire; destruction of equipment, building structures, communications; formation during the explosion and leakage from damaged devices of harmful substances, their content in the air in quantities exceeding the maximum allowable; fragmentation field.
During fires and explosions, a person receives burns of varying severity, injuries, injuries, poisoning by combustion products, electric shock.
Accidents and disasters in the subway (underground transport)
Transport accidents and catastrophes can also occur in the subway, which can lead to serious consequences - fires, explosions and lead to death.
Sources of fire or explosion are: electrical discharges, thermal manifestations of chemical reactions, sparks from impact and friction.
Security measures
The safety measures in case of emergencies in the subway, applied by passengers, are similar to the safety measures on railway transport.
To ensure the life of passengers, the metro needs to intensify work to improve security measures:
Use of fans in case of smoke;
Video filming and video recording (color, image preservation for three days, to consider a person's face);
Security of the wagon system;
Use of metal detectors and hazardous liquid detectors;
Arched detectors for the determination of explosives and narcotic substances;
Providing a searcher system;
Special X-ray units and scanners;
Screening installations to help identify explosives or weapons hidden under clothing;
In order to prevent emergencies, use printed media mass media(MEDIA);
Technical means of protection;
Intercoms that allow, if necessary, to contact the station staff or the police;
Inform passengers about how to survive in this situation.
Accidents at chemically hazardous facilities
Chemical accidents- this is a violation of technological processes in production, damage to pipelines, tanks, storage facilities, vehicles, leading to the release of emergency chemical hazardous substances (AHOV) into the atmosphere in quantities that pose a danger to human life and health, the functioning of the biosphere.
Chemical, pulp and paper and processing plants, mineral fertilizer plants, ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy plants, as well as cold storage plants, confectionery factories, etc. have large reserves of hazardous chemicals, mainly chorus, ammonia, phosgene, hydrocyanic acid, sulfurous anhydride and other substances. A chemical accident for humans and animals consists in a disruption of the normal functioning of the body and the possibility of long-term genetic consequences, and under certain circumstances, in a fatal outcome when AChB enters the body through the respiratory system, skin, mucous membranes, wounds, and along with food.
Security measures
At the warning signal of the population about the accident "Attention to all!" (sirens wailing and intermittent beeps of enterprises), it is necessary to follow the procedure for receiving it, the rules for sealing the premises, protecting food and water. Make and store in an accessible place cotton-gauze bandages for yourself and family members, as well as a memo on the actions of the population in case of an accident at a chemically hazardous facility. If possible, purchase gas masks with boxes that protect against the corresponding types of hazardous chemicals.
At the signal "Attention everyone!" turn on the radio and TV for reliable information about the accident and recommended actions. Close windows, turn off electrical appliances and gas. Put on rubber boots, a raincoat, take documents, necessary warm clothes, a three-day supply of non-perishable food, notify your neighbors and quickly, but without panic, leave the zone of possible infection perpendicular to the direction of the wind, at a distance of at least 1.5 km from the previous place of stay.
To protect the respiratory organs, use a gas mask, and in its absence, a cotton-gauze bandage or handy fabric items soaked in water with a 2-5% solution of baking soda (protection from chlorine), a 2% solution of citric or acetic acid " ammonia protection. If it is impossible to leave the contaminated area, tightly close windows, doors, ventilation holes and chimneys. Seal the gaps in them with paper or tape.
Do not hide on the first floors of buildings, in basements and semi-basements. In case of accidents on railways and highways associated with the transportation of hazardous chemicals, a dangerous zone is established within a radius of 200 meters from the accident site. Approaching this zone and entering it is strictly prohibited.
If you suspect a AHOV lesion, exclude any physical activity, take plenty of fluids (milk, tea) and consult a doctor immediately. Entrance to buildings is allowed only after a control check of the content of AHOV in them. If you are directly affected by AHOV, take a shower as soon as possible. Wash contaminated clothing, and if it is impossible to wash, throw it away. Carry out a thorough wet cleaning premises. Refrain from drinking tap (well) water, fruits and vegetables from the garden, livestock and poultry meat slaughtered after the accident, until an official conclusion about their safety.
Radiation accident- this is a violation of the safety rules for the operation of a nuclear power plant, equipment or device, in which there was a release of radioactive products or ionizing radiation beyond the limits provided for by the project safe operation leading to public exposure and environmental pollution.
The main damaging factors of accidents are radiation exposure and radioactive contamination. Accidents can be accompanied by explosions and fires. Radiation impact on a person consists in the violation of the vital functions of various organs (mainly the hematopoietic organs, the nervous system, the gastrointestinal tract) and the development of radiation sickness under the influence of ionizing radiation.
Radioactive contamination is caused by exposure to alpha, beta and gamma ionizing radiation and is caused by the release of unreacted elements and fission products of a nuclear reaction (radioactive hose, dust, fragments of a nuclear product) during an accident, as well as the formation of various radioactive materials and objects (soil) as a result of their exposure.
In the event of a radiation accident, by means of methods and means of notifying the population, create stocks of the necessary means intended for use (sealing materials, iodine preparations, food, water, etc.).
When warning about a radiation accident, while outside, immediately protect your respiratory organs with a handkerchief, scarf and hurry to take cover indoors. Once in the shelter, take off your outer clothing and shoes, place them in a plastic bag, and take a shower. Close windows and doors. Turn on the TV and radio for more information about the accident and guidance from local authorities. Seal vents, cracks in windows, doors and do not approach them unnecessarily. Stock up on water in sealed containers. Wrap opened products in polyethylene film and place in refrigerator or cupboard. For respiratory protection, use a respirator, cotton-gauze bandage or improvised fabric items moistened with water to increase their filtering properties.
When receiving instructions through the media, carry out iodine prophylaxis by taking one tablet (0.125 g) of potassium iodide for 7 days, and for children under 2 years old - 0.04 g of a tablet. In the absence of potassium iodide, use an iodide solution: 3-5 drops of a 5% iodine solution in a glass of water, for children under 2 years old - one or two drops.
The order of action of the population in a radioactively contaminated area. To prevent or reduce the impact of radioactive substances on the body, it is recommended: leave the room only if necessary and for a short time, while using a respirator, raincoat, rubber boots and gloves; in open areas, do not undress, do not sit on the ground and do not smoke, exclude swimming in open water and picking wild berries and mushrooms; periodically moisten the area near the house, and in the room carry out a thorough wet cleaning daily using detergents; before entering the room, wash your shoes, shake out and brush your outer clothing with a damp brush; wash your hands thoroughly before eating and rinse your mouth with a 0.5% solution of baking soda. Compliance with these requirements will help to avoid radiation sickness.
The action of the population during the evacuation
In preparation for the evacuation, prepare personal protective equipment, including improvised ones (capes, raincoats made of film, rubber boots, gloves), put clothes and shoes for the season in a suitcase or backpack, a one-day supply of food, underwear, documents, money and other necessary things. Wrap your suitcase or backpack in plastic wrap.
When leaving the apartment during the evacuation, turn off all electrical and gas appliances, take quickly perishable products to the trash bin, and attach the announcement “There is no one in apartment No. __” on the door. When boarding a transport or forming a pedestrian column, register with a representative of the evacuation commission. When you arrive in a safe area, take a shower and change your underwear and shoes for non-infected ones.
hydrodynamic accident- this is an emergency event associated with the failure (destruction) of a hydraulic structure or part of it and the uncontrolled movement of large masses of water, causing destruction and flooding of vast areas. The main potentially hazardous hydraulic structures include dams, water intake and water collection facilities (locks).
Destruction (breakthrough) of hydraulic structures occurs as a result of the action of natural forces (earthquakes, hurricanes, erosion of dams) or human impact (strike with nuclear or conventional weapons on hydraulic structures, large natural dams, acts of sabotage), as well as due to structural defects or errors design.
The consequences of hydrodynamic accidents are: damage and destruction of hydroelectric facilities and short-term or long-term termination of their functions; defeat of people and destruction of structures by a breakthrough wave formed as a result of the destruction of a hydraulic structure, having a height of 2 to 12 m and a speed of 3 to 25 km / h (for mountainous areas - up to 100 km / h); catastrophic flooding of vast areas with a layer of water from 0.5 to 10 m or more.
In the event of a threat of a hydrodynamic accident (hydroelectric complex), it is necessary to exit (leave) the danger zone in the prescribed manner to a designated safe area or to elevated areas of the terrain. Take with you documents, valuables, essentials and a supply of food for 2-3 days. Move some of the property that needs to be protected from flooding, but cannot be taken with you, to the attic, the upper floors of the building, trees. Before leaving the house, turn off the electricity and gas, tightly close windows, doors, ventilation and other openings.
In case of sudden flooding, to save yourself from the impact of a breakthrough wave, immediately take the nearest elevated place, climb a large tree or the top floor of a stable building. If you are in the water when a breakthrough wave approaches, dive into the depth at the base of the wave.
Once in the water, swim or with the help of improvised means get out to a dry place, preferably on a road or dam, along which you can get to a non-flooded area. When the house is flooded, turn off its power supply, give a signal about the presence of people in the house (in the apartment) by hanging a flag made of bright fabric from the window during the day, and a lantern at night.
For information, use the radio with self-powered. Move the most valuable property to the upper floors and attics. Manage food inventory and drinking water, their protection from the effects of standing water and economical use.
In preparation for a possible evacuation by water, take documents, emergency items, clothing and shoes with water-repellent properties, improvised rescue equipment ( air mattress, pillows). Do not attempt to evacuate yourself. This is possible only if the territory is not flooded, there is a threat of a deterioration in the situation, the need to receive medical care, food is used up and there are no prospects for receiving outside help.
After a hydrodynamic accident, before entering the building, make sure that there are no significant damages, ceilings and walls. Ventilate the building to remove accumulated gases. Do not use open flame sources until the room is completely ventilated and the gas supply system is checked for proper operation. Check the condition of the electrical wiring, gas supply pipes, water supply and sewerage. It is allowed to use them only after the conclusion of specialists about serviceability and suitability for work. Dry the room by opening all doors and windows. Remove dirt from floors and walls, pump out water from basements. Do not eat food that has been in contact with water.
The main causes of accidents
If you ask an ordinary layman about what, in his opinion, is the cause of traffic accidents, he will surely answer: violation of the Rules of the road. However, such an answer will be clearly incomplete: in addition, there are a number of reasons leading to accidents.
Most accidents occur due to the indiscipline of road users (drivers, pedestrians, cyclists, etc.), who disregard the Rules of the road.
A typical example is violation speed limit: which of us has not seen how, in the area of a sign that allows you to move at a speed of no more than 60 km / h, some cars “fly by” at a much higher speed.
The following violations that lead to accidents are also “popular”: driving into a lane intended for oncoming traffic, overtaking in prohibited places, violating the rules of maneuvering, driving at a traffic light, ignoring priority signs.
However, not only drivers violate the rules of the road. Pedestrians behave no better than them, who either cross the road in the wrong place (and often without even bothering to look around and make sure there are no vehicles in the immediate vicinity), or do it at a prohibitory traffic light.
The same goes for cyclists: riding too far from the edge of the road, neglecting others traffic rules for many - almost in the order of things.
Another common cause of road accidents is drunk driving. No further explanation is required here.
Often the cause of traffic accidents is overworking the driver up to falling asleep at the wheel.
Many accidents happen due to technical malfunction of cars. Recall that there is a legally approved List of technical malfunctions, in the presence of which the operation of vehicles is prohibited. In addition, with some malfunctions, even further movement is prohibited. The difference between operation and further movement is that in the first case, you have the right to drive on your own to the place of repair or parking, and in the second, any further movement is prohibited, and the car will have to be towed or transported on a tow truck.
For example, if on the road your headlight bulb burned out or the parking brake failed, you can drive to the place of parking or repair, but subsequent operation of the car is allowed only after troubleshooting. But if your brakes fail (for example, the pedal “falls through”), or the steering, or the windshield wipers do not work during rain, further movement is prohibited. Either fix the problem on the spot, or (in the case of windshield wipers) wait for the precipitation to end, or deliver the car to the place of repair or parking by towing or using a tow truck.
Neglect of these requirements often leads to serious traffic accidents. For example, if the steering fails, the car becomes completely uncontrollable, and it can be carried both into the oncoming traffic lane, and into a ditch or onto the sidewalk. Failure of the brake system is also extremely dangerous: you will not be able to stop the car when an obstacle appears, and it will be almost impossible to avoid an accident (especially at an intersection).
A common cause of traffic accidents is the inattentive attitude towards other road users by both drivers and pedestrians. For example, you are driving along the road without violating anything, but at this time you are abstractly thinking about something of your own. Consequently, your attention is dulled, and you do not have time to notice a pedestrian who has appeared on the roadway and, accordingly, react to a change in traffic conditions. Even if the pedestrian violated the rules of the road, but if you had been more attentive, you would have seen him earlier, and the collision could have been avoided. Well, as for pedestrians, many of them go out on carriageway where it pleases, done without noticing anything around.
Due to inattention, drivers often do not notice the brake lights of the car in front that have turned on, the direction indicator of another car has turned on, “lose” their lane, etc. All this can also eventually lead to an accident.
Often road traffic accidents occur due to the poor condition of the roads. Which of us has not come across potholes, potholes, open sewer manholes, and other “charms” on the road. But even small size a pit can cause the car to roll over or spontaneously leave it in the oncoming lane when driving not even on the very high speed(sometimes a speed of 70-80 km / h is enough for this, and on a slippery road - even 30-40 km / h).
It should be noted that if the cause of the accident was the unsatisfactory condition of the road, then the responsibility for the traffic accident can be fully or partially assigned to representatives of the road services, with all the ensuing consequences.
Serious traffic accidents are often caused by a malfunction of the technical means of organizing traffic. Most typical example- a faulty traffic light (meaning a faulty one, and not a broken one or with a flashing yellow signal). The worst thing is when all the traffic lights installed at the intersection are green. An accident with the most serious consequences is possible here - after all, all cars will move at a speed of green light. Drivers - participants in a traffic accident in such a situation will not be found guilty - the responsibility will be fully borne by the road services.
Sometimes it happens that in one direction at the spoiled traffic light the green light is on all the time, and in the other - red. Many hurried drivers in such cases simply wait for the crossed road to be empty, and, having chosen the moment, pass the intersection at a prohibitory traffic signal. If this leads to a traffic accident, the driver who ran the red light will be found responsible for the accident, although some of the blame should be placed on the road services, since it was they who did not ensure the normal operation of the road equipment. It is more correct in such a situation to turn around and go the other way, or call with mobile phone to the traffic police and ask to send a traffic controller.
Another common cause of road accidents is young drivers who have just obtained a driver's license and do not have sufficient driving experience.
In addition, some people, having studied at a driving school and received a license, long time do not drive. Someone went to study just “to be right”, someone plans to buy a car only in a few years, and is studying now “because there is time”, etc. When, after a few years, they finally decide to drive, by this time they completely forget everything they were taught in driving school. In this case, a driver's license gives them only the legal right to drive a car; but in order to have a moral right, you need to practice on deserted roads or drive at night (when there are almost no cars on the streets) in order to remember the basic skills and not create dangerous situations on the road several times per trip.
Dear drivers! We ask you to pay attention to these causes of accidents and be careful and careful on the roads.
Traffic Police Department of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation for the Korenovsky District

Traffic Police Department of the Ministry of Internal Affairs for the Korenovsky District calls on road users be mutually polite and follow the rules of the road
Methodical development № 5
The actions of employees of organizations in conditions of negative and
dangerous factors household character
Transport accidents and actions in case of:
B) accidents on public transport;
C) accidents in the subway;
D) accidents on railway transport;
D) accidents in air transport;
E) accidents on water transport.
2. Actions in case of fires, explosions.
3. Ways to prevent and overcome panic and panic.
1. Transport accidents and actions in case of:
a) car accidents
The peculiarity of car accidents is that 80 % the wounded die in the first 3 hours due to heavy blood loss. According to statistics traffic accidents most often occur during rush hour, on holidays, on the first and last days holidays. The road is especially dangerous in winter. The winter months account for 60% of accidents throughout the year. Rain and fog also complicate the traffic situation and often become the cause of a road traffic accident (RTA).
^ When a collision is imminent keep your composure. This will allow you to drive the machine to the last opportunity.
Tighten all the muscles and do not relax to a complete stop. Do everything to get away from the oncoming blow: a ditch, a fence, a bush, even a tree is better than a car moving at you.
Remember that in a collision with a stationary object, the impact of the left or right wing is worse than the entire bumper.
Protect your head if a collision is imminent. If the car is moving at low speed, press your back into the seat, and, straining all your muscles, rest your hands on the steering wheel. If the speed exceeds 60 km / h and you are not wearing a seat belt, press your chest against the steering column. When in the front passenger seat, cover your head with your hands and lie on your side, sprawling on the seat. Sitting in the back seat, try to fall to the floor. If there is a child next to you, cover him with you.
^ After the accident determine where in the car and what position you are in, whether the car is on fire and whether gasoline is leaking (especially when overturning). If the doors are jammed, leave the vehicle through the windows by opening them or breaking them with a heavy handy object. After getting out of the car, move away from it as far as possible - an explosion is possible.
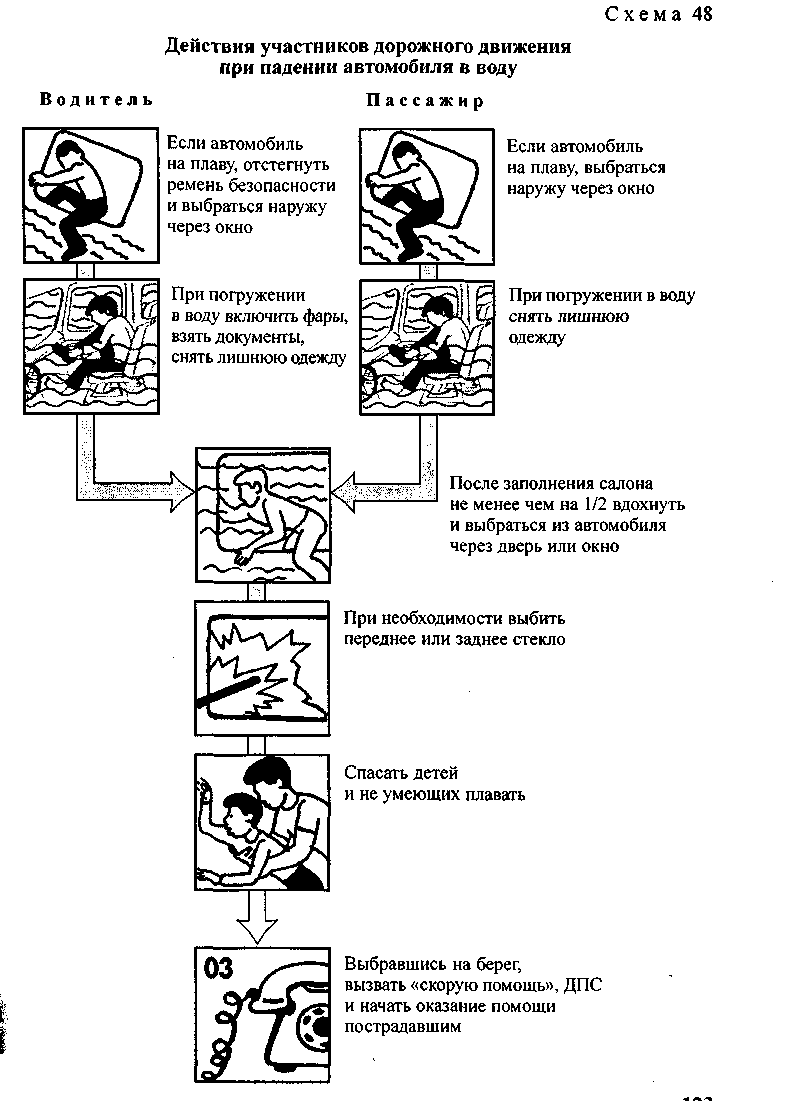
^ When a vehicle falls into water may stay afloat for a while. Get out through opened window, since when you open the door, the car will suddenly begin to sink. When diving to the bottom closed windows and through the doors, the air in the passenger compartment is kept for several minutes. Turn on the headlights (then it is easier to search), actively ventilate the lungs (deep breaths and exhalations allow you to fill the blood with oxygen “for the future”), get rid of excess clothing. Get out of the car when it is half full of water, otherwise you will be disturbed by the flow of water going into the passenger compartment. Break if necessary windshield heavy handy object. Squeeze out by placing your hands on the roof of the car, and then swim up sharply.
If you get into an accident, you should immediately stop and inspect the cars - yours and the injured driver (if you are the culprit of the accident). If there are casualties, under no circumstances leave them unattended. Report the incident by calling "02" or pass the information to the nearest traffic police post through drivers passing by. Do not leave the scene of the accident until the arrival of the traffic police. Keep as much trace of the incident as possible.
^
Being a witness to a traffic accident
collision or accident in which the driver fled, remember and immediately write down the number, brand, color and any signs of the car and the driver; after helping the injured, pass this information to the traffic police. If you are in a car, stop it before reaching the scene of the accident. Turn on the alarm. Describe in detail to the arrived traffic police everything that you saw at the scene.
^ In order to prevent traffic accidents, road users must:
driver- follow the rules of the road; to check before departure, and on the way to ensure proper technical condition car; when driving, be fastened with a seat belt; do not carry passengers who are not fastened with seat belts; skillfully assess the traffic situation and take into account how other drivers and pedestrians may behave;
passenger- be wearing a seat belt; to make landing and disembarking from the sidewalk or roadside after a complete stop; do not distract the driver from driving; do not open doors while driving;
a pedestrian- follow the rules of the road; walk on the sidewalk footpath, roadside; outside settlements go towards the movement of vehicles; cross the roadway pedestrian crossings; do not linger on the roadway and do not stop unnecessarily; wait for route vehicles at the landing sites.
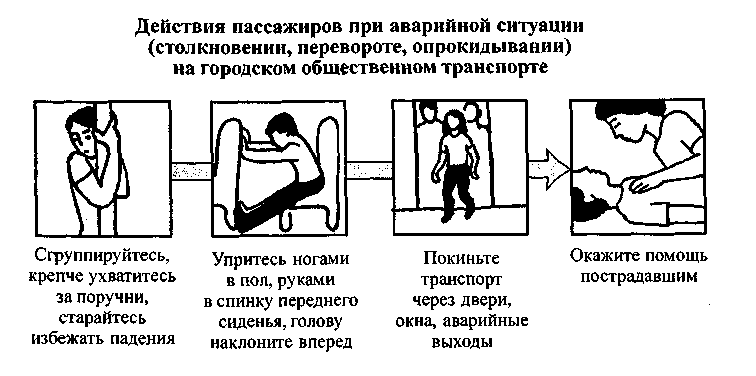
All passengers using urban public transport services are required to know and follow the basic safety rules: do not enter or leave the transport until it has completely stopped; do not lean against the doors, do not stick your head and hands out the windows; inside the tram, trolleybus and bus, try to hold on to the handrails in case of emergency braking (a reliable point of support is the handrail above your head); stand facing the direction of movement in order to be able to notice the danger in advance and have time to react to it (from this position, during a collision and braking, you will fall face forward, which is much safer than falling on your back); in the event of a collision and the inability to stay upright, try to group in a fall, cover your head with your hands and see the landing site.
Umbrellas, canes and other objects with sharp and protruding edges pose a certain threat in the event of sudden braking. It is unsafe to walk in a moving vehicle, instead of standing, holding onto the handrails, and also taking a nap. In these cases, the person simply does not have time to respond to the threat.
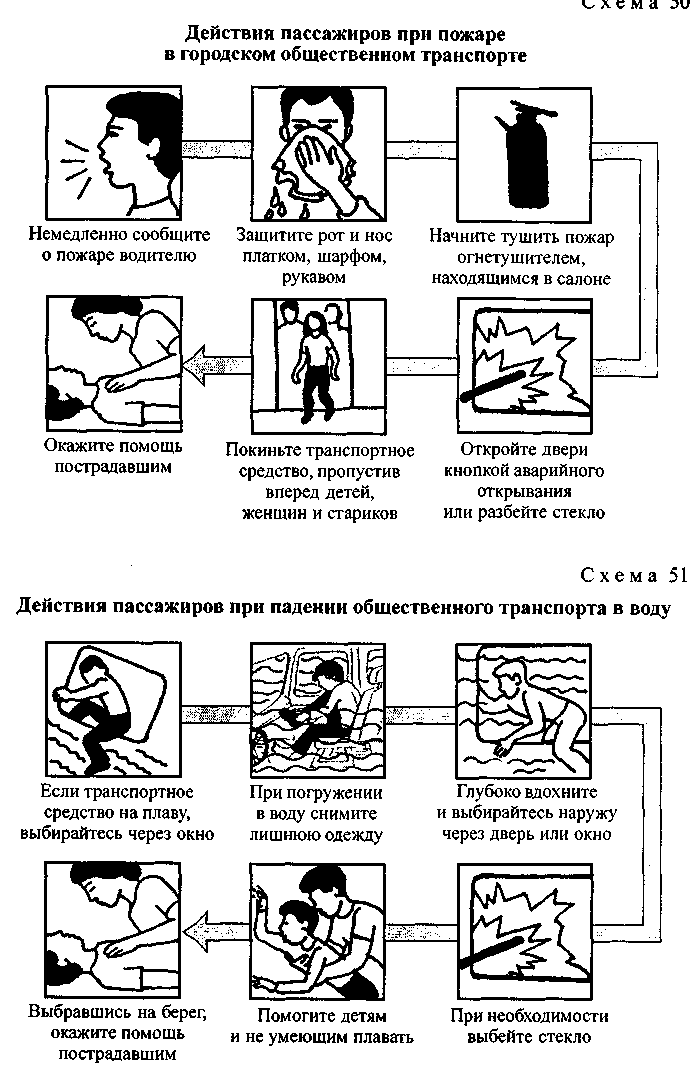
Any public transport, including electric, is a fire hazard. For this reason, after an accident, it is advisable to quickly leave the salon and move 10-15 m to the side. Use emergency exits if exit doors are jammed or crowded. Don't wait for the situation to become critical. Break windows, for which use any improvised heavy objects: a fire extinguisher located in the cabin, a hard diplomat, etc.; in last resort, knock out the glass with a strong kick to the corner of the window, hanging on your hands on the ceiling rails. Before leaving, be sure to clean the window opening from the remaining glass.
If there is a smell of burning, such measures should be recognized as mandatory, since passengers may not have time to stand in line leading to the existing exit. In case of fire, urban transport burns very quickly. In this case, the nose and mouth should be protected in advance with a scarf, sleeve or other material, if possible wetting it with any liquid.
In the event of a fire in the passenger compartment (diagram), notify the driver, open the doors (using emergency opening), emergency exits or break a window. If there is a fire extinguisher in the cabin, take measures to eliminate the source of fire. Get out of the cabin outside crouching, without touching the walls and metal parts.
In case of an accident in case of damage to the current-carrying wire, the safest places in a tram or trolleybus are seated. In this case, it is better to tear off your legs from the floor, and do not touch the walls and handrails. To get out of the electric transport, one should jump, simultaneously with two legs forward, without touching the body, so as not to close the electrical circuit with one's body.
If you fall into the water (scheme), wait until the cabin is half filled with water, hold your breath and emerge through the door, emergency exit or broken window.
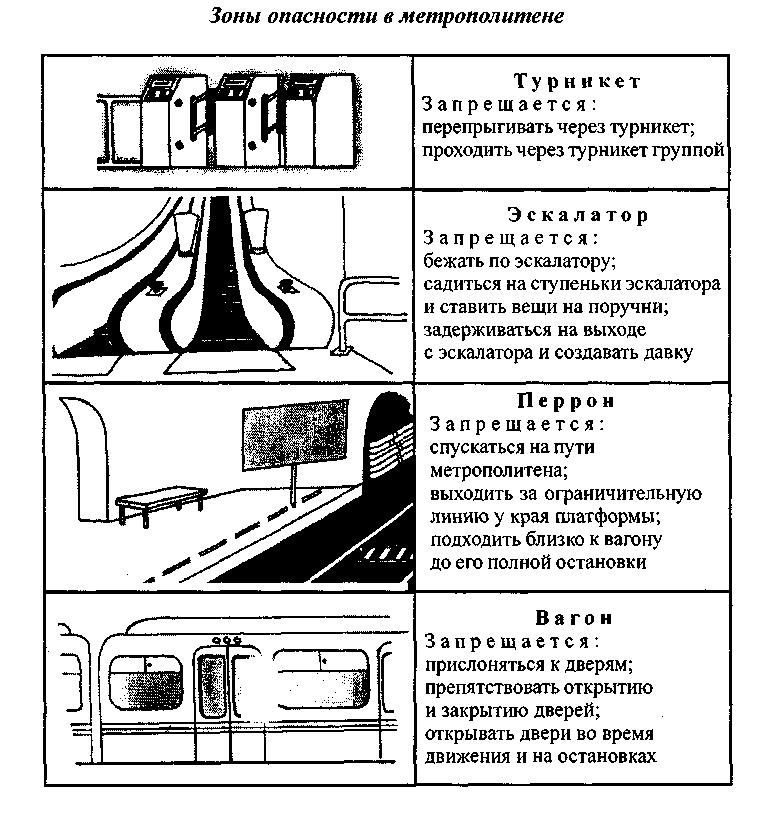
c) accidents in the subway
Emergencies and dangerous situations at stations, in tunnels, subway cars arise as a result of collisions and derailments of trains, fires and explosions, destruction of the supporting structures of escalators, detection of foreign objects in cars and stations that can be classified as explosive, spontaneously igniting and toxic substances, as well as falling passengers and their belongings on the station tracks.
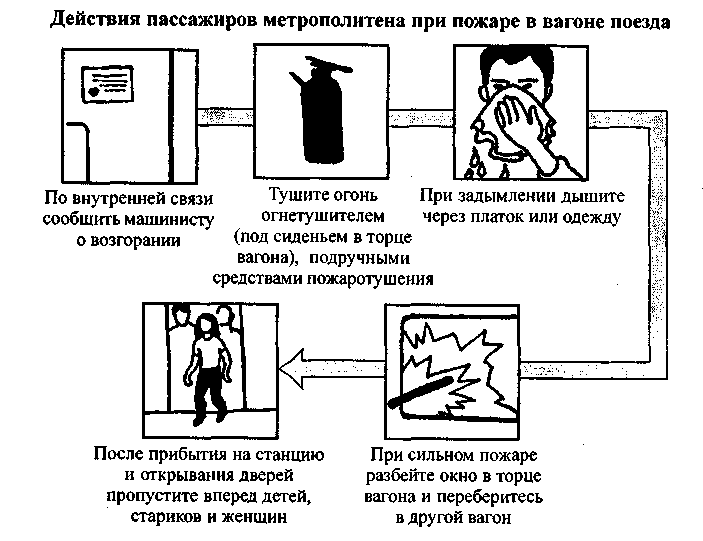
At emergency, for example, a fire in a train car, a loudspeaker or a megaphone is used to alert passengers at the station, and a train loudspeaker warning device is used in the train (Scheme 52).
Evacuation from the station can be carried out by escalators or by arriving trains. Disembarkation of passengers on the haul (Scheme 53) is carried out at the command of the locomotive crew, without panic, in compliance with personal safety measures. After exiting the cars, it is necessary to move through the tunnel in the indicated direction. In the event of a failure in the operation of the loud-speaking notification, passengers are informed by the locomotive crew in each carriage. Passengers are disembarked, as a rule, through the side doors of cars on one or two sides or through unlocked doors between cars, starting from the car closest to the station to which passengers will be directed. If a situation arises that threatens the safety of passengers in one or more cars, disembarkation is carried out first of all from them. In case of damage to the tunnel lighting, the driver of the locomotive crew turns on white headlights and a searchlight on the head car in the direction of the station where the passengers are going.
^ From the rules for using the subway. When people and objects fall on the subway path (Scheme 54), smoke, fire and other dangerous situations contact the station attendant or the train driver using the “passenger-driver” system.
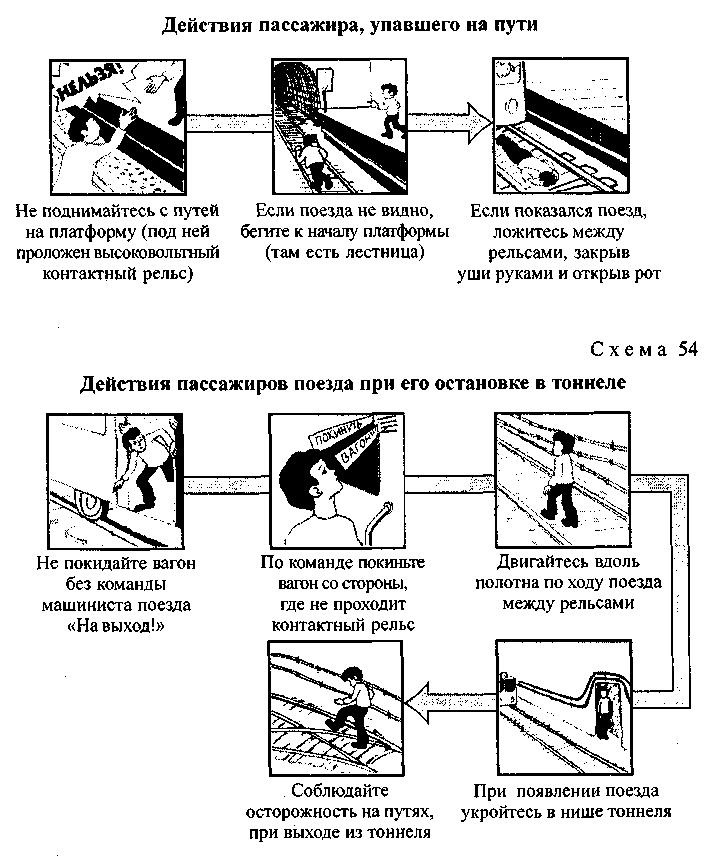
If you find forgotten, ownerless and suspicious things and objects in the subway or train carriage, immediately inform the police officers, subway workers or the train driver.
For safety reasons, it is prohibited to transport: flammable, poisonous, poisonous, explosive and malodorous substances; firearms; piercing and easily breaking objects and things without cases and proper packaging; animals and birds without cages and special containers (bags); long and bulky luggage.
d) railway accidents
The main causes of accidents and disasters in railway transport are malfunctions of the track, rolling stock, signaling, centralization and blocking, dispatcher errors, inattention and negligence of drivers. Most often, rolling stock derails, collisions, collisions with obstacles at crossings, fires and explosions directly in the cars occur.
Everyone who goes on a trip by rail needs to know that the safest places in the car are the compartment shelves located in the direction of movement. In case of emergency braking or a collision of trains, you will only be pressed against the wall, while passengers from opposite shelves will fly to the floor. The last person to fall after a complete stop is a person lying on the top shelf in the direction of travel.
The greatest threat to passengers is the first and last cars of the train. The first is crushed and thrown off the path in a head-on collision. With the latter, the same thing happens in a collision from behind, only on an even more catastrophic scale, since, unlike the first, it is not buffered by a locomotive and a baggage car.
^ When traveling, observe following rules:
when the train is moving, do not open the outer doors, do not stand on the steps and do not lean out of the windows;
carefully stow your luggage in the overhead bins and do not overload them with things or secure them so that you do not become a victim of your own suitcases or boxes during sudden braking;
do not pluck the stopcock unless absolutely necessary; remember that even in case of fire it is impossible to stop the train on the bridge, in the tunnel and in other places where evacuation will be complicated;
smoke only in designated areas;
do not carry flammable, chemical and explosive substances with you;
do not plug into the wagon's electrical network Appliances;
if you smell burning rubber or smoke, contact the conductor immediately;
in case of a real threat, immediately leave the car through the vestibule doors and emergency exits; in extreme cases, knock out window panes with improvised objects (ladders-ladders, hard briefcases-diplomats, tables torn from nests and clothes shelves);
do not reach for suitcases, drop them; your life is not worth the things in them.

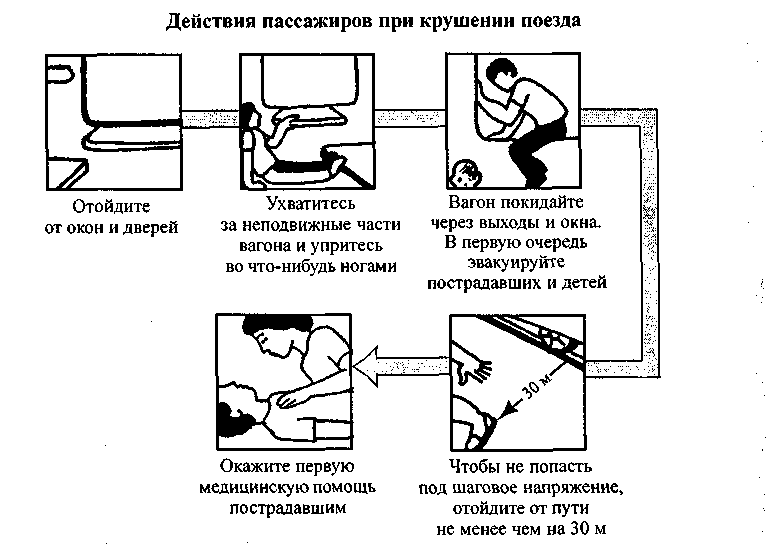
In a crash or emergency braking
Brace yourself so you don't fall. To do this, grab the handrails and rest your feet against the wall or seat. It is safest to get down on the floor of the car. After the first blow, do not relax and keep all the muscles tense until it becomes completely clear that there will be no more movement.
In collision and emergency braking accidents, most injuries are caused by falls from shelves. To avoid them, or at least soften the blow, in addition to securing luggage, unsafe items should be removed from the tables.
Bottles, glasses, etc. Bend, especially on the shelves on which children sleep, mattresses with outside or put a folded blanket under them or unwanted clothes to form a protective roller that is difficult to roll over. Completely, before fixing, close or open the doors of the compartment so that during a sudden stop they do not cause injury to a hand or head caught in the opening.
In case of a serious crash, you must immediately get out of the car (only, jumping out, do not fall under an oncoming train!) And help the injured passengers. Look carefully for fallen current-carrying wires nearby: they can be a mortal danger.
A fire in a train (Scheme 56) is terrible not with a flame, but, first of all, with poisonous combustion products of synthetic finishing materials. Poisoning occurs in a matter of minutes, and with intensive combustion - seconds. To avoid this, in a moving car, go to the next car, preferably in the direction of movement, in a stopped one - to the street, if possible from the side where there are no railway tracks. Do not scatter in all directions, as the rescuers who have arrived will look for you near the canvas.
In case of strong smoke in the car, cover your nose and mouth with a cloth moistened with water - a towel, a pillowcase, a sheet, a piece of torn clothing. In half-empty cars, you can move on your knees, since there is less smoke below (near the floor).
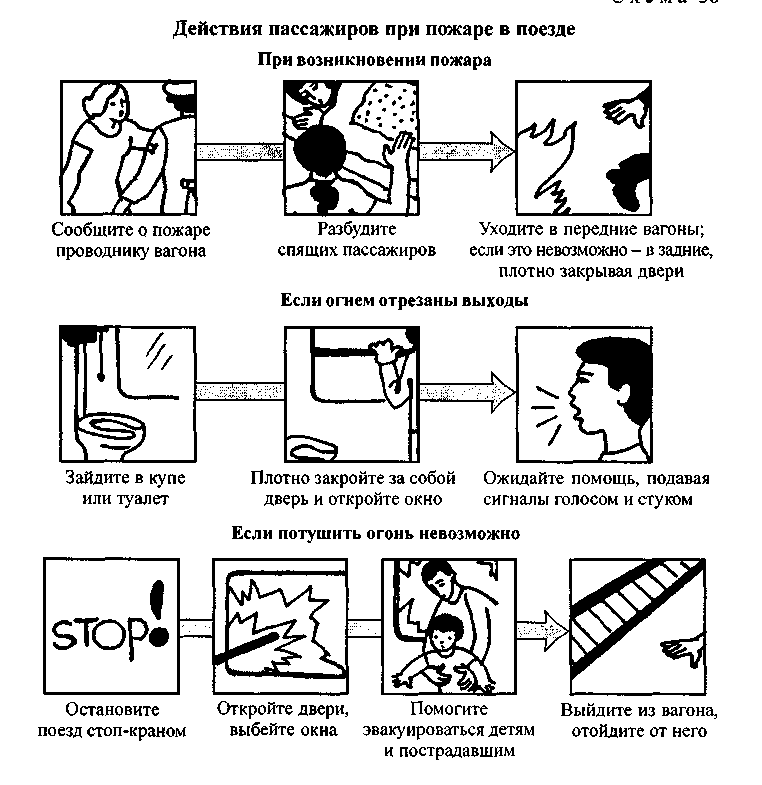
There are situations when a moving train cannot be stopped. In such cases, it is necessary to act according to scheme 57.
After the accident, quickly get out of the car through the door or windows - emergency exits (depending on the situation), as there is a high probability of a fire. Quickly opening windows in the 3rd and 6th compartments from the side of the transverse shelves serve as an emergency exit from the cars. Break the compartment window only with heavy improvised objects. When leaving the car through the emergency exit, get out to the other side railway track where there is more free space, taking with you documents, money, clothes or blankets. Once outside, immediately engage in rescue work: help passengers in other compartments break windows, pull out victims, etc.
Fuel may spill during an accident. In this case, move away from the train to a safe distance, as there is a risk of fire and explosion. If the current-carrying wire is broken and touches the ground, move away from it with jumps or short steps to protect yourself from step voltage. The distance over which the electric current spreads along the ground can be from 2 (dry) to 30 (wet) meters. (Wet) meters
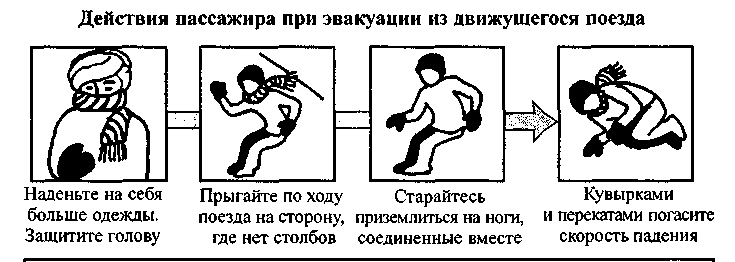
^
Jump out of a moving train only in case of direct danger to life.
e) accidents in air transport
Aviation accidents and catastrophes are possible for many reasons and lead to serious consequences. Takeoff and landing accidents are among those where there is hope for rescue, since they usually occur when the aircraft is still on the ground or not high above it, and its speed is relatively low. Moreover, they tend to happen in the area around the airport, where there are rescue teams and the necessary equipment.
Unlike a car, an aircraft, flying into a stationary structure or any vehicle, usually does not stop, but rushes on. Therefore, passengers are not subjected to sudden impacts. An exception to this would be when the plane collides with a mountain. In this case, the chances of salvation are scanty.
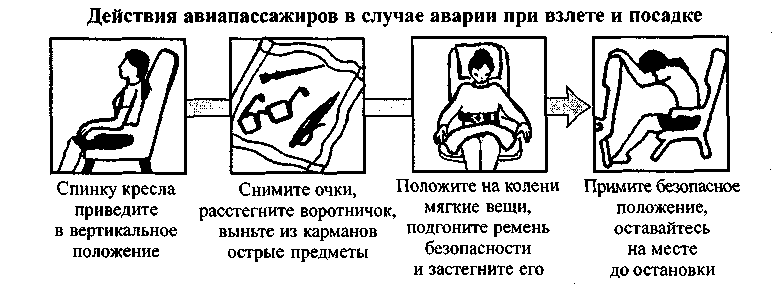
In other cases, in the event of an emergency in flight, the crew may decide to make an emergency landing. When preparing it (Scheme 58), you must immediately clear the aisles and take seats in your chairs, the backs of which should be brought to a vertical position. In addition, it is necessary to remove glasses, dentures, remove sharp objects from inside pockets (pens, knives, lighters), remove shoes on high heels, loosen the tie and unbutton the collar. After that, put soft things on your knees to protect your head and torso, fasten and tighten the seat belts tightly. At the command of the flight attendant "Attention landing!"
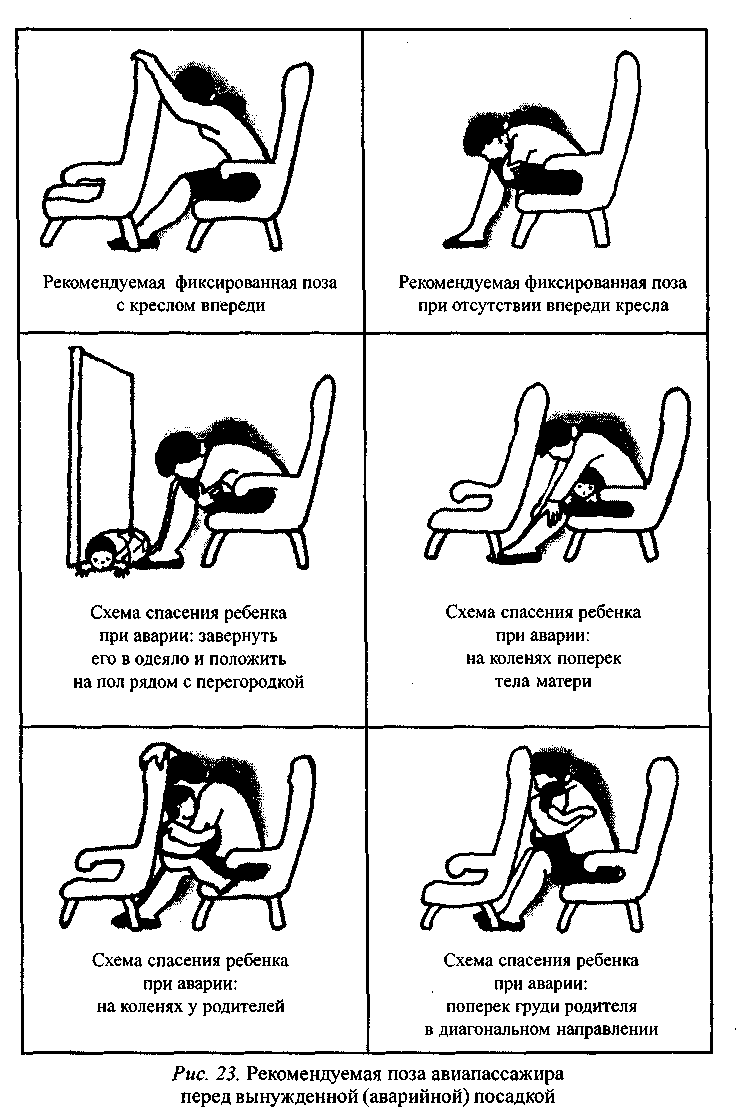
you should lean forward, cover your head with soft things and put it on your hands, which clasp your knees. You need to stay in this position until the aircraft comes to a complete stop (Fig. 23).
After the plane stops, unfasten your seat belts and prepare for evacuation. For emergency evacuation of the aircraft by passengers and crew, all main and emergency doors, as well as emergency exits, located, as a rule, are used on the left and right sides fuselage. Exits for passengers, approaches to them and means of opening are prominently marked to facilitate their detection. All inscriptions are illuminated from the inside, regardless of the main lighting system. The device of emergency hatches and their locks with handles is made simple, noticeable and does not require much effort to open. Instructions for opening them are printed on the doors (hatches). In places where emergency exits to the wing are located, the aisles between the seats are wider than elsewhere, and do not interfere with the opening of hatches and the exit of passengers.
When you leave your seat, do not take with you luggage taken on board as hand luggage. This is dictated by security measures, as it is likely that some items in your bag have sharp corners and edges. This can cause damage and deflate the inflatable life slide, which in turn will lead to injury, and possibly death, to passengers waiting for their turn to evacuate.
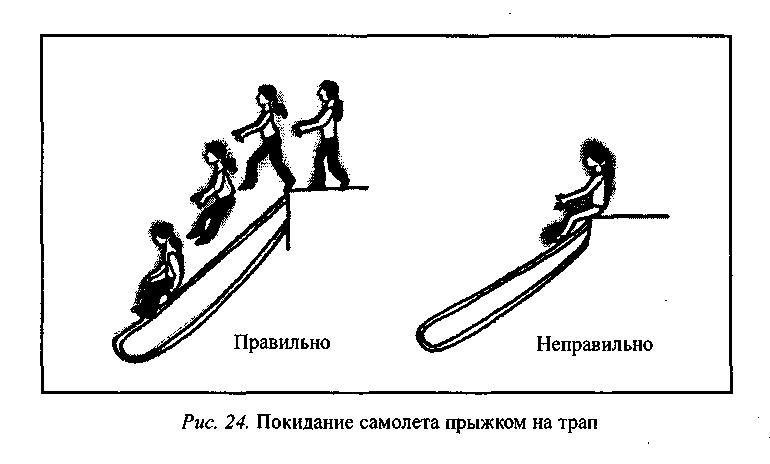

Leaving the plane through the exit with the ladder released and inflated, you need to jump on it without stopping, and not sit on the edge, and then slide down. Only by jumping is an increase in the speed of evacuation achieved (Fig. 24, 25).
try to wear a coat or jacket made of slow-burning and hard-to-melt materials;
think about what shoes to wear; avoid high-heeled shoes, but if you wear them, and you have to use an inflatable escape slide during the evacuation, then remove them when you leave the plane;
at each takeoff and landing, make sure that the seat belt is pulled tight around your hips;
know what fixed position you need to take in an emergency landing; keep track of what is happening on board the aircraft; if everything indicates that an accident is imminent, take the right posture;
know where the exits are on the plane and how they open.
During decompression, i.e. rarefaction of air in the cabin as a result of depressurization, the latter is filled with dust and fog. Visibility is sharply reduced, air quickly leaves the lungs of a person, and it cannot be delayed. At the same time, ringing in the ears and pain in the intestines may occur. Rapid decompression usually begins with a deafening roar (air escapes). In this case (Scheme 59), without waiting for the command, immediately put on an oxygen mask. Do not try to help anyone before you put on the mask yourself, even if it is your child: if you do not have time to help yourself and pass out, then both will be without oxygen. Fasten your seat belts immediately after donning your mask and prepare for a steep descent.
^
In the event of an aircraft fire
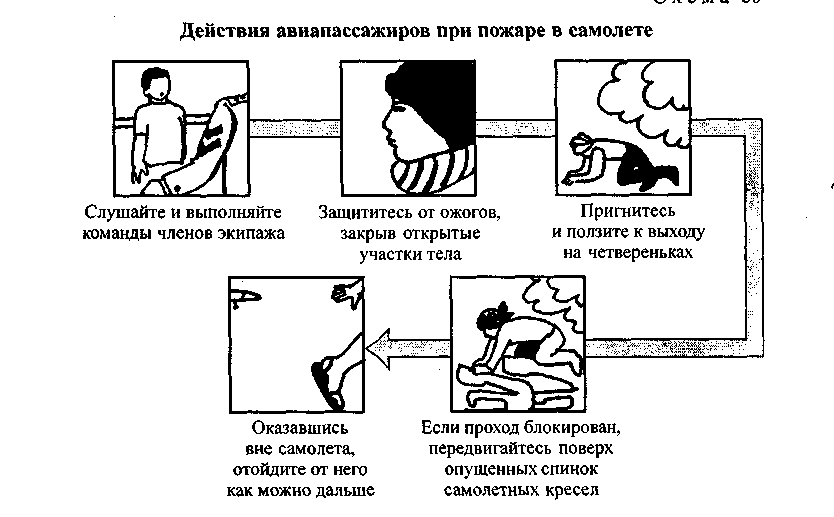
(diagram 60) remember that the greatest danger on board is smoke, not fire. Breathe only through cotton or wool clothing, dampened with water if possible. When making your way to the exit, move crouching or on all fours, as there is less smoke at the bottom of the cabin. Protect exposed areas of the body from direct exposure to fire by using available clothing, blankets, etc.
After landing and stopping the plane, immediately head to the nearest exit, as there is a high probability of an explosion. If the passage is littered, make your way through the chairs, lowering their backs. When evacuating, get rid of hand luggage and avoid exit through hatches near which there is open fire or heavy smoke. After exiting the plane, move away from it as far as possible and lie on the ground, pressing your head with your hands - an explosion is possible.
^ Aircraft forced landing happens rarely. Before sinking, the aircraft can be afloat from 10 to 40 minutes. However, if the fuselage is damaged, this time is much shorter.
Aircraft with wing-mounted engines will float in a horizontal position, while those with two or more tail-mounted engines will float tail down.
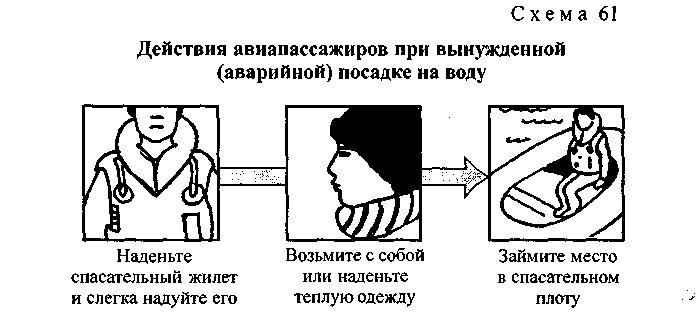
When splashing down, which is always unexpected, there is practically no time for preparation. In one case, the plane can touch the surface so smoothly that it is not clear whether it landed or splashed down, in the other, it can fall apart and quickly sink. Therefore, when splashing down, it is necessary to act on the command of the crew commander or flight attendant (Scheme 61), i.e. put on a life jacket and inflate it, take or put on warm clothes and go to the exit indicated by the flight attendant to board the life raft.
After a forced landing on the water, life rafts descend. Time to bring the raft in working condition is approximately 1 min in summer and 3 min in winter. If splashdown occurred during the cold season, you need to take more warm clothes on the raft. Do not forget about the supply of water and food. The raft comes with an emergency supply, which may not be enough if the voyage is long. The command of all passengers on the water is assumed by the aircraft crew commander.
Using oars and improvised items, you need to move away from the dive site of the aircraft. After that, straighten and throw overboard a floating anchor, which will reduce the speed of the raft drift in the wind and will keep those fleeing in the area of the accident.
f) accidents on water transport
Majority major accidents and accidents on ships occur under the influence of hurricanes, storms, fogs, ice, and also through the fault of people - captains, pilots and crew members.
Abandonment of the ship in case of an accident or shipwreck is carried out only on the instructions of the captain. He gives such an order in the following cases:
there are clear signs of the impending death of the vessel (dangerous roll, entry into the water of the deck, stern, bow);
the vessel remains afloat, but the spread of water over the vessel leads to its flooding, and the crew does not have sufficient means to deal with water;
cargo shifting or icing of the ship occurs, which will eventually lead to its capsizing, and the crew does not have the means to deal with cargo shifting or icing;
Under the influence of wind, waves or currents, the ship drifts on reefs, where it can be broken or capsized; at the same time, the ship does not move or is deprived of the ability to be controlled and cannot counteract the force of nature, etc.
On large sea and river vessels, all actions related to self-rescue are reduced to the fastest possible exit to the boat deck and the precise execution of the commands of the crew organizing rescue operations. When a boat alarm is announced, all collective rescue equipment is brought to working position, and the crew is preparing to leave the ship (Scheme 62).
All participants in the swim must wear spare clothing at their disposal - cotton and wool underwear, sweaters, waterproof, better waterproof outerwear, if available, a wetsuit and, of course, a life jacket. It is better to wear layered clothing. Two thin sweaters are preferable to one. It is advisable to wrap the neck with a scarf, in extreme cases, with a towel or a sleeve of a torn sweater, a torn leg, since it is more susceptible to hypothermia in water than other parts of the body. One or two tight-fitting woolen caps should be put on the head, a hood should be put on and tightened, mittens or gloves should be put on the hands. You should strive to protect places that are particularly prone to heat loss - the chest below the armpits, the groin area, neck, head. It is better to wear shoes that are spacious, with two or three woolen socks, but in such a way as not to restrict the movement of the toes.

Each sailor must be able to handle individual means salvation. It is best to learn this in advance. It must be remembered that an incorrectly worn life jacket can not only not help, but even accelerate the death of a person on the water:
First, according to the ancient sea rule, children, women, wounded, weakened people pass to the collective means of salvation. They need to organize insurance, for which one adult man can go down to the rescue equipment.
The captain is the last to leave the ship, after personally making sure that all members of the crew, passengers, and emergency equipment are in the survival craft.
Before boarding inflatable rescue equipment (rafts, boats), it is necessary to tightly wrap the metal parts of the shoes with cloth - horseshoes, buckles, protruding nails that can damage the rubber lining. When boarding inflatable rafts and boats, it is advisable to avoid jumping. If it is impossible to do without a jump, you should try to fall on inflatable elements - onboard balloons, inflatable beams, cans and racks. In this case, it is desirable to come into contact with the skin, possibly larger area body to reduce the impact load on the inflatable structure. If a person lands on their feet, they can break through the bottom of a lifeboat or raft.
The people who were the first in the life-saving equipment should insure it from damage - push off the vessel with oars or hands, drive away objects floating on the surface of the water that pose a threat, and also help their comrades.
Leaving a sinking ship can be carried out on lifeboats and inflatable rafts, by going on board an approaching rescue ship, evacuating aboard a rescue helicopter and jumping into the water.
^ Features of leaving the ship by jumping into the water (Scheme 63). Before leaving the vessel, crew members must remind passengers of the rules for jumping into the water and further behavior on the water. For a jump into the water, such places are chosen to be carried away from the vessel by the current. If possible, it is better to go down to the water along the ladder. The life jacket must be protected from damage.
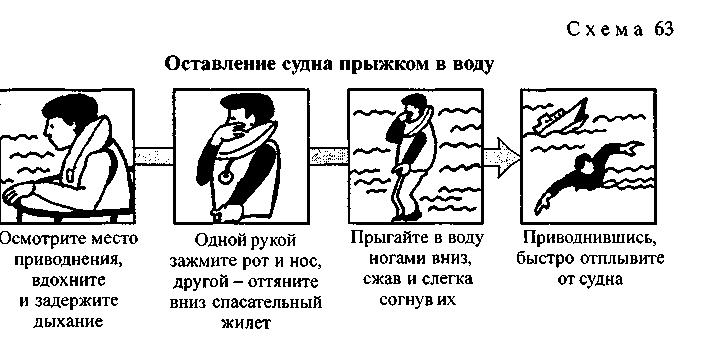
When jumping into the water, tuck your chin to your chest, but do not tilt your head forward so as not to hit your face on the water, tighten the back of your head. Press the clothes with one hand, close the nostrils and mouth with the other. Jump with your feet down, press your feet against each other, bend your legs slightly and strain. Take a deep breath before jumping. Once in the water, dive with open eyes, avoiding getting hit by a ship, boat or raft. After recovering your breath, turn to face the oncoming wave, then look around for danger from nearby ships.
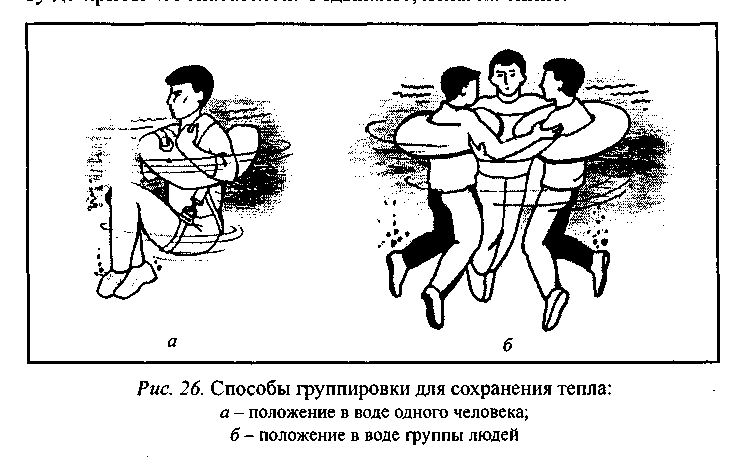

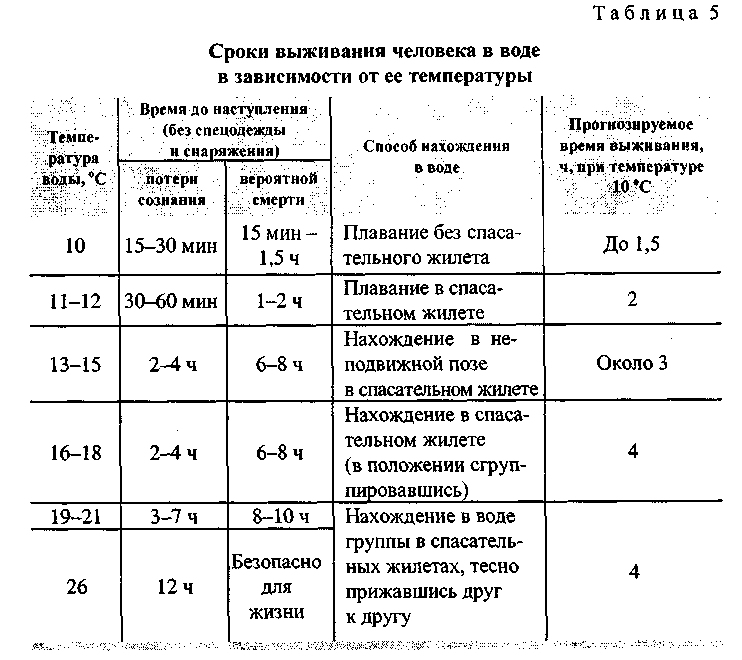
In the absence of rescue equipment, while in the water, give signals by whistling or raising your hand. Move as little as possible to keep warm. Heat loss in water occurs several times faster than in air, so movement even in warm water should be reduced to just keeping afloat. In a lifejacket to keep warm, group up, wrap your arms around your chest from the sides and lift your hips higher so that the water washes less of the groin area (Fig. 26). This method will increase the estimated survival time in cold water by almost 50% (Table 5). If you are not wearing a life jacket, look for a floating object with your eyes and grab onto it to make it easier to stay afloat until the rescuers arrive. Rest lying on your back.
^ While on a lifeboat take your seasickness pills. To save heat, stay close to other victims, do physical exercise. Let's drink only to the sick and wounded. If there is no reasonable hope of reaching the shore or entering the shipping lanes, try to stay close to other boats near the place of the ship's sinking.
Keep your feet as dry as possible. Lift and move them regularly to relieve puffiness. Never drink sea water. Keep fluid in the body by reducing useless movements. Moisten clothing during the day to reduce perspiration, and moisten the outer shell of the raft with water to reduce the temperature inside the raft. Drink no more than 500-600 ml of water per day, dividing them into numerous small doses with the largest in the evening. Eat only emergency food. Save the smoke bombs until there is a real possibility that your signal will be noticed. Do not use checkers all together in the hope of discovering yourself, entrust this to one person.
^ 2. Actions in case of fires, explosions
The city of St. Petersburg is rife with fires. The main causes of fires and explosions in the city are: short circuit in electrical wiring, gas leakage, careless handling of fire, especially while intoxicated.
In case of fires, residential and service buildings are completely or partially destroyed or go out of order.
The main damaging factors of a fire are:
direct impact on a burning object;
high air temperature, smoke;
dangerous concentration carbon monoxide and other harmful products
combustion;
collapse of building structures.
People, domestic and farm animals get burns of various degrees and die.
^ The main damaging factors of the explosion are an air shock wave and fragmentation fields created by flying fragments of destructible structures.
The secondary consequences of explosions are the destruction of people inside objects and premises by fragments of collapsed building structures.
During fires and explosions, people receive thermal and mechanical damage.
Burns of the body and upper respiratory tract, craniocerebral trauma, multiple fractures and bruises, and combined injuries are characteristic.
^ To the main prevention measures residents of our city should be reminded:
avoid storing a significant amount of flammable and combustible liquids in the house, on loggias, balconies;
do not heat mastics and varnishes, aerosol cans on an open fire, do not wash in gasoline;
Do not store on stairwells old furniture, combustible materials, arrange pantries in the niches of sanitary cabins, store waste paper in waste bins;
Do not install electric heaters near combustible objects;
Petersburgers spend a significant part of their free time watching TV and sometimes there are tragic consequences if the rules of operation are not followed.
When using TVs, the following rules must be observed:
use only a standard fuse, the ratings of which are indicated in the manual;
do not install the TV in close proximity to flammable and fire-propagating objects;
do not install the TV near heating appliances or in furniture walls where it does not cool well;
If a fire occurs in the TV, unplug the power cord; if the burning does not stop, fill the TV with water through the holes in the back wall, cover it thick cloth, clothing to stop air from entering the TV case.
It should be remembered that neglecting at least one of the listed rules (by no means all of them!), Can lead to a fire, death of people, especially defenseless children and the elderly.
What to do if there is a fire? What should I do, what rules should I follow?
Briefly about them:
In case of fire, it is necessary to leave the building immediately, without panic, while maintaining self-control (calmness);
At the beginning of a fire, you should try to localize (extinguish) it, using all available fire extinguishers (fire extinguishers, water, blankets, sand, etc.), remembering the life rule: “Trust in God, but don’t make a mistake yourself!”
To burn out two-roomed flat takes an average of 12-15 minutes. Of course, when a fire starts, you must immediately call "01".
It must be remembered that the fire on the power supply elements cannot be extinguished with water. First you need to turn off the voltage or cut the wire with an ax with a dry wooden handle.
An important condition for observing safety measures in case of fire is the rescue of victims from burning buildings:
do not enter a burning room, rooms, if the visibility of smoke is less than 10 meters; it is dangerous to enter this zone unnecessarily; smoke and high temperatures are especially dangerous in basements and on the upper floors of buildings;
before entering a burning room, cover your head with a damp dense cloth;
move in a smoky room. Crouching or crawling;
to protect against carbon monoxide (CO), breathe through a damp cloth;
when looking for children, inspect the corners of the rooms, cabinets, underbed space;
having found a person in burning clothes, throw a coat, cloak, coverlet over him and press tightly on the place of the bandage burns;
elevators are not allowed.
^ 3. Ways to prevent and overcome panic and panic.
What is the opposite of panic? One of the best means in the fight against panic is reliable, convincing and fairly complete information about what happened, a reminder of the rules of conduct and actions, periodic informing about the measures taken and the progress of the work performed and completed. And if, nevertheless, a panic arose, what to do in such a situation?
Panic should be stopped immediately, resolutely, and preferably as soon as possible, when it is superficial, unstable, and has not captured large masses of people.
First of all, it is necessary to distract, at least for a short time, the attention of people from the source of fear or the causative agent of panic. Switch attention from alarmists to a sober-minded person with composure. Commands and orders in such cases should be given in a loud, authoritative voice. Alarmists, screamers and spreaders of rumors should be isolated from the main mass of people. We must immediately involve everyone in the fight against danger. Each to entrust a specific area of work. If the panic nevertheless seized a significant number of people, they need to be divided into smaller groups, each of which will be much easier to deal with.
Remember! Conversations with people, clarification of the situation, competent orders, maintaining order, organization, a personal example of courage in critical situations sometimes has a decisive influence on people's behavior, on their activity and stamina in critical situations.





