What is better - foam or foam for insulation? Penoplex and Expanded polystyrene: properties, myths, use cases. What is better foam or expanded polystyrene? Differences between penoplex and expanded polystyrene
In the construction industry and many other areas of industry, materials such as foam plastic and expanded polystyrene are in demand. What are their specifics?
What is penoplex?
Under penoplex traditionally understood as a material obtained from polystyrene by means of foaming, as well as extrusion with pressing. It is actively used as a heat-insulating material in the field of construction.
The structure of the penoplex is presented large quantity isolated cells that are filled with air. Their size is usually less than a millimeter. The material is characterized by high strength. The foam density is about 29-35 kg / cu. m, the thermal conductivity index is about 0.029-0.039 W / (m * K). The material has low water absorption and vapor permeability.
What is polystyrene foam?
Under polystyrene foam, or foam plastic, refers to a material that, like foam plastic, is made from polystyrene by foaming, but without the use of extrusion with pressing. As a result, significantly larger cells are formed in the structure of the material - a few millimeters in diameter.
Foam plastic can, in principle, be used for the same purposes as foam plastic - as a heat-insulating material. In addition, expanded polystyrene is often used in factory packaging. household appliances- due to the combination of lightness, softness and elasticity.
Expanded polystyrene is much less durable than expanded polystyrene, has a higher thermal conductivity. The density of the foam is about 17-18 kg / cu. m. Its water absorption is noticeably higher than foam, but the vapor permeability of both materials is approximately at the same level.
Comparison
The main difference between penoplex and polystyrene foam is that the first material is produced using extrusion with compression, as a result of which small cells are formed in its structure. Styrofoam is produced without using the noted technology - and therefore its cells are larger. The specificity of the manufacture of materials predetermines the difference in their density, thermal conductivity, water absorption.
Having determined what is the difference between penoplex and polystyrene foam, we will reflect the conclusions in the table.
Table
| Penoplex | Styrofoam |
| What do they have in common? | |
| Both materials are made from foamed polystyrene and are interchangeable in many cases. | |
| Comparable in terms of vapor permeability | |
| What is the difference between them? | |
| Manufactured using extrusion compression | Manufactured without the use of extrusion with pressing |
| The structure of the material is represented by small cells | The structure of the material is represented by significantly larger cells |
| Has a lower thermal conductivity | Has a higher thermal conductivity |
| Has a higher density | Has a lower density |
| Has less water absorption | Has great water absorption |
Penoplex (Extruded polystyrene foam) and expanded polystyrene are building materials that are popular today. Both of them are made from polystyrene by foaming. Both are used as a building thermal insulation material. However, they have different physical and mechanical properties. Before you read the article, I want to express my general opinion about these materials in order to give you the correct intonation when reading. Well ... by correct, I mean exactly the one with which I myself wrote this article. So. I consider these materials to be really good, with exceptional consumer properties, and I myself use them in my practice.
In this regard, I remember a funny incident. A colleague writes to me somehow on ICQ ... I don’t remember exactly what was the matter, but like “Can you tell me this and that?”. I am programming. You have to search, but it's hard to get distracted. I think: "At least I'll finish the phrase ..." And I write him "ShA". He answered in a second - "Shcha - is it like wait, or like went to hell?" Since then, I know that you can read an article by putting any intonation into the written words. And different intonation can change the meaning of what is written exactly to the opposite.
Styrofoam- this is the one Styrofoam, about which so many articles have been written on the site project and many copies have been broken. Penoplex- this is the domestic name for extruded or extruded polystyrene foam. Let's consider these two materials with an armed eye and with prejudice.
Myths and popular claims regarding the materials in question
They say that expanded polystyrene is not combustible, and even more so foam
I DO NOT BELIEVE! I set it on fire many times. Burning for a sweet soul! What am I going to convince you! Take a glass of yogurt. It's probably polystyrene. Light it up and make sure it burns. The foamed one will burn even better because there is more air in the foamed one. Yes indeed, there is a so-called self-extinguishing polystyrene foam. In order for expanded polystyrene to become self-extinguishing, it is impregnated with flame retardants. But, as is usually the case in nature, if it decreases from one place, it must definitely arrive in another. Self-extinguishing polystyrene foams are characterized by increased opacity during combustion and, accordingly, increased toxicity of the smoke itself. But due to flame retardants, this material will not ignite from a spark, and most likely will not ignite from a cigarette butt.
The incombustibility of expanded polystyrenes, both extruded and conventional, is a myth propagated by its sellers. According to official information, which I love to understand so much, polystyrene foam is a combustible building material and has an appropriate class fire safety. To make it clear, I note that according to official information and in my experience, expanded polystyrene burns no worse than wood and smoke, by the way, is about the same in terms of toxicity. But the good thing is that polystyrene foam does not flare up like gasoline.
For reference
If someone thinks that fire safety classes are given only to non-combustible, that is, fire-resistant substances, then he is in a sweet delusion.
Flammability classes building materials:
Building materials are combustible (G) and non-combustible (NG).
Combustible building materials are divided into:
- Slightly combustible G1
- Moderately combustible G2
- Normal flammable G3
- highly flammable G4
Expanded polystyrene belongs to the G3 group, and extruded polystyrene foam to the G4 group. That's it!
Why are we witnessing such different assessments of the combustibility of the material? But because in our country there are several, and completely mutually exclusive, assessments of the combustibility of building materials. According to one, polystyrene foam belongs to the G3 group (normally combustible), and according to others, to the G1 group (low combustible). Whichever is more profitable - we use those.
And what are these methods? I am speaking in a very simplified way. We take the wall. We stick polystyrene foam on it. On the side where there is no polystyrene foam, we begin to heat up. Does Styrofoam burn? Not! It only heats up, melts, flows and stinks very unpleasantly. But it doesn't burn! So it's not combustible!
It is claimed that penoplex and expanded polystyrene have a unique, incomparable low thermal conductivity.
The fact that the thermal conductivity characteristics are good is true, and I have written about this many times. I argued that any good building material can reach the thermal conductivity of Styrofoam, but never exceed it. According to the latest information, it seems that penoplex has these characteristics better, albeit by an insignificant amount. Note that I, as your favorite author Dmitry Belkin, admit my mistakes and (or) can change my mind.
Thus, the thermal conductivity is good, just wonderful, but not unique! Don't mislead people! Besides, what can you compare it to? Thermal insulation materials available in different densities. "Heavy" polystyrene foam may have worse thermal conductivity characteristics than "light" mineral wool.
They say that penoplex and polystyrene foam are almost eternal
And this is also true. However, it needs to be clarified. The fact is that the specificity of the molecular structure of expanded polystyrenes is such that such factors as heat, air, light, radiation, and so on destroy them. Of course, Styrofoam and Penoplex are very resistant substances, but try leaving them on. fresh air under the scorching sun. I assure you, you will very quickly lose your such eternal building material.
Expanded polystyrenes practically do not absorb moisture. 50 freeze-thaw cycles is practically nothing for them. At the same time, expanded polystyrenes are much more breathable than expanded polystyrene. Let's remember this fact. I will definitely return to it when I consider the scope of this or that material.
High-quality polystyrene foam type PSB. In a break - polyhedrons of the same size are firmly connected to each other, in some places the break passes through the living.

Poor quality polystyrene foam type PSB. In a break - rounded balls different size. The fault goes along the contact zone between them.
They say that penoplex and polystyrene foam are used for sound insulation
I do not believe!!! I bet 3 exclamation points, because publications quite respected by me (manufacturers' materials and independent expert publications) also write about the use of these materials as sound insulation. But honestly, I could never be convinced of this. Moreover, I have always been convinced of the opposite! the sound passes through the polystyrene foam completely unhindered, but it does not pass through the mineral wool! penoplex is soundproofing? But no. I will be principled! Until I know for sure, I won't believe it.
Environmental aspect (is polystyrene and products made from it safe)
Polystyrene and products made from it are safe if they do not contain harmful impurities. Above, I wrote that in order to reduce flammability, polystyrene foam insulation is impregnated with fire retardants. This is generally a poison and such treated heaters are dangerous. They must be handled in well-ventilated areas and using protective equipment.
How can you tell if your Styrofoam has been recycled? Ask the seller. Unfortunately, I don't know any other way. I've never sniffed flame retardants and don't know what they smell like. I hope, by the way, that I will never know.
And of course, you should not inhale the smoke from burning plastic. Smoke is always either unhealthy or frankly harmful.
Applications
From the above properties, we can conclude that both expanded polystyrene and foam plastic are very valuable building materials and have a number of invaluable properties. What properties can be mentioned in addition to those indicated?
- the lightness of both materials, in the sense of weight, and the ease of their processing, in the sense of simplicity;
- the possibility of transportation, storage and processing (cutting, laying) without the use of protective equipment.
- compressive strength;
- breathability of expanded polystyrene;
- practical air not penoplex permeability
And here, finally, I come to the most important section, for the sake of which I started the article. Note! For each application, I consider only styrofoam and polystyrene foam. For some application, there may be better options. I admit it, but I consider only these two and no others. I also want, after apologizing in advance, to insert a small watermark into the article and remind you that I always prepare articles for reprint strictly individually, and if right now you are reading this article not on the Belkin Labs dot ru website, but on some other website, then this means that the article was taken and used without my knowledge, that is, stolen. I ask you to read my articles on my website, namely on Belkin Labs dot ru. Of course, in Latin letters.
What material should be used for external wall insulation of a residential building?
What goals do we pursue when we build a house? Absolutely obvious. We need to make the house comfortable and that the construction of this house does not cost us too fatally. That is, the pocket, of course, will suffer, but the main thing is that it does not die from too strong a beating. And how can we achieve this? Obviously, you need to use progressive building materials and not invent anything too complicated and abstruse, since everything reliable and ingenious is always simple. Still very important point which is usually forgotten. To ensure the desired simplicity, we need to use for insulation exactly the material that is intended for this, and not the one that the market economy as a whole and the individual seller in particular advise us.
If you choose between expanded polystyrene and foam for external insulation of the wall of a residential building, it wins polystyrene foam, not penoplex. Why? Yes, because it is more breathable and we can not make vapor barrier with expensive materials with inside Houses. At the same time, we get a breathing wall, which is good, because it gives us additional comfort (at least it should give) and we do not use vapor barrier, which is also good, because we save money and time on this, which, ultimately, is also money.
Both expanded polystyrene and penoplex allow plastering on metal mesh. This makes it possible to save on exterior finish, because until recently plastering was one of the cheapest options for exterior decoration.

Warming of a facade on a brick. One of the most common external insulation methods in Germany (more than 200 million sq.m. are insulated in this way).
For external insulation of the wall of a non-residential building or roof?
You can use both. You can take the one that gets cheaper, because in this case we don’t need anything other than thermal insulation from the material. On the uneven walls or roofs, both materials are difficult to use. This material implies very even bases on which it fits.
For a flat roof?
Both materials will work. Here, the key property is extremely low moisture absorption and low thermal conductivity. I honestly think that flat roof- in general, the idea, to put it mildly, is controversial (I don’t use the word “idiotic” only because of a good upbringing, innate political correctness and tolerance acquired over the years), and the only digestible way to implement this idea is to lay a thick (10 centimeters) layer of one or another polystyrene on a continuous layer of some kind of waterproof glue, and then pour everything with a layer of bitumen 2 centimeters thick, no less with a roofing lining with significant overlaps.
To insulate the ceiling?
Both materials can be used. Penoplex, even better. If you carefully put it, then you can not do any floor coverings in the attic and walk right along the foam. If you use polystyrene foam, then you should not cover it with anything, because moisture can collect under the covering material (or it may not collect - it depends on the specific implementation). It's not fatal, but annoying.
To insulate the wall from the side of the living room?
Either none, because of the danger of shifting the dew point, which I have repeatedly mentioned, or penoplex, since its careful use will reduce the need for additional vapor barrier. Here, the key property of the material is its air not permeability. We do not forget that both materials can be impregnated with flame retardants, which are toxic and "glow" in any condition, not necessarily only in case of fire.
To insulate a balcony?
Definitely penoplex. The reasons are the same as in the previous question.
For floor insulation?
Any. Both of them fit great. The key properties are compressive strength, water resistance, good (in the sense of low) thermal conductivity. I believe that both materials are just perfect for flooring. Cheap and tough! We make a draft floor on the logs. We use simple unedged boards in two layers obliquely. Just don't forget to peel. We attach polystyrene foam or foam plastic to the boards. We pour a screed directly onto the plates (2-3 centimeters). We put anything on the screed. Not a floor, but a feast for the eyes! Just lick your fingers, what a wonderful.

The use of expanded polystyrene for thermal insulation of the floor
To fill a frame wall?
Here I will answer evasively. I would not use the described materials in frame construction. And I will emphasize! Only one property of these materials played a role - their low, again in my experience, sound insulation. Imagine, you built a house, but in the end it turns out that you can hear everything that is done outside. Cars are driving, roosters are crowing, birds are chirping, planes are flying, people are talking loudly at night... And there is no hiding! In horror something! But if there is no other way, then I would use penoplex. Firstly, maybe it doesn’t let noise through as well as polystyrene foam, and secondly, air would play a role not penoplex permeability.
For thermal insulation of foundations and plinths of buildings?
For this purpose, as well as for the base of runways, hockey rinks, ice arenas, sports grounds, grounds for railways on especially heaving soils and for construction highways through the swamps is perfect penoplex. For this purpose, it fits almost perfectly and cannot be replaced by any other material. If someone inherits a swamp, the Grimpinskaya bog, then I will offer to build my family estate on the basis of foam. True, the plates should be about a meter thick, according to my concepts.
For a snack, some information from the section on the market economy
Dear friends, what do you think, have I described the wonderful characteristics of such wonderful materials? Not! left one property for a snack. But in fact, it is this property that is perhaps the main one.
Both polystyrene and foam are phenomenally cheap to manufacture. That is why in any box with a TV, or with a computer, or even with furniture of this polystyrene foam, it is simply za-wa-lis.
This property is especially liked by sellers of building materials, since this material allows you to put into practice the basic principle of business - buy low and sell high!
In preparing the article, I used various materials reference and advertising character. I want to express my special gratitude to the wonderful resource
Foam and Penoplex heaters are often compared, because they are made from the same raw material and are practically “relatives”. But the styrene granules that are needed for their production go through completely different technological processes. In the first case, they are steamed in special molds where they expand and stick together. In the second, styrene balls, after preliminary swelling and sintering, are pulled through the extruder, and then the final foaming takes place.
Differences in the technology of production and molding of plate heaters also determined the difference in their structure. PSB turned out to be more brittle: due to weak bonds between hollow granules, it begins to crumble at the slightest mechanical impact. Penoplex has a homogeneous structure, and air bubbles are evenly distributed throughout the entire plate. And the walls of the granules after forcing through the extruder turn into a single complex system jumpers.
From this follows the main difference between the two types of thermal insulation - mechanical strength. Penoplex plates, depending on the density, hold pressure well of 250-500 and up to 1000 kPa for bending. While for polystyrene, the corresponding characteristics do not exceed 200 for the same positions. The monolithic structure of EPPS provides it with minimal water absorption - 0.2-0.4% versus 2-3% for PSB. That is why high-quality insulation of the facade of the house from the outside, as well as the protection of other external structures, requires the use of Penoplex.
As for performance indicators, there are special differences in technical descriptions no. Both materials do a good job of insulating, since their main characteristics are largely determined by their low density. True, among the foams there are no plates with a coefficient R \u003d 0.03 W / m K - their thermal conductivity is in the range of 0.038-0.05. And for EPPS, such a figure is quite real with a weight of 28-33 kg / m3. That is, objectively - extruded sheets are warmer.
AT basic version Penoplex and ordinary PSB have different group flammability: G4 and G3, respectively. However, the fire hazard of these heaters forced manufacturers to use special fire retardants in their manufacture, thanks to which polystyrenes gained the ability to self-extinguish. However, high smoke generation, as well as a critical amount of toxins released into the air during combustion, for both types of thermal insulation remains weak side.

And if we take for comparison the cost of both types of styrenes from our review, it turns out that the foam plastic wins only in this parameter. However, the overall score is still not in his favor. And if you decide what is better to use for home insulation, without being too interested in the price of the issue, the answer will be unambiguous: Penoplex plates. True, here you will also have to spend money on a vapor barrier, since EPPS does not “breathe” at all compared to foam plastic, which can lead to condensation on the main surface. Low air permeability, according to experts, is a common problem with polymer thermal insulation, although the difference between the characteristics of Penoplex and PSB is especially noticeable: 0.007 mg / m h Pa for the first and up to 0.2 for the second.
These two materials have other common features:
- Light weight.
- Ease of thermal insulation in processing.
- Low temperature resistance.
- Fear sunlight, as well as solvents.

In what cases is Penoplex better?
If the protected structure will experience mechanical stress (the weight of the finish on the walls or people walking on the surface), it is better to buy Penoplex. It's not that it is warmer - just its high rigidity in this case is the most in demand. But the lack of pressure, say, on the walls will force you to choose a more affordable foam.
Also, extruded polystyrene foam is out of competition when it is necessary to simultaneously perform high-quality thermal and waterproofing of objects. That is, in the case of the basement of a house or damp basement low water absorption of Penoplex will only play into the hands. In frame buildings, EPS is also preferred if it is necessary to ensure enough level soundproofing. The reason is that ordinary foam not only does not delay noise, but also amplifies them.
The decision in favor of Penoplex is also made in case of insulation of too cramped rooms from the inside, since its effective layer is about 25% thinner than when using foam. That is why for loggias, where every centimeter of area counts, it is better to choose extruded polystyrene foam.

Reviews
 “To the disadvantages of polystyrene, I would add the fundamental impossibility of working with thin sheets. Even the standard 50 mm are too flimsy, and sometimes it’s scary to mount them on a vertical. With 100 mm, it is already easier and more convenient to manage, and in the case of Penoplex, this thickness may not be needed at all if the insulation is not too serious.
“To the disadvantages of polystyrene, I would add the fundamental impossibility of working with thin sheets. Even the standard 50 mm are too flimsy, and sometimes it’s scary to mount them on a vertical. With 100 mm, it is already easier and more convenient to manage, and in the case of Penoplex, this thickness may not be needed at all if the insulation is not too serious.
Oleg Danilov, Kursk.
 “I would not recommend completely fixing the EPPS outside the residential building at all, otherwise moisture will condense in the wall itself. At my dacha, I glued Penoplex thermal insulation only on the base, so that there would be no problems from soil movements and constant dampness. And the rest of the facade was simply covered with foam. For the money, it was the best option for me.”
“I would not recommend completely fixing the EPPS outside the residential building at all, otherwise moisture will condense in the wall itself. At my dacha, I glued Penoplex thermal insulation only on the base, so that there would be no problems from soil movements and constant dampness. And the rest of the facade was simply covered with foam. For the money, it was the best option for me.”
Roman, Perm.
 “At one time, the insulation of the walls from the outside did not give the desired effect, since no one performed calculations / calculations: they just threw 100 mm mineral wool, sewed it up with siding and calmed down on that. From hopelessness, I had to warm up from the inside. After reading the reviews, I settled on Penoplex in order to somehow save usable area. The third year everything is fine - no dampness or problems with the walls. As I understand it, my EPPS now works as a vapor barrier itself.
“At one time, the insulation of the walls from the outside did not give the desired effect, since no one performed calculations / calculations: they just threw 100 mm mineral wool, sewed it up with siding and calmed down on that. From hopelessness, I had to warm up from the inside. After reading the reviews, I settled on Penoplex in order to somehow save usable area. The third year everything is fine - no dampness or problems with the walls. As I understand it, my EPPS now works as a vapor barrier itself.
Leonid, Moscow region.
 “There are no questions: Penoplex is really more expensive than polystyrene, but do not forget that due to its low thermal conductivity, it will take less in thickness (and in cubic capacity). That is, the difference will not be so significant. And how many cans of foam do you need to pour in order to collect a layer of eternally crumbling PSB? With smooth or L-shaped EPS edges, this question does not arise at all.
“There are no questions: Penoplex is really more expensive than polystyrene, but do not forget that due to its low thermal conductivity, it will take less in thickness (and in cubic capacity). That is, the difference will not be so significant. And how many cans of foam do you need to pour in order to collect a layer of eternally crumbling PSB? With smooth or L-shaped EPS edges, this question does not arise at all.
Kirill Bannikov, Rostov-on-Don.
 “Choosing Penoplex for facades is an option from the category of“ money has nowhere to go. It is good to use it for its intended purpose: under the screed (concrete or floating), underground or somewhere closer to the foundation. In all other cases, it is better to stop at the foam.
“Choosing Penoplex for facades is an option from the category of“ money has nowhere to go. It is good to use it for its intended purpose: under the screed (concrete or floating), underground or somewhere closer to the foundation. In all other cases, it is better to stop at the foam.
Mikhail, St. Petersburg.
 “My father-in-law’s house has been insulated from the outside with the most ordinary foam for 7 years: nothing gets damp, moldy or falls off. They did everything together with him: aerated concrete walls, PSB-S25-f on top. Judging by the reviews, it would have turned out much worse with Penoplex - it is very dense and completely impervious to air.
“My father-in-law’s house has been insulated from the outside with the most ordinary foam for 7 years: nothing gets damp, moldy or falls off. They did everything together with him: aerated concrete walls, PSB-S25-f on top. Judging by the reviews, it would have turned out much worse with Penoplex - it is very dense and completely impervious to air.
Nikita, Moscow.
Penoplex and polystyrene actually differ slightly from each other, although some features of EPPS make it necessary to choose it for carrying out certain types works: insulation of structures experiencing mechanical loads, in the ground or in conditions high humidity. In all other cases, only the price decides everything - even the desired thermal conductivity can be selected by operating on the density and thickness of the sheets. So if there are no special requirements for surface insulation, it is most reasonable to stop at ordinary polystyrene, and it is better to purchase Penoplex for serious work.
In the conditions of an excess of offers of various types of thermal insulation, choose suitable option material for insulation is quite difficult. Ravaterm, polyspen, styrex, penofol, penoplex and technoplex are just some of the foam materials used for insulation of external and interior spaces. There is not much truthful information about what a modern styrene polymer-based insulation is, so many experts prefer to collect practical reviews, which is better, technoplex or penoplex. This is a difficult and time-consuming path, therefore, for starters, it is better to compare the characteristics and conclude how foam and technoplex differ, and what is the difference between them.
What is expanded polystyrene
Penoplex is produced by the company of the same name according to its original technology and is a pressure foam, extruded polystyrene. Approximately the same data can be obtained from open sources about technoplex insulation, manufactured by TechnoNIKOL. details technological process TechnoNIKOL and Penoplex are not reported, but according to fragmentary data, the following conclusion can be drawn:
- Granular raw materials - high-purity polystyrene are mixed with a gasifier, heated to a high temperature and forced through calibrated micro-holes;
- When passing a nozzle with several hundred micro-holes, the main flow of polystyrene is broken into microfilaments, the polymer molecules are stretched, form bonds between themselves and are simultaneously strengthened by pressure;
- At the moment of exit from the spinnerets, polypropylene foams in a dosed manner and turns into a porous material from millions of tiny frozen bubbles.

The general picture of the production of technoplex and foam is the same, but there are slight differences in the composition of materials and strength characteristics. According to TechnoNIKOL, the technoplex includes not a large number of amorphous carbon or graphite, so that the rolling rolls can better form a sheet of the required thickness.

Note! In the cheapest and simple technologies In production, light freons mixed with carbon dioxide are used as pore-forming gases. Modern methods production involves the use of powder and liquid gas-forming agents.

Compare technoplex and penoplex
In fact, the composition of technoplex and penoplex is much more complicated, it includes stabilizers, fire retardants, antioxidants and substances that slow down secondary polymerization. The difference may be in temperature, pressure and the use of a blowing agent.
What is the difference between expanded polystyrenes
What is the difference? Powder or liquid blowing agent can be better mixed and distributed throughout the volume of polystyrene granules, therefore, such insulation materials have more stable thermal insulation characteristics.
But this is not the only reason why the modern production technoplex and penoplex refuse to use freon:
- In the sealed cells of a new, not yet used material, freon gas remains for some time, which is formally considered safe, but in practice it is better to get rid of it, since it often leads to problems with the lungs, especially in children;
- Over time, the gas is displaced by air and water vapor. If not the purest raw materials with styrene residues were used for the production of expanded polystyrene, then gradually part of the contents of the technoplex cells will be squeezed out into the environment.
For "technical" grades of XPS, for example, penofol, such processes are not of particular importance. According to the manufacturer, it is better to use penofol for insulating foundations, basement parts of a building, for use in the construction of highways, therefore, a mixture of freon and carbon dioxide is used for its production. The contact compressive strength of penofol is approximately equal to the strength characteristic of technoplex.


The use of an extrusion process makes it possible to obtain a linearly oriented structure and very dense elongated pores. As a result, extruded polystyrene foam resists water and water vapor much better, has higher bending and compressive strength. Therefore, all extruded polymer foams used for insulation - penofol, technoplex, penoplex, have the best strength characteristics, how they differ from polystyrene foam, or in another way - polystyrene foam.
The main characteristics of technoplex and penoplex
Most reliable way to determine which of the heaters is better - to compare their main characteristics. The most important parameter is thermal conductivity, for foam plastic the coefficient is 0.029-0.030 W / m∙K, for technoplex - 0.030 W / m∙K. The difference is negligible, so both materials retain heat equally well.
The second characteristic concerns durability. According to reviews, penoplex is better cut and less deformed during installation. The bending strength of technoplex is almost two times lower than that of foam plastic, but its manufacturer initially states that its products are better used for internal thermal insulation, and foam plastic is better able to withstand pressure from heaving of the soil and the mass of the concrete foundation.
The third characteristic concerns water absorption. In this part, foam plastic resists water better than TechnoNIKOL products, almost twice - 0.1% versus 0.2%. But both indicators are much better than foam -0.5% and mineral wool- almost 10%. In addition, extruded polystyrene foams practically do not change their characteristics even after thousands of freeze-thaw cycles.
The last factor is the price of the insulation, in this case the technoplex looks better, with the cost per square 10-15% lower than the competitor.

Comparison of expanded polystyrene with other types of insulation
The main competitor of expanded polystyrenes are mineral felts and fiber mats. When asked which is better, penoplex or mineral wool, it can be argued that for private one-two-story buildings it is better to use penoplex as the most effective heat insulator. For exterior finish high-rise buildings it is better to use mineral wool, for one reason - absolute fire safety. Expanded polystyrene, even with fire retardant additives, can release a large amount of toxic gases during high-temperature heating, so for high-rise buildings it is better to avoid undue risk.

On the other hand, it is better not to use mineral wool for damp basements and semi-basements, since the fiber instantly absorbs water. In addition, in the production of certain grades of mineral or basalt wool phenol-formaldehyde resin is used, which is highly toxic and carcinogenic. Such brands are better, in general, not to be used for insulation of residential premises.
One of the competitors for the technoplex is isolon, a material based on foamed and modified polyethylene. Izolon, of all the listed materials, is best suited for insulating walls and ceilings inside residential premises. The coefficient of thermal conductivity and water absorption of PPE grade polyethylene foam is practically equal to the similar characteristics of the technoplex. The PPE layer withstands prolonged heating up to 80 ° C for 24 hours. Isolon PPE has good sound and noise insulation, and the main advantage is that the environmental friendliness and safety of such thermal insulation is better than that of the most expensive EPPS brands.
Polyethylene foam, even with strong heating, does not emit toxic decomposition products. The main drawback of the material is its excessive flexibility and softness. The isolon laid on the wall requires additional finishing with hard boards, for example, drywall or MDF. It is impossible to put a layer of plaster on isolon or stick wallpaper, so it is better to use it in tandem with external insulation made of XPS.
Conclusion
An attempt to compare the characteristics of which insulation is better, foam or technoplex, can only be accepted as a preliminary assessment of materials. Most of the foamed polystyrenes have very similar characteristics, so in order to get the full picture, you need to take into account the feedback on the practical use of different brands of insulation.
Innovations in modern construction technologies include the use of insulation to save other building materials and energy. There are enough varieties of insulating materials on the market, and the most popular are foam or polystyrene foam, which are made from artificial components. Penoplex is one of the variable transformations of foam plastic, and their parameters are similar in many respects, but they differ in some ways. Therefore, when choosing, polystyrene or foam plastic is better for warming a house, it is recommended that you familiarize yourself with their parameters and performance characteristics in detail.
General information
It is possible to compare which of these products works best for insulation only after their performance characteristics have been studied. What does the marking of material PSB or PSB-S mean:
- PS - expanded polystyrene;
- B - non-pressed manufacturing;
- C - self-extinguishing non-combustible material;
- The numbers in the marking mean the density and resistance to mechanical stress.
| Characteristics | PSB-S-15 | PSB-S-25 | PSB-S-35 | PSB-S-50 |
| Density, kg/m3 | ≤ 15 | 15,1-25 | 25,1-35 | ≥ 35,1 |
| Compressive strength at deformation 10%, ≥ MPa | 0,041 | 0,032 | 0,15 | 0,15 |
| Bending strength, MPa | 0,065 | 0,17 | 0,21 | 0,32 |
| Thermal conductivity at 25 0 C +/- 5 0 C, ≤ W (m K) | 0,042 | 0,042 | 0,032 | 0,032 |
| Burning time, ≤ seconds | 4,01 | 4,01 | 4,01 | 4,01 |
| Humidity, ≤ | 12,15% | 12,15% | 12,15% | 12,15% |
| Moisture absorption per day, ≤ | 4,15% | 3,1% | 2,2% | 2,3% |

Styrofoam is made from artificial substances, causing them to react to the addition of gaseous fillers and blowing agents. The gas bubbles formed as a result of this reaction increase during the production process, turning into foam balls. light weight and high thermal conductivity. These balls are then pressed or fused into slabs of various densities and used in construction and renovation. Yes, warming frame house Penoplex is considered one of the most effective and cheapest methods of insulation.
Penoplex is a variant of foam plastic with much the best performance. Penoplex is also called extruded polystyrene foam, as it is made by melting or extrusion in special equipment - an extruder (thermal furnace with high pressure). In the extruder, the balls are fused into a molded blank, which is a cooled and hard foam, similar to the assembly building after hardening. 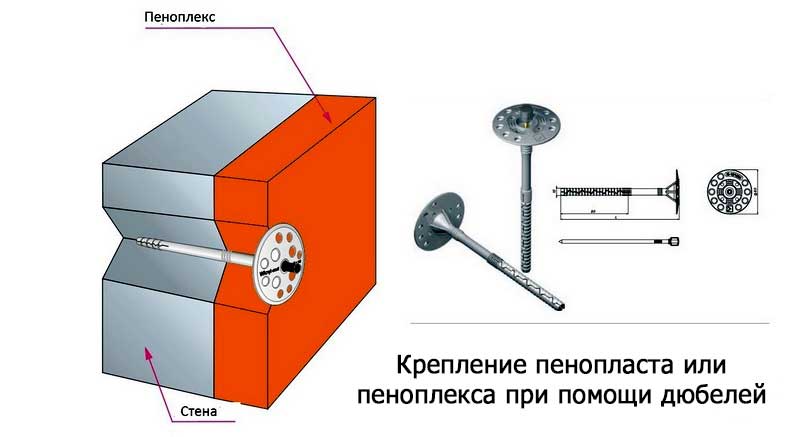
A clear negative point in the characteristics of the foam is high flammability, since it does not burn, but supports combustion.
Features of foam insulation
Important parameters:
- Thermal conductivity of the material: 0.04 W/m;
- Operating temperatures: -40/+70 0 С;
- Styrofoam density in compression: 7-9 t/m 2 ;
- Moisture absorption: 2.1%;
- Service time: up to 30 years;
- Flammability: G4;
- Practical board thickness in use: ≥ 10 cm.
Other characteristics are shown in the tables above. 
Features and characteristics of foam insulation
Penoplex (extruded polystyrene foam) and polystyrene differ in many respects, and above all, in the method of manufacture. Penoplex is a more dense and solid thermal insulation, the surface of the plates covered with extruded polystyrene foam remains strong and warm in any conditions, even when the floor is insulated, which cannot be said about the foam layer of thermal insulation. When insulating the EPPS floor, you can not even assemble the frame for its fastening, but lay the slabs directly on the rough concrete or wooden floor. The top decorative laminate flooring (when laying linoleum or carpet, chipboard or OSB is first laid) will not allow the weight of residents or furniture to push through the surface of the expanded polystyrene. In addition, the increased ability to retain heat is reflected in the quantitative indicator - polystyrene foam will need much less than other types of thermal insulation to get not only a warm, but also a durable floor.
As an example, we can give, in which foam plates 8-12 cm thick were used, while 3-4 cm thick was enough to insulate the EPPS floor. This will make it warmer. Such high rates allow the use of extruded polystyrene foam even in the Far North. This indicates quite accurately that better styrofoam or penoplex.

Of the negative aspects during the operation of expanded polystyrene, high vapor permeability and cost can be noted. But the price justifies the quality that you get when using XPS, and for a good layer of thermal insulation, which will help save on energy in heating season, and on the use of other materials and methods of building insulation, you can slightly increase the one-time costs for interior decoration.
Main settings:
- Thermal conductivity: 0.029-0.031 W / m;
- Operating temperatures: -50/+75 0 С;
- Compressive density: - 20000-22000 kg / m 2;
- Moisture absorption: 0.5%;
- Flammability class G3;
- Service time: ≥ 50 years;
- Practical board thickness in use: ≥ 3 cm.

Comparison of Styrofoam and Styrofoam
As you can see, the question of which foam or foam is better remains on the conscience of the developer, since the performance characteristics of each of the presented heaters should be used to the maximum, but this often requires different initial conditions. Penoplex clearly wins at first glance, except for the cost, since the main indicators that are of interest to the owners of private housing construction are the coefficient of thermal conductivity, which is almost twice as good for EPPS.
In addition, penoplex (aka extruded polystyrene foam) retains moisture almost four times stronger, preventing it from passing inside the material, which means that water will almost never pass through the foam layer. The material almost does not burn, and compared to polystyrene, this is its clear advantage. Although the foam is usually protected from fire by plastering. 
The next parameter of expanded polystyrene is density ( physical strength), which is 2.5 times higher than that of polystyrene. In practice, this is expressed in the fact that when insulating the floor, EPS can not even be protected with denser sheets, but immediately lay a finishing layer on it. floor covering. Styrofoam will burst under similar loads immediately. Therefore, there is no question of insulating the floor with polystyrene foam - only the walls and the ceiling are insulated with it, and it is recommended to insulate only the outer walls, since internal surfaces can be easily damaged by furniture or just an accidental blow.
But if it is necessary to insulate these particular surfaces without insulating the floor, foam plastic is, of course, preferable precisely because of its low cost and ease of use. For the insulation of external walls, the thickness of the heat insulator layer does not play any role, as does the degree of moisture absorption - after all, the foam layer will still be closed, for example, by siding or clapboard, tiles or facing bricks.





