Organization of technical measures to ensure fire safety. Organizational and technical fire prevention measures
Fire safety- the state of the object, in which the possibility of a fire is excluded, and in case of its occurrence, it is necessary to take measures to eliminate the phenomenon of negative dangerous factors on people, buildings and material values.
Fire mode is a complex established norms and rules of human behavior, performance of work and operation of the facility, aimed at ensuring fire safety
Fire safety at the facility is established by measures:
Organizational
development of rules, briefings on fire safety
organization of instruction, training of workers and employees
monitoring compliance with the established fire prevention regime by all employees
organization of volunteer fire brigades
organization of daily fire safety checks after work
development and approval of an evacuation plan and a procedure for alerting people in case of a fire
organization of compliance with reliable fire supervision of facilities
organization of inspection of fire-technical equipment.
Technical
compliance with fire regulations, requirements and rules in the construction of buildings, structures and warehouses
sub-e in good condition heating systems, ventilation, electrical equipment
automatic device fire alarm, system automatic fire extinguishing, fire water supply
prohibition of the use of equipment, fixtures and tools that meet the requirements fire safety.
proper organization of labor in the workplace with the use of fire hazardous tools and devices
fire protection
In order to prevent the occurrence of fires of their spread and to fight them, all workers undergo briefings and training in a special program.
There are 4 types of tutorials:
1. Opening- all workers pass before admission to work. It is carried out by the person responsible for fire safety at the enterprise. During its implementation, workers are introduced to the basic requirements of the laws of Ukraine on fire safety, with the fire safety rules established at the enterprises and places where it is forbidden to use fire or smoke.
2. Primary- newly hired people pass it directly at the workplace or when they are transferred to another workshop or to another position. Workers are introduced to the fire safety of the workshop, site and fire safety rules. They show emergency exits, fire extinguishers and fire extinguishing equipment, check the practical actions of the worker in case of fire.
3. Repeated- carried out 2 times a year directly in the workshop, set by the heads of the enterprise at the place of work of the employee.
4. unscheduled– when changing fire safety, technological process, the use of new fire hazardous materials, spontaneous combustion, etc.
Measures applied for fire protection grouped into 2 groups:
1. Passive- provided for in the design of buildings and structures.
fire breaks between buildings to prevent the spread of fire. The magnitude of these gaps depends on the fire resistance of the building, number of storeys and categories. fire hazard in production.
zoning of territories, i.e. the location of fire hazardous in-in and warehouses on the windward side;
fire-transforming - devices that prevent the spread of flame;
smoke protection - reduces smoke.
2 Active– fire detection and elimination of the source of ignition.
use of automatic fire alarms;
electrical fire alarm (detectors)
Fire detectors are: manual and automatic.
Fire automatic detectors
light - act on a bright flash
combined
thermal - they work when t rises to 70 in the surroundings. environment
Application automatic installations. They are: water action and gas
Stationary cars. installations - a network of pipelines with sprinklers, accommodating. on the protected object.
Machine. installations are divided into:
sprinkler - localize small fires
drencher - irrigate all fires
internal fire water pipelines with fire hoses
primary funds
On the large enterprises engineering and technical facilities should be provided. Every worker who discovers a fire or a small fire
must report to the fire department.
start extinguishing the fire.
call the administration to the scene of the fire.
The administrator must:
check the fact of the fire service;
notify the manager
organizing the evacuation of people;
org-t stop pr-dstva;
turn off electricity;
activate the smoke exhaust system;
call emergency services;
power grid representative;
upon arrival of the fire department, provide all the information about the source of ignition, the presence in the room fire hazardous.
(Graduate work)
n1.doc
28. Organizational and technical fire fighting measures.Fire safety- the state of the facility, in which the possibility of a fire is excluded, and in the event of its occurrence, it is necessary to take measures to eliminate the phenomenon of negative hazardous factors on people, structures and material values.
Fire mode- this is a set of established norms and rules for the behavior of people, the performance of work and the operation of the facility, aimed at ensuring fire safety
Fire safety at the facility is established by measures:
Organizational
development of rules, briefings on fire safety
organization of instruction, training of workers and employees
monitoring compliance with the established fire prevention regime by all employees
organization of volunteer fire brigades
organization of daily fire safety checks after work
development and approval of an evacuation plan and a procedure for alerting people in case of a fire
organization of compliance with reliable fire supervision of facilities
organization of inspection of fire-technical equipment.
Technical
compliance with fire regulations, requirements and rules in the construction of buildings, structures and warehouses
under-e in good condition heating, ventilation, electrical equipment
automatic fire alarm device, automatic fire extinguishing system, fire water supply
prohibition of the use of equipment, fixtures and tools that comply with fire safety requirements.
proper organization of labor in the workplace with the use of fire hazardous tools and devices
fire protection
There are 4 types of tutorials:
1. Opening- all workers pass before admission to work. It is carried out by the person responsible for fire safety at the enterprise. During its implementation, workers are introduced to the basic requirements of the laws of Ukraine on fire safety, with the fire safety rules established at the enterprises and places where it is forbidden to use fire or smoke.
2. Primary- newly hired people pass it directly at the workplace or when they are transferred to another workshop or to another position. Workers are introduced to the fire safety of the workshop, site and fire safety rules. They show emergency exits, fire extinguishers and fire extinguishing equipment, check the practical actions of the worker in case of fire.
3. Repeated- carried out 2 times a year directly in the workshop, set by the heads of the enterprise at the place of work of the employee.
4. unscheduled- when changing fire safety, the technological process, the use of new fire hazardous materials, spontaneous combustion, etc.
The measures applied for fire protection are grouped into 2 groups:
1. Passive- provided for in the design of buildings and structures.
fire breaks between buildings to prevent the spread of fire. The magnitude of these gaps depends on the fire resistance of the building, the number of storeys and the categories of fire hazard in production.
zoning of territories, i.e. the location of fire hazardous in-in and warehouses on the windward side;
fire-transforming - devices that prevent the spread of flame;
smoke protection - reduces smoke.
use of automatic fire alarms;
electrical fire alarm (detectors)
Fire automatic detectors
thermal - they work when t rises to 70 in the surroundings. environment
smoke
light - act on a bright flash
combined
Stationary cars. installations - a network of pipelines with sprinklers, accommodating. on the protected object.
Machine. installations are divided into:
sprinkler - localize small fires
drencher - irrigate all fires
internal fire water pipelines with fire hoses
primary funds
must report to the fire department.
start extinguishing the fire.
call the administration to the scene of the fire.
check the fact of the fire service;
notify the manager
organizing the evacuation of people;
org-t stop pr-dstva;
turn off electricity;
activate the smoke exhaust system;
call emergency services;
power grid representative;
upon arrival of the fire service, provide all information about the source of ignition, the presence of fire hazardous substances in the room.
The conditions for the development of a fire in structures are mainly determined by the degree of their fire resistance. fire resistance- the ability of material designs to delay the spread of fire in hours.
fire resistance building structures are characterized by their fire resistance limit, which is understood as the time in hours, after which they lose their bearing or enclosing capacity, that is, they cannot perform their normal operational functions.
Loss bearing capacity means collapse of the structure.
Loss protecting ability- heating the structure in case of fire to temperatures, the excess of which can cause spontaneous ignition of substances located in adjacent rooms, or the formation of through cracks or holes in the structure, through which combustion products can penetrate into neighboring rooms.
The fire resistance limits of structures are established empirically. To do this, a life-size sample of the structure is placed in a special furnace and at the same time it is subjected to the required load.
The time from the start of the test to the appearance of one of the signs of loss of bearing or enclosing capacity is considered the fire resistance limit. The maximum heating of a structure is an increase in temperature on an unheated surface by an average of more than 140 o C or at any point on the surface by more than 180 o C compared to the temperature of the structure before testing, or more than 220 o C, regardless of the temperature of the structure up to tests.
least limit fire resistance have unprotected metal constructions, a greatest- reinforced concrete.
Required degree of fire resistance of industrial buildings industrial enterprises depends on the fire hazard of the industries located in them, the floor area between the fire walls and the number of storeys of the building. The required degree of fire resistance must correspond to the actual degree of fire resistance, which is determined according to the tables of SNiP P-2-80, containing information on the fire resistance limits of building structures and the limits of fire propagation through them.
For example, the main parts of buildings of I and II degrees of fire resistance are fireproof and differ only in the fire resistance limits of building structures. In buildings of the I degree, the spread of fire along the main building structures is not allowed at all, and in buildings of the II degree, the maximum limit of the spread of fire, which is 40 cm, is allowed only for internal bearing walls(partitions). The main parts of buildings of the V degree are combustible. The limits of fire resistance and the spread of fire for them are not standardized.
Degree of fire resistance The ability of a building as a whole to resist destruction in a fire is called. Structures according to the degree of fire resistance are divided into 8 degrees (I, II, III, IIIa, IIIB, IY, IYa, Y). The fire resistance of structures is characterized by the fire resistance limit, which is understood as the time in hours, after which the structure loses its load-bearing or enclosing capacity.
Classification of structures by fire resistance:
I degree - all structural elements are fireproof with a high fire resistance limit (1.5 - 3 hours).
II degree - all structural elements are fireproof with fire resistance limits (0.5 - 2.5 hours).
III degree - the main load-bearing structures are fireproof, non-bearing - hardly combustible with a fire resistance limit (0.25 - 2 hours).
IY degree - all structures - difficult to combust with fire resistance limits (0.25 - 0.5 hours).
Y - degree - all structures - combustible.
30. Fire extinguishing agents.
A fire-extinguishing agent that, when it enters the seat of a fire, reduces the burning rate or stops burning completely. There are: gaseous (water vapor), liquid (water, foam), solid (sand, earth, powders), asbestos or tarpaulin covers.
According to the principle of action are divided:
cooling (water) - the better it is hot, the faster the evaporation
insulating (powder, foam, blankets) - isolating the combustion zone from oxygen access
dilution of combustible liquids or reduction of oxygen content (steam, water, carbon dioxide)
flame retardation (powders)
Water – most common fire extinguishing agent. Once in the combustion zone, the water heats up and evaporates, absorbing a large amount of heat. When water evaporates, steam is formed, which makes it difficult for air to reach the combustion source. Water cannot extinguish the combustion of such substances and materials as alkali metals, calcium carbide, aluminum powder, etc., when interacting with water, a large amount of heat, combustible gases, etc. are released. Water is a good conductor electric current therefore, using it to extinguish fires in electrical installations that are energized can lead to electric shock. Water in the form of compact jets must not be used to extinguish fires of flammable liquids. Water cannot be used to extinguish varnishes, gasoline (because they are lighter), live electrical equipment (water is a good conductor), and cannot be used to extinguish valuable items.
Advantages water: availability, low cost, high heat capacity, chemical neutrality.
Water Disadvantages: low wettability, therefore, surfactants are added - soap, powders.
Aqueous solutions of salts are classified as liquid fire extinguishers. Solutions of sodium bicarbonate, calcium and ammonium chlorides, etc. are used. Salts, falling out of an aqueous solution, form insulating films on the surface of the burning matter, which take away heat. During the decomposition of salts, non-combustible gases are released.
Foam - for extinguishing all solid combustible substances for which extinguishing with water is also applicable. Methods for obtaining foam:
chemical - a combination of alkali and acid, it is impossible to extinguish electrical equipment with this
air-mechanical - foam generators: mixing special powders with water and dispersing the jet on special grids.
chemical foam obtained by the interaction of alkaline and acidic solutions in the presence of foaming agents. This produces gas. Gas bubbles are enveloped in water with a foaming agent, resulting in a stable foam that can remain on the surface of the liquid for a long time. In-va, which are necessary for the production of carbon dioxide, are used either in the form of aqueous solutions or dry foam powders. The use of chemical foam in practice is declining, it is increasingly being replaced by air-mechanical foam.
Air-mechanical foam - a mixture of air - 90%, water - 9.7 and foaming agent - 0.3%. The characteristic of the foam is the multiplicity - the ratio of the volume of the resulting foam to the volume initial in-in. Foam of normal expansion (20%) is obtained using air-foam barrels. Water under pressure, pre-mixed with a foaming agent, enters a special device that provides air leakage. Recently, high-expansion (200) foam has been used in the practice of extinguishing fires, which is much more voluminous and lasts longer. It is obtained in special generators, where air is not sucked in, but forced under some pressure.
water vapor used to extinguish fires in rooms up to 500 m 3 and small fires in open areas and installations. The steam moistens the burning objects and reduces the oxygen concentration. The fire extinguishing concentration of water vapor in air is approximately 35% by volume.
Extinguishing with carbon dioxide - is carried out by releasing carbon dioxide from a container with high pressure.
Fire extinguishing powders - finely ground mineral salts with various additives that prevent their caking and clumping. They have a good fire-extinguishing ability, several times greater than the ability of flame retardants such as halocarbons, as well as versatility of application, as they suppress the combustion of materials that cannot be extinguished with water and other means.
In confined spaces for extinguishing use and inert gases
. As reactors of inert gases - a jet from a jet engine.
Fire extinguisher
- a portable or mobile device for extinguishing fires, after putting it into action, a jet of extinguishing agent is released. Fire extinguishers come in weights from 2 kg to 100 kg.
extinguishing agent: chemical or air-chemical foam, liquefied carbon dioxide, powders.
Kinds:
liquid (water or water with additives);
chemical foam (acid and alkali) - when it is activated, a chemical neutralization reaction
carbon dioxide - a reusable device, filled with liquefied acid. Jet length - 2-3 m, duration - 30-40 sec.
powder - the container is filled with powder, inside there is 1 more container - air. Duration - 30 sec.
Successful firefighting depends on early detection and prompt response. measures taken to eliminate the source of fire.
31. fire fighting equipment to protect objects.
Fire trucks: intended for the production of fire extinguishing agents. There are mobile and stationary. Fire trucks: extinguishing fires at large distances from the location, the most common is water. Motor pumps.
fire truck- a vehicle on a wheeled chassis equipped with technical means and units for storing and supplying fire extinguishing agents, performing special work on fire and intended for delivery to the fire site of personnel, firefighters technical equipment and equipment, conducting combat operations to extinguish fires in accordance with its functional purpose.
fire trucks are motorized vehicles with equipment intended for use in firefighting.
Fire engines are: cars, planes, helicopters, trains, ships, motor pumps.
Fire trucks are designed for:
delivery to the required area of combat crews, fire-extinguishing media in the centers of combustion;
submission to required quantity fire-extinguishing agents in the centers of combustion;
performing a number of special works before and during fire extinguishing.
Main are used to deliver combat crew, fire equipment and a supply of fire extinguishing agents to the fire site, as well as to supply them to the fires. They are divided into two groups: fire engines for extinguishing fires in cities and settlements called fire trucks general use, and fire trucks for extinguishing fires at enterprises, which are called fire trucks for the intended use. Special- designed to perform special work when extinguishing fires. These include fire ladders, vehicles of technical service, gas and smoke protection service and others. Auxiliary provide refueling, transportation of goods, repair of fire equipment.
The primary tactical unit in the fire department is a tank truck (ATs) or pump-hose fire truck (ANR). These fire trucks are technical basis armament of fire departments.
largest specific gravity in the production of fire trucks occupy tank trucks (over 80%), which, due to their versatility, are widely used in divisions fire brigade all branches of economic facilities, and in fire fighting units of civil defense units and formations.
Truck pumps differ from tank trucks in the absence of a water tank, an expanded set of fire fighting equipment, a large number places for combat crew and increased capacity of the foam tank. Autopumps, as a rule, are used in conjunction with tankers, however, they can be successfully used independently when extinguishing fires in areas with a well-developed water supply network.
The main fire vehicles of the target application. These include:
foam extinguishing fire engines are used when fires can be extinguished with air-mechanical foam;
powder extinguishing fire trucks are designed to extinguish fires at industrial facilities of the chemical, oil refining, nuclear energy industries, as well as in structures and on aircraft;
fire engines of gas-water extinguishing for extinguishing fires of gas-oil fountains;
gas extinguishing fire trucks for extinguishing fires of electrical equipment under voltage, valuables in museums and archives, fires in hard-to-reach places;
combined extinguishing fire trucks. The layout can be different (powder, foam, water-foam);
fire aerodrome vehicles for rescuing passengers and crew of an aircraft, extinguishing a possible fire and carrying out work to eliminate the consequences of an accident;
firefighters pumping stations for supplying water through the main fire hoses directly to mobile fire monitors or to fire trucks, followed by supplying water to a fire;
fire planes and helicopters for air patrolling and delivery of people and means to extinguish fires from the air to the fire site.
fire ships to provide emergency assistance to watercraft and coastal facilities in case of fire. They deliver combat crews, fire equipment and weapons, fire extinguishing agents and supply water to the fire site both through hose lines and powerful fire monitors. They can also extinguish fires of petroleum products;
fire trains - for extinguishing fires at facilities and in rolling stock of railway transport.
fire escapes for delivery of combat crew, evacuation of people from burning buildings and provide protection from strangers pumping unit supply of fire extinguishing agents to the source of combustion by hand or fire monitors, in addition, they can be used to lift loads weighing up to 300 kg, illuminate the fire site with spotlights mounted on the top of the stairs;
fire lifts, as well as ladders, are used to carry out work related to extinguishing fires and rescuing people at height.
fire trucks of the gas and smoke protection service - for delivery to the fire site of the combat crew, smoke removal equipment, personal protection respiratory organs, special tools and are used for reconnaissance in smoky rooms, helping people and creating conditions that facilitate work in a smoky room. The technical equipment of the gas and smoke protection service also includes smoke exhaust vehicles, which are designed to deliver combat crew, technical equipment to the fire site and serve to pump smoke, toxic gases from premises, supply fresh air inside the premises and providing insulating gas masks with regenerative cartridges and oxygen cylinders at the fire site;
fire hose vehicles for mechanized laying and cleaning of main hose lines, as well as for extinguishing fires with water or air-foam jets using stationary or mobile fire monitors;
communication and lighting fire trucks for managing divisions in a fire, providing information, lighting the divisions' work places. This group of vehicles includes: communication and lighting vehicles, communication vehicles, lighting vehicles;
fire trucks of the technical service for the delivery of the combat crew to the place of fire, the performance of rescue operations, the creation of normal working conditions for the combat crew in smoky rooms;
auxiliary vehicles are designed to provide auxiliary work when extinguishing fires (tankers, mobile repair shops, laboratory vehicles, buses, etc.), for operational and service activities ( cars) and transport and economic works in fire departments ( trucks, tractors, etc.);
fire motor pumps - for supplying water from water sources to the fire site both in rural areas and at small industrial facilities where the maintenance of tank trucks and pump-hose vehicles is impossible or impractical due to economic reasons. They are also used to extinguish forest fires, to fill the water tanks of fire helicopters, adapted agricultural machinery and transport tankers used to supply water to the fire site.
To prevent a fire, it is necessary: to prevent the appearance of a combustible environment, i.e., do not use, if possible, combustible materials; not exceed allowable concentration combustible gases, vapors or combustible dusts in the air; prevent the formation of ignition sources in a combustible environment or the appearance of sources of ignition in it, i.e. prohibit smoking in the wrong place, eliminate the conditions for spontaneous combustion of grain, coal, peat; arrange lightning protection; use only machines, tools and materials that cannot cause a fire.
In explosive areas (where, for example, hydrogen or gasoline and solvent vapors are released that can explode from an electric spark), special electrical equipment must be used (Fig. 1 and 2). Wiring is laid there by cable or in sealed steel pipelines and connected to electric motors using special input devices and couplings (Fig. 3).
Rice. 1. The device of an explosion-proof oil-filled magnetic starter:
1 - cable entry; 2 - a plug of an opening for input of wires; 3 - grounding screws; 4 - control handle; 5 - oil gauge 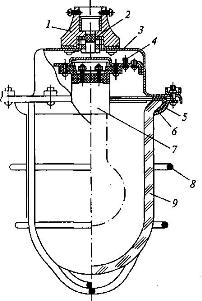
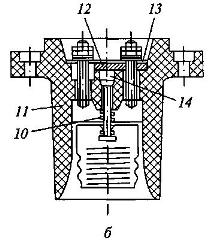
Rice. 2. Scheme of a lamp of increased reliability against explosion:
a - general form; b - spark-proof cartridge; 1 - vial; 2 - rubber seal; 3 - body; 4 - screw for zeroing; 5 - ring for attaching a glass cap; 6 - gasket; 7 - spark-proof cartridge; 8 - protective mesh; 9 - protective glass cap; 10 - spring contact; 11 - cartridge case; 12, 13 - fixed and movable cartridges, respectively; 14 - spark chamber 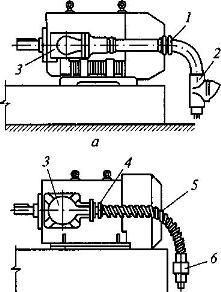
Rice. 3. Scheme for connecting electrical wiring to an explosion-proof electric motor in steel pipe(a) and in a flexible metal hose (b):
1 - coupling; 2 - filling fitting; 3 - input device; 4 - threaded tip; 5 - flexible metal sleeve; 6 - union with union nut
Organizational firefighting measures are as follows: the creation of voluntary firefighting brigades (FPD) or teams; training workers, employees and the entire population in fire safety rules; development of instructions on the rules for working with flammable materials and actions in case of fire; production of special posters and leaflets.
Technical fire-fighting measures are: ensuring the evacuation of people and economic values; from burning buildings (presence required number exits, corridors of the required width, construction of premises from fire-resistant materials, use of smoke protection); limiting the spread of fire (observance of fire breaks between buildings and the installation of fireproof fire walls, equipment production facilities fire extinguishing means); the use of observation towers, fire alarms, reservoirs, entrances to them and buildings, fire escapes when extinguishing.
On fig. 4 shows a fire shield with fire extinguishing equipment. The device of the water intake platform (Fig. 5) near the fire reservoir must withstand the weight of a fire truck with a pump and have a stop beam. The height at the lower water level must not exceed the length of the existing suction hoses.
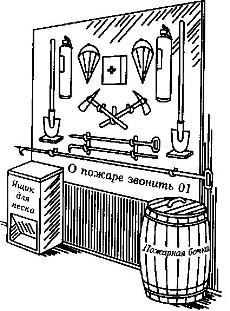
Rice. 4. Fire shield with fire extinguishers and fire tools 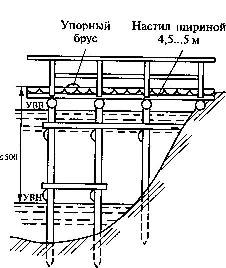
Rice. 5. Scheme of the water intake area:
UHV and UHV - water levels, respectively, upper and lower
The main causes of fires in the countryside are violation of the rules for the design and operation of heating stoves; careless handling of fire at work or at home (improper installation or use of kerosene heating and lighting devices, lightning discharges or from static electricity); malfunction of machines and non-compliance with the rules for their operation (sparks from an internal combustion engine or wire overload, overheating and sparking in places of poor contacts).
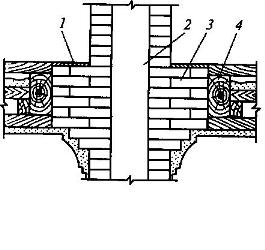
Rice. 6. Scheme of horizontal fire cutting of a brick chimney:
1 - fire-resistant insulation; 2 - chimney; 3 - cutting; 4 - combustible floor beams 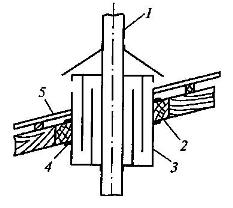
Rice. 7. Scheme of a permanently ventilated air cutting of a metal smoke or exhaust pipe of a stationary internal combustion engine:
1 - pipe; 2 - crossbar; 3 - cutting; 4 - sheet asbestos; 5 - roof
During the construction of houses, the outer walls of the furnace must be made at least half the length of a brick thick and plastered or protected with a casing made of sheet iron. In one-story buildings, the furnace foundation must be separated from the building foundation so that the furnace does not crack due to its settlement. The wall of the chimney at the point of passage through the combustible floor and roof structures is made thick to avoid overheating (Fig. 6). To pass through non-attic ceilings of metal chimneys or exhaust pipes from stationary internal combustion engines, a constantly ventilated air cutting is used (Fig. 7).





