Complications after influenza vaccination. Flu shot: contraindications and possible complications
In itself, the flu virus is not too scary. Much more devastating are the effects of the toxins that appear in our body after the virus has begun its work. The flu shot is perhaps the most the right way make sure that your child does not get sick and enjoy the winter to the fullest. Side effects from vaccines are rare these days, but unfortunately they can happen.
Why is it needed?
Why do you need a flu shot at all, which has numerous side effects and complications? Are you sure that your child has excellent immunity and receives all the necessary vitamins so that the body can fight the flu virus on its own? In addition, children are more sociable, so if one child gets sick in the classroom, in the garden or in the yard, everyone will soon go to bed. The flu shot is a kind of body training so that it learns to determine which of the aliens is the enemy of health and therefore does not get sick. And it is done in order to side effects and complications after the flu did not become fatal. The flu vaccine can contain both live viruses, which are weakened, and killed, that is, inactivated. The second type of influenza vaccine is used much more often and is also divided into such varieties as split (split), whole-virion, and also subunit. Complications most often occur after vaccination of the second type, the latter are the safest and side effects after they are rare.
In addition, she has contraindications.
Contraindications
- So, the flu vaccine is not administered to children under six months old, as well as to children who have recently (about 14 days ago) had a cold;
- Also, you can not do it to children and adults with intolerance to proteins and other components;
- There are contraindications for those who suffer from allergic dermatitis;
- With bronchial asthma;
- If there were complications after the previous vaccination. If the child did not tolerate other vaccinations well, then this one will not be better tolerated;
- After and during the exacerbation of all chronic diseases;
- With neurological diseases.
Side effects
Side effects can often be due simply to the flu shot being given incorrectly. For example, if contraindications were not observed or the doctor did not find any available. Poor-quality vaccine, violations of the rules for its transportation and storage, as well as the technique and basic rules of vaccination may also be to blame.
If contraindications are not observed and children with congenital immunodeficiency are vaccinated with a live vaccine, this is fraught with the most negative consequences;
If the safety rules are violated, then there may be such troubles as suppuration or allergies, it also happens that after an incorrectly performed vaccination, the child immediately fell ill with lymphadenitis.
O poor quality vaccines may indicate that a group of children vaccinated at the same time had exactly the same complications.
If the rules of storage and transportation have been violated, the effectiveness of vaccination may decrease. Also, the properties of the vaccine may change and this will lead to allergic reactions.
Complications can make themselves felt if the child fell ill before the vaccination itself, and this was not noticeable if the drug itself was toxic or if the patient's sensitivity turned out to be increased.
For any complications, first of all, you need to call a doctor who will prescribe the necessary antiallergic drugs, as well as antibiotics and cleansing drugs. You cannot assign all this to yourself.
As for the specific side effects after a flu shot, they can be both local and general. Local are expressed in the form of swelling and redness of the injection site, pain and severe inflammation. There is also allergic dermatitis at the injection site. Lymph nodes may be slightly enlarged. In these cases, you can do nothing, or you can take an antiallergic medicine. Pain and redness may appear after the injection was made subcutaneously, and not into the muscle.
Among the general reactions, the most frequent are fever (but not severe), loss of appetite, cold hands and feet, headaches, sleep problems, dizziness. It is extremely rare for a loss of consciousness to occur. All this is considered normal by doctors: it’s just that the body reacts aggressively to the antigen, and at this time immunity is developed. If the temperature really interferes with the baby or you, the usual antipyretic will come to the rescue.

Post-vaccination complications
In fact, these are isolated cases, but they still took place. Rarely, but still there is neuralgia, that is, pain along the course of one of the nerves. The child may also complain of numbness of the legs and arms, cramps and spasms. Thrombocytopenia, that is, a drop in the level of platelets for a while, is also considered a complication.
A rare occurrence is anaphylactic shock, that is, a severe allergy that causes disruption of the heart. Also found among the complications of lymphadenitis, systemic vasculitis and disruption nervous system.
It also happens that a child or an adult gets sick immediately after vaccination. Usually, however, this is not a flu virus, but usually ARVI and the disease has entered the body, whose immunity is “in confusion” after vaccination. That is why the ideal option would be vaccination in the summer or autumn. Unfortunately, at this time you can get vaccinated against the wrong virus that will come in winter and there will be little benefit. But some kind of vaccination is still better than completely unprotected immunity.
In order to avoid any consequences of vaccination, it is better to stay in the clinic for some time after the injection so that you can immediately consult a doctor: anaphylactic shock most often appears after 30 minutes, allergic reactions can make themselves felt even earlier. Watch your child at home: the next few days may not bring the most pleasant surprises. Usually everything goes without problems, but anything can happen ...
 Influenza and preventive vaccination against it
Influenza and preventive vaccination against it
Influenza and vaccination
Influenza belongs to the group of acute respiratory viral diseases, the danger of which is often underestimated - this leads to refusals of the flu shot. During epidemics, various preventive measures are used - wearing masks, frequent washing hands, wet cleaning using aggressive disinfectants. The usefulness of such actions has been proven more than once, but they cannot create a barrier between the virus and a healthy body.
A vaccine is an immunobiological drug that prepares the immune system to meet the pathogen. Despite the fact that people very often get sick with the flu, a strong immunity is not formed to it, which allows them to avoid infection in the future - the virus is constantly changing. To be on the safe side, vaccinations should be given before the predicted rise in incidence and should be repeated annually.
Immunity is created only against those strains of the virus that are declared as part of the vaccine preparation.
Knowing the patterns of the epidemic process and tracking cases helps researchers figure out which type of influenza threatens the population - this affects the choice of vaccines used. Information on the types of viruses expected to circulate in the new flu season is provided by the World Health Organization (WHO).
Types of vaccines
Influenza vaccination is carried out using:
- live vaccines;
- inactivated vaccines.
For the manufacture of a live vaccine, weakened recombinant strains of the influenza pathogen are used, the circulation of which is predicted by WHO. They are cultured in chicken embryos. The composition of the vaccine preparation includes at least 3 variants of the virus, monomycin, nystatin, egg white. The advantage of a live vaccine is the formation of not only general (humoral, cellular) immunity, but also local immune protection. Influenza vaccination allows you to create a barrier on the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, which become the "entrance gate" of the infection.
Virions, surface and internal antigens of the influenza virus can be included in the composition of inactivated vaccines. Virions, that is, viral particles, are contained in whole-virion vaccine preparations, the use of which is limited due to high reactogenicity (the ability to provoke unwanted side effects). According to research and reviews of flu shots, split or split vaccines, as well as subunit vaccines, are considered the safest. They form predominantly humoral immunity and are suitable for vaccination of children, patients with chronic pathology.
Indications for vaccination
Vaccination is preferably carried out between October and mid-November.
It takes several weeks for the antibodies to form. The opinion that one should not be vaccinated during the height of the “flu season” is true in relation to live vaccines; immunization with inactivated drugs is permitted. But if you give the vaccine to a person who is already infected (in the incubation or prodromal period of the flu), it will not be effective.
Vaccination is necessary primarily for persons included in risk groups:
- medical workers;
- employees of retail chains;
- employees of kindergartens, schools, institutes;
- patients with chronic diseases;
- elderly people;
- children aged 6 months to 15 years.
Vaccination is carried out in order to: 
- Flu prevention.
- Prevention of influenza complications.
- Relief of the course of the disease.
Influenza vaccination is needed for both healthy children and those suffering from chronic pathology. The vaccine does not suppress the immune system, but it reduces the risk of complications, which are more dangerous, the weaker the body.
Contraindications to vaccination
The presence of contraindications to the introduction of a flu shot is determined by the doctor; the list includes:
- acute febrile conditions of infectious and non-infectious etiology;
- exacerbation of chronic pathologies;
- allergy to egg white.
Fever and deterioration chronic diseases are temporary barriers to vaccination. In the first case, immunization is carried out after the temperature returns to normal values, in the second - after the onset of remission.
Influenza vaccines are recognized as low-reactive, although some patients experience local or general reactions (redness and swelling at the injection site, weakness, fever to subfebrile numbers). They are not dangerous, they go away on their own without special treatment. However, a contraindication for vaccination is a severe febrile reaction (temperature of 40 ° C or more) observed after the introduction of the vaccine in the past.
Possible contraindications also include:
- last trimester of pregnancy;
- an active form of tuberculosis infection;
- chronic lung diseases;
- hypertension;
- atherosclerotic vascular disease.
In the conditions specified in the list, as well as in the presence of allergic diseases and bronchial asthma, diffuse connective tissue diseases, lesions of the nervous system and adrenal glands, the decision on the possibility of vaccination is made by the doctor, taking into account the risk of possible complications.
One of the most relevant topics for parents in the autumn-winter period is the flu shot for children, which is proposed to be put in all medical institutions. On the one hand, I want to protect my child from the virus through vaccination. On the other hand, there are so many myths about the dangerous consequences that can be after that that parents have a completely understandable fear.
So what is more dangerous: flu or vaccination against it - we are trying to figure it out.
Vaccination effectiveness
Their doubts about whether or not to vaccinate against the flu for children, parents can decide on their own only after they weigh all the pros and cons. Vaccination is a voluntary matter, so when making a decision, the most important thing is not to make an unfortunate mistake. Parents should clearly understand the benefits of this vaccine and how effective it is.
- You need to understand that flu shots for children are not protection against infection with the virus. Their task is fundamentally different: if it is present, the disease simply proceeds in a mild degree, without complications. Unfortunately, doctors do not fully inform parents about this, and the latter, as a rule, hope that the vaccination given to the child is a guarantee that he will not get the flu.
- The vaccine has a long-term effect on the human body. It promotes the development of immunity to the virus within two weeks. It will be effective for six months and even more. In accordance with these indicators, vaccination begins well in advance of the planned influenza epidemic, so that immunity has already developed.
- Imported vaccines are highly effective (up to 90%), so it will not be superfluous for parents to study the ampoule that is used for injection.
- The advantages include the important fact that a child can be vaccinated against influenza simultaneously with vaccination against many other diseases - tetanus, diphtheria, whooping cough.
The most commonly offered influenza vaccines, like Vaxigrip, Fluarix, Agrippal, Influvak, etc. However, if flu shots had only advantages, no one would doubt whether to give them to their child or not.
This is due to the presence of shortcomings - contraindications, non-compliance with which leads to complications. It is because of the rather serious consequences that many parents are afraid to vaccinate their babies against the flu.
Contraindications
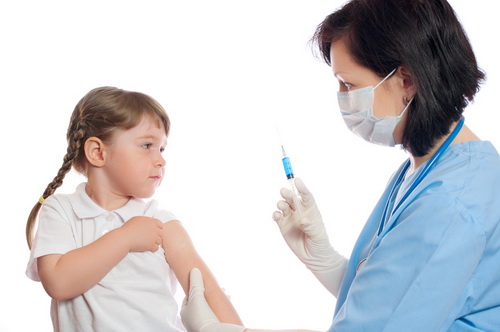
Doctors must definitely inform parents what contraindications for flu vaccinations for children should be observed in order not to bring the matter to dangerous complications. And be sure to identify them before vaccinating.
Contraindications include:
- age up to 6 months: children under one year old are not vaccinated against influenza if a live vaccine is used (shown only after 3 years) or inactivated (successful is considered only after 7 years); many doctors say that the safest thing to do is to vaccinate against the flu for children under 3 years old, since before this age they already have to go through a whole list of necessary vaccinations;
- heart disease of any severity;
- a recent cold;
- lung diseases that have become chronic (for example, bronchitis);
- high temperature at the time of vaccination;
- , cough;
- constant contact of the child with an already flu person (for example, if someone in the family has already caught this virus);
- if the baby is already sick;
- allergy to chicken protein;
- hydrocephalus;
- individual intolerance.
Before conducting influenza vaccination, the doctor should conduct an examination, especially if the vaccine is given to the child for the first time. Blood and urine tests are taken, individual intolerance to the drug is revealed, a map of recent diseases is studied. On the day of vaccination, the child's state of health is clarified, the temperature is measured.
Only after such events, in the absence of contraindications, is a vaccination given. Otherwise, undesirable consequences may begin, which everyone around is talking about so zealously.
Consequences of vaccination
There is a lot of talk these days about how dangerous the flu shot can be for a baby's health. Instead of vain doubts and empty fears, parents should understand one thing for themselves: all of them are possible only if contraindications are not observed. If there are no special problems with the child's health, vaccination should be successful and fulfill its function - to save, not harm.
Dangerous and not very consequences after unsuccessful influenza vaccination include:
- a slight increase in temperature;
- swelling or redness at the injection site;
- headache;
- weakness;
- drowsiness;
- high body temperature;
- , which is accompanied by a sharp drop blood pressure and disruption of the heart;
- death in the presence of serious internal diseases.
Most of these effects are short-lived, localized and quickly disappear. The danger threatens only those children who have serious pathologies and major health problems. Here we need additional consultations of many doctors - narrower specialists who will be able to determine the level and degree of threat of the influenza vaccine.
Every year in late autumn, and more often in winter, another influenza epidemic begins. Doctors strongly recommend that people prepare for such an event by resorting to various preventive procedures. In particular, vaccination is considered the most effective prevention of this infection. Although it cannot be definitely called universal, since the flu shot has certain contraindications.
Feedback on contraindications

This means that not everyone will be able to resort to this method protection against influenza infection. But all this should be told in more detail.
There are certain contraindications in which the flu vaccine should not be given.
First of all, it should be noted what are the vaccines that help prevent the development of influenza:
- Injections are considered the most sought after. As a rule, only inactivated viral strains are used in this case.
- Spray can- they traditionally contain live viruses, although they are weakened.
But you should be prepared for the fact that after any procedure side effects are possible. Sometimes it depends individual features human body.
Here are the most common health defects, sometimes noted after vaccination:
- feeling of weakness, overwork, drowsiness;
- feverish state, feeling of heat;
- headache;
- runny nose, symptoms of pharyngitis.
Perhaps the most severe complication is the phenomenon of anaphylactic shock. But it is quite rare.
From time to time you also have to deal with:
- pain sensations;
- swelling;
- redness (at the injection site).
But, as a rule, you don’t have to worry much, since most side effects disappear soon after the injection - after a few hours. AT last resort they last a couple of days.
As for the more dangerous consequences, it is quite possible to avoid them if you know in advance the list of possible contraindications.
What can be contraindications?
So, it is better to look for some alternative to flu shots with the following contraindications:
- Vaccination should not be carried out if a person has an acute form of a cold and a high temperature. First you need to wait for recovery, and then wait another month or at least three weeks.
- In the presence of allergic reactions to the protein. Most vaccines are made on its basis.
- If a previous vaccination went through with serious side effects, it is likely that the doctor will cancel the upcoming procedure.
- In the presence of serious diseases of the nervous, as well as endocrine system other options for prevention are also selected.
- If there are problems with the functioning of the kidneys and adrenal glands, you may need additional counseling before the procedure.
- Some vaccines (for example, Grippol) are undesirable to use if a person suffers from chronic ailments of the lungs, as well as the respiratory tract.
- Infants and toddlers under six months of age are generally not vaccinated.
- Diseases such as asthma, hypertension, anemia, and heart failure may also be considered as contraindications for influenza vaccination.

Babies who are under 6 months old are not vaccinated
That is why it is necessary to consult with a medical specialist before vaccinating - especially when adults and children may have certain contraindications to the flu shot.
Doctor carefully:
- examines the patient's medical history;
- wonders if there were any problems in the past after immunoprophylaxis;
- carefully asks about the state of health;
- checks for allergies to the flu shot;
- perhaps even directs the person to undergo some examinations.
Only then can he decide whether the patient can be vaccinated against the flu.
However, vaccination should not be considered a panacea for colds. More or less guaranteed protection against influenza becomes possible only if you follow the entire range of preventive measures, which, of course, include:
- healthy lifestyle;
- proper nutrition (as many vitamins and natural products as possible);
- walks in the fresh air;
- moderate physical activity;
- minimizing contact with those infected with influenza.
Remember that with strong immunity, the body fights infection much easier and has much more chances.
That's just not always even the strongest the immune system is unable to resist the spread of the influenza virus without outside help, which is ensured by timely vaccination.
The meaning of immunoprophylaxis
Why is it important to get vaccinated on time? The fact is that after the vaccination is done, you must wait at least another two weeks until immunity from the viral strain is formed. Until it has formed, the body remains defenseless and prone to infection.
The very meaning of vaccination lies in the introduction into human body weakened or inactivated virus. Therefore, for people with a too weak immune system, such a procedure may not be safe. Here, in fact, is the answer to the question: who is contraindicated for the flu vaccine?
What is the point of a person getting vaccinated if after this procedure he gets sick with the flu? This is when you shouldn't get the flu shot. At least to begin with, it is desirable to carry out a series of measures to strengthen immunity (although, as is clear, such results cannot be achieved in one day or even a week).
The dangers of the flu
Influenza infection usually affects the human respiratory system. The first symptoms of this disease are:
- runny nose;
- elevated temperature indicators;
- headache;
- cough.

Headache is one of the first symptoms of the flu.
If the disease is not treated, it is likely that there will be complications - up to irreversible damage and death. That is why they say that it is better to prevent such a disease than to waste time and last strength on the course of treatment.
And since doctors call vaccination the most effective preventive measure, people are wondering if the flu shot is dangerous, as is often the case with a wide variety of medications.
So here, speaking allegorically, "a stick with two ends":
- influenza itself can be extremely dangerous to human health, leading to serious complications, sometimes difficult to treat;
- vaccination, if carried out, despite the existing contraindications, can lead to no less problems.
There may also be some side effects - although in most cases they are safe and short-lived (with the exception of anaphylactic shock, but this occurs extremely rarely). So they should not be feared.
Listed above are contraindications for influenza vaccination. But speaking of them, one cannot help but recall those categories of people who are vaccinated against the described infection, on the contrary, it is indicated and recommended:
- those who are in poor health and prone to colds;
- those who suffer from chronic ailments;
- those who, on duty, are forced to constantly contact people;
- children (from six months of age) and the elderly.
Only by being vaccinated, representatives of these categories protect themselves by about 70 percent from infection during the epidemic. Sometimes infection still occurs even after vaccination, but in this case it is possible to do without complications.
Vaccinations for pregnant women
An equally important question is immunoprophylaxis during pregnancy, that is: is this condition, in which most female representatives are from time to time, included in the number of contraindications to influenza vaccination?
- individual characteristics of the patient;
- her state of health;
- the presence or absence of difficulties in carrying a child, and so on.
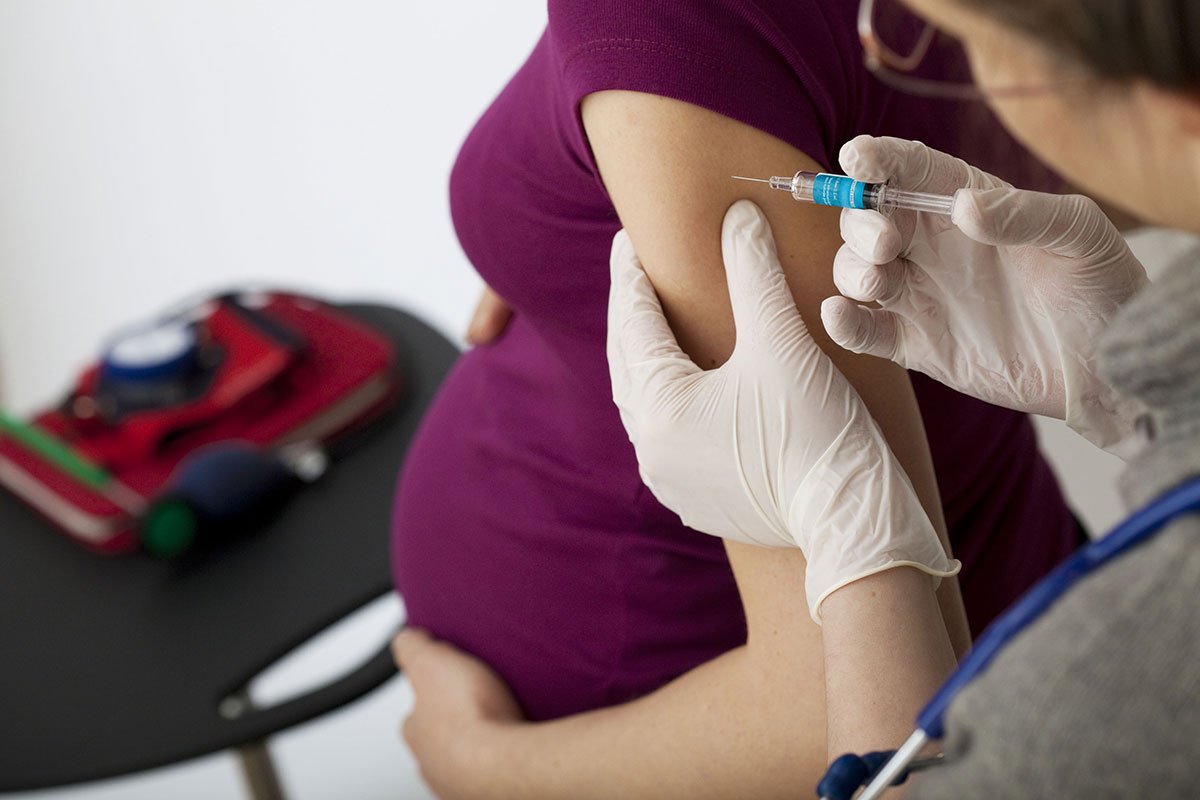
Pregnant women should be vaccinated in the third trimester
In general, such prevention procedures for pregnant women are traditionally allowed no earlier than the third trimester begins (when the fetus has already formed). It minimizes possible risks both for the new mother and for the unborn child.
Annual virus mutations
Scientists develop new vaccines every year because the flu virus cannot stay the same all the time. Shortly before the expected start of the epidemic, WHO experts predict exactly what the dominant viral strain will be this time.
That is why you should be vaccinated once a year. It is best to do this in early or mid-autumn - before the epidemic begins, so that the body has time to get stronger and gain enough strength. More precisely, antibodies are produced that prevent the infection from infecting the respiratory system and other human organs. Even if infection does occur, such a disease in the presence of antibodies is faster and easier to cure.
Actually, the aforementioned phenomena ensure the regular change of the components of anti-influenza sera.
Which vaccines are the most and least dangerous?
The following types of vaccines are actively used in anticipation of the epidemic:
- live- they contain living, albeit weakened, strains. That is why after the introduction of such a drug, a person may experience flu-like symptoms. Thanks to all this, a strong immune system is formed (protected, at least, from specific viral infections). These vaccines have perhaps the most contraindications.
- Inactivated(they are also called whole-virion). These strains are inactive: they are traditionally cultured from chick embryos and inactivated with formalin or ultraviolet radiation. The most common contraindication in both adults and children in this case is an allergy to the flu shot.
- split. These preparations contain fragments of the protein structure of the virus, which are obtained as a result of the chemical destruction of the strain and subsequent additional purification. As a result, the vaccine is no longer as toxic, but still has good immunogenicity.
- Subunit. The least reactogenic, although the most purified preparations. If you want the safest vaccine, this is the option you need. True, the effectiveness of such immunoprophylaxis is significantly less compared to other drugs.
Live substances are often administered using sprays and drops (intranasal method). Split as well as subunit vaccines are traditionally given by injection.
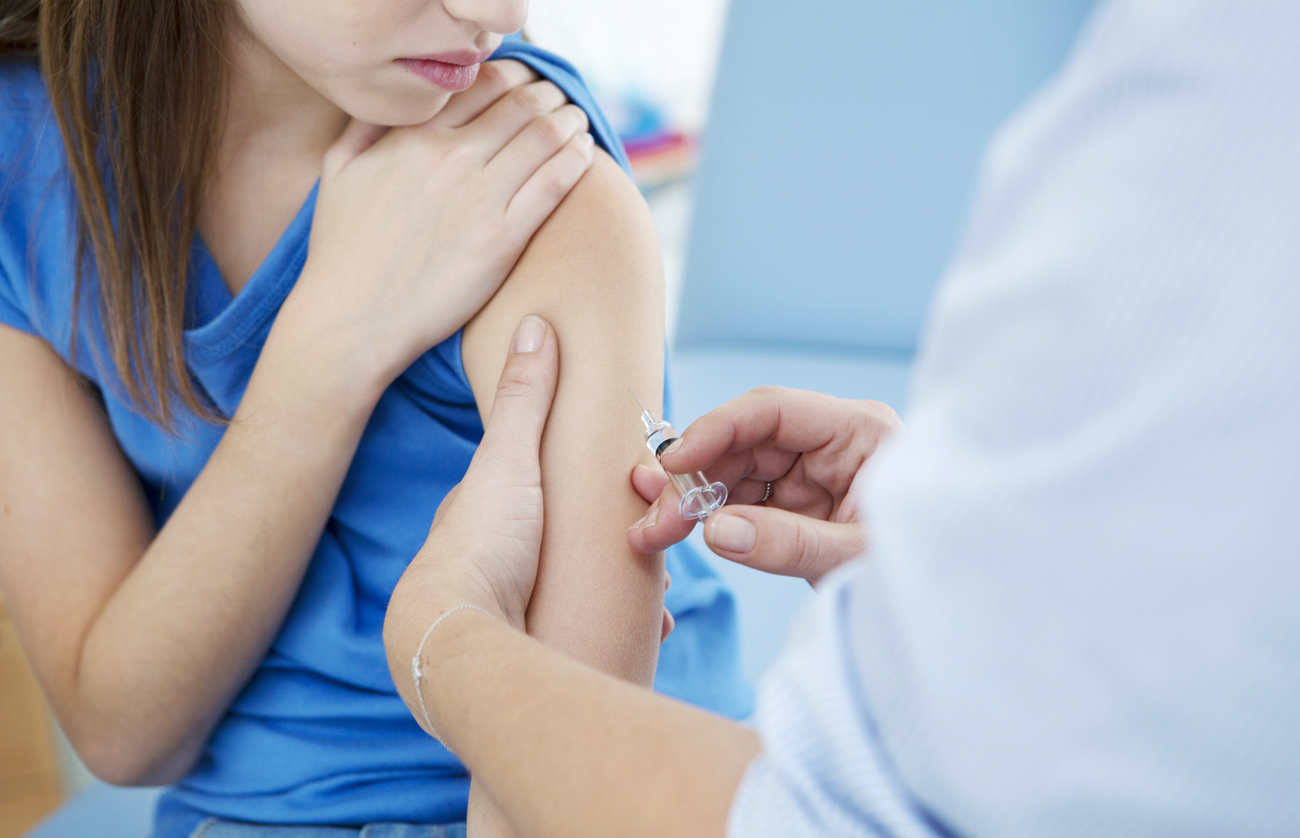
Flu shots involve intramuscular injections
As for the injection method of administration, doctors recommend intramuscular vaccinations. This helps to ensure a positive effect. Adults are usually grafted into the upper arm (specifically, the deltoid muscle). Children who have not reached three years of age, injections are made in the thigh.
Anti-influenza injections into the buttocks are almost never done because it is not as effective.
Conclusion
Why is the flu vaccine dangerous? Basically, nothing if:
- correctly approach the preparation of this procedure;
- take into account all possible indications and contraindications;
- choose the right vaccine for you;
- check for allergies and individual intolerance to the components of the drug.
Done right, getting vaccinated can bring a lot of benefits.. Infection with the flu, of course, is still possible - especially infection with other colds. However, you will know for sure that the disease will pass without complications and can be quickly cured.
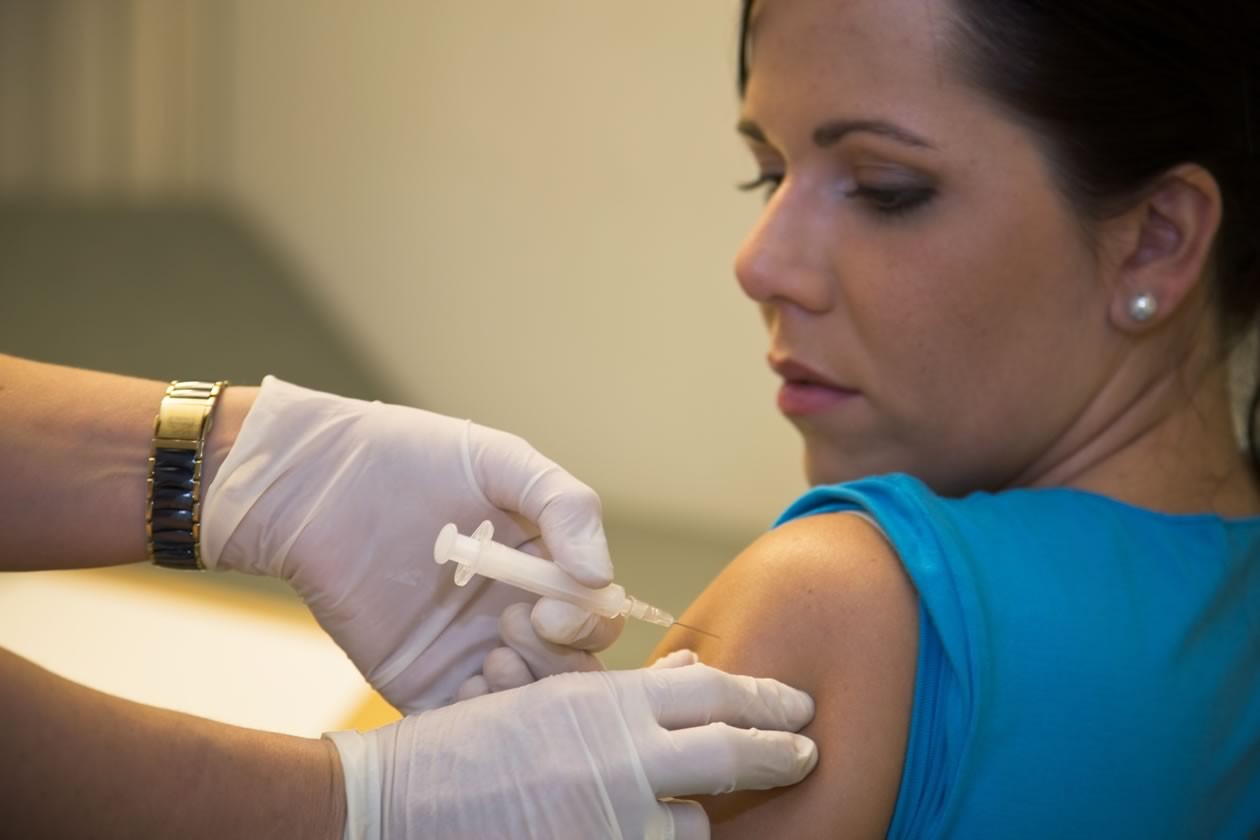
If there are no contraindications, vaccination will only benefit
Therefore, if you have not yet decided whether to vaccinate or not, think carefully and analyze the pros and cons of this procedure. Surely, this will allow you to see for yourself that vaccination is not in vain called the most effective option for preventing influenza.
Text: Evgeniya Bagma
No matter how you strengthen your immunity and eat tons of lemons, the most effective tool The only protection against influenza is vaccination. Vaccination can prevent the disease by 80-90 percent! But, alas, not everyone is suitable for the flu vaccine - it has very serious contraindications.
Who needs a flu shot and why?
Vaccination - best method influenza prevention. But influenza vaccination contraindications somewhat detract from the versatility of this tool, although they do not reduce its popularity. Most optimal time for its implementation in our region - September-November. It is during these months that influenza epidemics begin and it is advisable to prevent them, since it can take up to two weeks to develop immunity to the disease. The flu shot does not protect against other viral infections or respiratory diseases, and does not preclude other measures to prevent illness. The modern vaccine contains three strains, and, contrary to popular myths, does not cause the disease on its own and does not make it worse if it has already occurred. The chance of getting sick from a vaccine lasting 1-2 days is only 1%. Especially the flu vaccine is indicated for children and the elderly, pregnant women, as well as people who are extremely undesirable to get sick - for example, doctors, teachers and teachers, parents of small children.
Influenza vaccination - contraindications
Before getting vaccinated, be sure to consult your doctor, otherwise vaccination may lead to undesirable health consequences. Influenza vaccination contraindications are as follows:
- allergic reaction to previous vaccines;
- allergy to chicken protein, which is part of the vaccine;
- acute illness with high fever;
- asthma;
- heart failure, hypertension (II and III stages);
- diseases of the kidneys and adrenal glands;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- chronic diseases of the lungs and upper respiratory tract;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- blood diseases;
- Influenza vaccination is contraindicated in children under 6 months of age.
To find out what specific contraindications for flu vaccination may be in your case, first visit a doctor.
The contraindications for influenza vaccination do not make it less effective way prevention. The vaccine will not protect you 100%, but it will make the disease much easier. So, if the flu shot has no contraindications in your case, do not risk your health and protect yourself.