Departure on alarm of the duty guard of the fire brigade. conducting classes in fire drill training with personnel. Radiation, chemical and biological protection
When collecting, leaving and following
INSTRUCTIONS
on labor protection during the collection, departure and following
on fire trucks on the signal "Alarm"
1. General requirements labor protection
1.1. An employee who has passed the initial training, passed the test and has been instructed in labor protection is allowed to collect, leave and follow in cars at the “Alarm” signal.
1.2. The worker must wear combat clothing.
1.3. The head of the unit establishes the procedure and place for gathering and boarding the duty shift in fire trucks (in the garage or outside the garage)
1.4. When collecting on an “Alarm” signal, it is forbidden to throw clothes, equipment and household items on the paths of movement, stop in the aisles in the flow of those running or interfere with each other when moving.
1.5. Get into the car on the move, close the car door behind you, without making sure that there are no people in the doorway.
1.6. The head of the guard, the commander of the department and the driver of the car are responsible for observing safety measures when driving a car.
1.7. It is allowed to be in a fire truck for persons indicating the direction of movement to the place of the call (fire).
2. Labor protection requirements before starting work
2.1. Before boarding a car outside the garage, personnel must go to the area in front of the garage after the exit of the fire truck (FA).
2.2. The head of the guard must monitor the safety of landing and the reliability of closing the cabin doors.
2.3. After making sure that the shift on duty has taken their places, and the doors of the PA are tightly closed, the head of the guard himself gets into the car and gives the command to move.
3. Requirements for labor protection during work
3.1. When leaving the garage and moving to the place of call (fire), the driver of the PA must turn on special sound and light alarms.
3.2. To warn public transport and citizens about the departure of the PA from the garage, special traffic lights are lit. In the event of a malfunction of a special traffic light, the guard on the facade is obliged to give a red flag, and at night to give signals with a red lantern.
3.3. The movement of the PA is allowed only when closed doors cabins and doors of the body (compartment).
3.4. When following a fire, PA drivers are required to strictly observe traffic rules.
3.5. Drivers of vehicles equipped with special sound signal type "siren" and others, may allow some deviations from traffic rules, provided that traffic safety is ensured, namely:
Ø move at a speed that ensures the timely completion of the task and make sharp turns, but without endangering others;
Ø continue driving at any traffic signal, making sure that other drivers give way and provided that the gestures of the traffic controller do not oblige him to stop;
Ø drive through the places of work, regardless of the established signs, signs and safety lines, with the exception of driving in the opposite direction to traffic;
Ø use sound signals at any time of the day.
3.6. It is forbidden to use a special sound signal when following the PA not to a call (fire) and when returning to the unit.
3.7. Parking PA at night should be marked with lighting devices.
3.4. While the vehicle is in motion, personnel are prohibited from:
Ø smoke and use open fire;
Ø protrude from the cab;
Ø open doors;
Ø stand on the steps, except for the cases of laying a hose line;
Ø jump out of the car until it comes to a complete stop.
4. Labor protection requirements in emergency situations
4.1. In the event of a traffic accident (RTA), the driver involved in it must immediately stop and turn on the alarm, and in case of its malfunction or absence, put up a sign at a distance of 30-40 m behind the car emergency stop or a flashing red light and do not move the car and objects related to the incident, and inform the head of the guard.
4.2. If necessary, the guard personnel and the driver must provide first aid to the injured and call an ambulance medical care": if this is not possible, then the victims should be sent by passing car to the nearest medical institution.
4.3. It is necessary to report the incident to the traffic police: if there are eyewitnesses to the accident, you should write down their names and addresses and wait for the arrival of traffic police officers.
4.4. If the accident did not cause harm to people's health or significant material damage, with mutual agreement in assessing the circumstances of the incident and the absence of malfunctions of vehicles with which their further movement is prohibited, drivers can arrive at the nearest traffic police post to file an accident.
4.5. If necessary, tow a faulty car, towing can be done either on a rigid or on a flexible hitch; in this case, the driver of the towed vehicle must be at the wheel of his vehicle.
4.6. A vehicle with a trailer must not be used as a towing vehicle.
4.7. When towing on a flexible hitch, the towed vehicle must have a working brake system and steering, and when towing on a rigid hitch, steering.
4.8. A rigid hitch should provide a distance between cars of no more than 4 m, and a flexible one - within 4-6 m, with a flexible hitch, the cable should be marked with signal flags every meter.
4.9. The towing speed must not exceed 50 km/h.
4.10. When towing during daylight hours, regardless of visibility conditions on the towing vehicle headlights must be on. And on towed at any time of the day - side lights.
4.11. The driver of a vehicle towed on a flexible hitch must ensure that:
Ø so that the tug is always tight; this will protect it from breaking, and the car from jerking, and exclude the possibility of a towed car colliding with a towing car in case of sudden braking.
4.12. Towing a car on a flexible hitch in icy conditions is prohibited.
4.13. In the event of a fire, the vehicle must be equipped with primary fire extinguishing equipment.
5. Requirementslabor protection at the end of work
5.1. The head of the guard, who took part in extinguishing the fire, after its liquidation is obliged:
Ø check the presence of guard workers, as well as the placement and fastening of fire extinguishers on fire trucks.
5.2. At the end of the duty, the driver and guard workers must hand over the car and fire fighting equipment to the driver and guards on duty, to conduct, together with them, daily Maintenance fire truck and fire fighting equipment.
5.2. If the driver and guard workers have comments on technical condition car, fire-technical equipment, they must report this to the head of the guard, the mechanic of the garage.
Collection and departure on alarm
It is desirable to conduct training in gathering and leaving on alarm in 2 stages.
First stage- the appointment of a combat crew, its construction at the fire truck and landing in the cockpit, dismounting.
Second phase- collection on alarm, putting on combat clothes and equipment, landing in the cabin of a fire truck and leaving the garage.
First stage: the squad leader lines up the squad in front of the fire truck (PA). Announces the topic, the purpose of the lesson and the rules of labor protection, drawing Special attention to the fact that landing in the cabin is carried out only during parking and outside the garage gate. In any case, firefighters should not stand on the carriageway.
Then the commander appoints a combat crew, naming the name of the fireman, for example: "Fireman Ivanov". Hearing the answer: "I!", assigns him a combat crew number: "First number!". After the fireman replies: "There is!", the squad leader indicates his place when building on command: "Department- TO THE CAR!" or "Separation - BECOME!".
Fireman Ivanov takes his place at the PA, and the commander calls the next fireman by his last name. Having built a squad on the right (left) side, with its back to the PA in the direction from the axis of the rear wheel to the cab of the car, the squad leader explains that firefighters who are assigned numbers 1, 3, 5, 7 stand in the first rank, and No. 2, 4 , 6 and the driver - in the second (fig.); at the tank truck, firemen No. 1, 3 and the driver become the first line, and firemen No. 2, 4 become the second. Combat crews of less than 5 people line up at the PA in one line from the right (left) side from the rear wheel axle to the cab back to the car, the driver on the left flank.
By command: "Set aside!" combat crew returns to its original position. The squad leader announces that the formation must be completed at a fast pace, and gives the command: "Squad - TO THE CAR!". Then he checks the correctness of the construction of the combat crew. For example, it declares: "Second number!". The second number says his last name ("Fireman Sidorov!"). Thus, the commander calls 3-4 firefighters. The squad leader commands: "GET OUT!", and the construction of fire PA is made from different positions, places, premises.
After making sure that the firefighters have learned the order of building a combat crew from the PA, the squad leader reports that on command: "In places!" or "Anxiety!" the combat crew is boarded in the PA cabin, and each firefighter takes his place, starting with those who should sit in the middle of the seat. Firefighters No. 1 and 2 sit down last, close the gates (if they do not close automatically) from the left and from the right side. The squad leader sits next to the driver.
In the cabin of the combat crew of the autopump, firefighters No. 1, 3 and 5 sit on the first seat, firefighters No. 7, 4, 6 and 2 sit on the second.
The combat crew sits in the cockpit in the following sequence: on the right side on the first seat - firemen No. 3 and 5, on the second - fireman No. 4, 6, 2; on the left side on the first seat fireman number 1, on the second - fireman number 7.
When building a combat crew on the left side, firefighters No. 2 and 5 sit on the right side, and the rest of the firefighters sit on the left: firefighters No. 3 and 1 sit on the first seat, firefighters No. 6, 4 and 7 sit on the second.
Firefighters exit the PA cabin in reverse order and line up on the right (left) side. Firemen 1 and 2 open the gate if it does not open automatically. The landing is considered completed when the firefighters took their places in the car and closed the cabin doors. The procedure for boarding the personnel of the department in fire trucks in the garage or outside it is established by the chief of the fire department. Then the landing of the combat crew is performed several times at a fast pace. The squad leader checks the correct landing of the combat crew in the cockpit and formation at the PA.
Second phase: the squad leader informs that the squad will perform the exercise "Gathering and departure on alarm" and explains the correct order for its implementation (pack combat clothing and equipment in the first (second) way, at the signal: "Anxiety!" put it on and take your place in the cockpit of the combat crew).
The department executes the following commands: "Combat clothes and equipment first(second) way- STAY!" and "Anxiety!". The landing is considered completed when the combat crew takes their places in the car and closes the doors.
This step is repeated 2-3 times. Then the collection on alarm is carried out with the departure from the garage for a while (fulfillment of the standard), while the personnel are on the facade, in the classroom and in other rooms of the unit. On signal or command: "Anxiety!" firefighters, regardless of location, run to the garage. When executing a command, it is forbidden to throw clothes and service items on the way, to stop in the aisles. When using the descent pole, each firefighter must maintain the interval, watch the firefighter descending in front and not touch him with his feet. Touching the mat with your feet, you should push off the pole and quickly move away.
Firefighters put on combat clothing and equipment, get into the cab, the driver starts the engine, the squad leader receives a ticket, announces the address of the fire, firefighters No. 1 and 2 open the gate (if they do not open automatically), get into the cab and close the doors. The squad leader gives the command to the driver: "March!". After leaving the garage, the squad leader commands: "Stop!" The driver stops the car. The squad leader commands: "Department- BECOME!"- and personnel are being built at the PA. The squad leader checks the refueling of combat clothing and equipment and commands: "The car in the garage - PUT!", "Combat clothes and equipment in the first way - LAY!". The exercise is repeated several times, since this standard must be performed at least "good" in summer and winter conditions. The squad leader sums up the lesson.
When leaving for a fire, it is allowed to button up a jacket and put on a fire belt in the cab of the car. The head of the guard (commander of the squad) receives vouchers, announces the address of the fire and gives vouchers to the commanders of 2-3 squads, gives the driver a command: "March!".
While the vehicle is in motion, it is forbidden to smoke, lean out of windows, open doors, stand on the steps, get out of the vehicle until it comes to a complete stop.
1.5 Safety requirements when collecting and leaving on an "Alarm" signal
Gathering and departure on alarm of the guard are provided in accordance with the established procedure. By signal: "Anxiety" the personnel of the guard arrives at the fire trucks, and the lighting in the guardroom and garage should automatically turn on. It is forbidden to leave clothes, household items, etc. on the routes.
When using the descent column, the personnel must maintain the necessary interval, follow the descender in front to prevent injury. When descending the pole, one should not touch its surface with unprotected parts of the hands, but after descending, make room for the next descent.
The procedure for boarding guard personnel in fire trucks (in the garage or outside it) is established by order of the head of the State Fire Service, based on security conditions and local characteristics. When landing, it is forbidden to run in front of cars leaving on alarm.
When landing outside the garage building, the exit of the guard personnel to the site is allowed only after the fire trucks leave the garage.
The movement of a fire truck is allowed only with closed cabin doors and body doors. The landing is considered completed after the personnel of the guard take their places in the cab of the vehicle and close all doors.
In this case, it is prohibited:
give a command for the movement of a fire truck until the end of the landing of the guard personnel;
presence in fire trucks of unauthorized persons.
APPROVE
Head of PC-3
major of internal service
S.V. Korovin
"___" _________ 2008.
Methodical plan
conducting fire drill training with personnel
1st guard on June 2, 2008
Subject: Development of standard No. 4. "Collection and departure on alarm"
Time: 1 hour.
Goals: 1. Train personnel.
2. Check the combat readiness of the guard personnel.
1.Literature: 1. Fire drill training. Bushmin V.A.
2. Standards for fire drill training. 1994
2. Expanded lesson plan
|
No. p / p |
Study questions |
t | ||||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|||
|
1. | TB |
Conduct a briefing with personnel on safety measures when fulfilling standard No. 4, "Gathering and leaving on alarm (with landing in a car outside the garage gate)". Combat clothes and equipment are stowed in any way. A belt with a carbine attached to it and a fire ax in a holster lies in front of the clothes. The podkasnik can be located next to the stowed combat clothing or inside the helmet. Canvas mittens (gaiters) are placed in the pockets of the jacket, in the absence of pockets - under the belt. The staff of the guard on duty is located in the guardroom and is located arbitrarily. |
||||
|
2. |
Performing an exercise |
An "alarm" signal is given. The personnel quickly put on combat clothes and board the car outside the garage gate. Landing in the car is made after combat clothing and equipment are fully put on; it is allowed to fasten combat clothing and put on a fire belt in the cab of a car. End: the car is outside the garage gate, the personnel of the departments are in the car. The doors are closed. The result is recorded at the moment of closing the last car door. |
||||
|
Compliance with the standard in the composition: | Compliance time, s |
|||||
|
Great |
well |
satisfactorily |
||||
|
branches |
30 |
34 |
38 |
|||
|
sentry |
34 |
38 |
42 |
|||
Note: for vehicles with the KAMAZ brake system, the standard time is increased by 60 s.
Lesson leader:
lieutenant of the internal service Klepinin D.S.
The commander builds a squad, announces the exercise and the goal, tells and shows the rules for packing combat clothing and equipment in the first way, puts firefighters at the place where combat clothing and equipment are laid. Then he gives a command for laying combat clothing and equipment in the first way and, moving from one firefighter to another, monitors their actions. After making sure that all firefighters have correctly packed their combat clothing and equipment, having built the squad in one line, the commander tells and shows the rules for putting them on, gives the command to put on combat clothing and equipment. At the same time, he pays special attention to the fact that firefighters perform all the tricks without fuss. He corrects the errors he makes as soon as they are discovered, then, briefly explaining the error, requires repeating the reception.
The commander reinforces their knowledge by repeating this part of the exercise in the same sequence.
Laying combat clothing and equipment in the second way and putting it on are practiced in the same sequence as in the first way.
At training sessions, after announcing the exercise, the squad leader, having called one or two firefighters out of action, orders to pack combat clothing and equipment in the first or second way, checks "
the correctness of the installation, indicates the mistakes made. Then he gives a command for putting on (combat clothes and equipment and checks the correct execution.
The task of the commander conducting training sessions with the squad is not only to issue a command, but also to monitor the actions of each firefighter, to notice and eliminate errors. To sum up the results of the exercise, the commander conducts a test in accordance with the requirements of the standards for fire drill training.
Commands for performing the exercise for packing combat clothing and equipment: "Put combat clothing and equipment in the first (second) way, for putting on combat clothing and equipment:" Put on combat clothing and equipment.
Fig.1. Laying of military clothes.
a) the first way;
b) the second way.
Laying of military clothes and equipment. A belt with a carbine and an ax fixed on it in a holster, folded in half or three times, is placed on a table (bench); buckle on top, hatchet in left side along the table (bench).
A canvas jacket, folded in the first or second way, fits on the belt, canvas trousers - on the jacket. The helmet is placed on the trousers with a protective visor towards the fireman. The podkasnik can be located next to the stowed combat clothing and equipment or inside the helmet. Canvas mittens, if the jackets have side pockets, are placed in pockets, in the absence of pockets - under the belt. The canvas jacket and trousers can be stowed in one of two ways.
First way. The jacket is folded lengthwise three times, inside out and doubled at the waist with the back up with the floors folded under it and fit with the collar to the edge of the table or bench.
Canvas trousers are first folded along the longitudinal seams of the trousers, then three times with an "accordion" so that the front section of the trousers is at the top with the edges bent outward, the straps are tucked into the folds of the trousers; Pants are placed on the jacket with a belt to the edge of the table (benches), a helmet on the trousers with a protective visor to the edge of the table (bench) (Fig. 1, a),
The second way. The canvas jacket is folded face up at the seams at the sides (right side on top), the sleeves are tucked back, then folded in half at the waist. - The collar is facing the farthest edge of the table (bench) from the fighter, ^ ^^^^ra^gp^^ the right and left sides are folded back. Tarpaulin trousers are folded along the length and tripled with an "accordion", the straps are tucked between the folds of the trousers. Pants are placed with a belt to the edge of the table (benches), a helmet on the trousers (Fig. 1.6).
The overalls of the driver keep within a cabin of the fire truck. The cloak and equipment of the head of the guard are hung on a hanger located at the lead vehicle. The helmet is placed on the hanger with the protective visor forward.
Putting on canvas trousers. The trainee removes the helmet from the combat clothing and puts it on the table (bench) to the right (left) side of the combat clothing. He takes with both hands the edges of the trousers belt bent outward, removes them from the place of laying, lowers them down - forward. Raises the right (left) leg, bent at the knee, with the toe extended down, threads it into the leg of the trousers until the foot comes out of the leg. In the same way, he passes the left (right) leg and the left (right) leg of the trousers and with the movement of both arms, bent at the elbows, up through the sides to the shoulders, without releasing the straps from the hands, puts them on the shoulders and fastens the button of the front of the trousers.
Putting on a canvas jacket. The trainee threads the hands of the outstretched hands into the sleeves of the jacket, then raises them up above the head (at the same time the jacket rises) so that its floors fall behind the back; puts his hands in the sleeves, lowers his hands, fastens all the buttons.
If the jacket is stowed in the second way, it is put on by alternately putting the hands through the sleeves. With this method, the helmet is put on before putting on the canvas trousers.
Putting on a belt. The fireman takes a step forward with his left foot, with his left hand he takes the belt from above at the buckle, thumb picks it up from below. Brings down with his left hand with a belt left hand, bent at the elbow, back to the waist and at the same time the right arm, bent at the elbow, also brings back. brush right hand(palm) grabs the belt at the end with the thumb from above.
With the movement of both hands forward, he circles the belt around himself, the left hand is at the buckle, the right hand is at the end of the belt, left leg attaches to the right. With his fingers, he threads the end of the belt into the buckle, fastens it, straightens the folds on the jacket.
Laying and putting on clothing special for protection against water and surfactant solutions. Special clothing is designed to protect firefighters from water and solutions on fires.
Clothing consists of a jacket and trousers. A jacket with a turn-down collar, single-breasted, fastened with four metal fasteners, has a waterproof chest valve, a detachable yoke. Trousers with shoulder straps have a removable warming lining up to the line of knees. The trousers have 24 cm long zippered vents at the bottom. "There is a shoulder strap under the jacket for carrying a holster with a fire axe.
Laying of military clothes and equipment.
The jacket is placed on the table (bench) in the first or second way; a life belt folded in half or three is placed on the jacket; on the belt - pants. The helmet is placed on the trousers with a protective visor (emblem) forward.
Putting on combat clothes and equipment. On command or signal - "Alarm" the fireman takes off his helmet and puts it next to the table or puts it on his head if the jacket is stowed in the second way; then he puts on trousers, a life belt with a carbine and an ax; puts on a jacket, fastens it with four metal fasteners, puts on a helmet (Fig. 2).
Thermal reflective suit. The heat-reflecting suit is placed on the table. First, gloves are placed, a jacket made of metallized fabric, then a rescue belt with a carabiner. Semi-overalls are placed on top. Next to the suit, a helmet and a helmet-mask are placed.

Putting on a heat reflective suit. A firefighter in a padded jacket and trousers tucked into leather (tarpaulin) or felted (with galoshes) boots stands at a distance of 1 m from the place where the heat-reflecting suit is laid.
At the command "Heat-reflecting suit - put on", the fireman puts on a semi-overalls with shoe covers on his legs and secures it with the help of shoulder straps. , He puts on a fire belt with a carbine on semi-overalls. Then he puts on a jacket made of metallized fabric on a wadded jacket and fastens it with all buttons. He puts on a helmet on his head and over it a helmet-mask with a cape, which is attached to the jacket with buttons in front and behind. He pulls mittens on his hands and fastens them with fastening straps using metal half rings.
Collection and departure on alarm. It is advisable to divide training in gathering and leaving on alarm into two stages: the first stage is building a squad, assigning a combat crew, building a combat crew at a fire truck, getting into the car and dismounting, the second stage is gathering on alarm, putting on combat clothes and equipment, landing in car, leaving the garage and following to the place of the call.
Development of the first stage. The squad leader builds a squad on the right side of the car, facing it, announces the content and purpose of the lesson, appoints a combat crew and shows the location of the squad near the car. To assign a combat crew, the squad leader calls the name of the fireman, assigns him the number of the combat crew. For example: firefighter Smirnov (Smirnov answers "I") - the first number (Smirnov answers "is"), etc.
The construction is performed several times. Then the squad leader shows each firefighter a place to get into the car and trains the squad from various positions to take a seat in the cab.
At the command "To the cars" or "Squad - stand up" the squad is built near the car, starting from the axle of the rear right wheel to the cab, in the first line the squad leader, firefighters No. 1, 3, 5, 7, in the second - firefighters No. 2, 4 , 6 and the driver (Fig. 3).
At the command "In places", the squad gets into the cab of the car, firefighters No. 1, 3, 7, 2 in the back seat, firefighters No. 4, 5, 6 - in the front. The squad leader sits next to the driver. On the tank truck, the squad sits in the second cabin in the order No. 1, 3, 4, 2. The commander is next to the driver.
The landing is considered completed when the combat crew takes their places in the car and closes the cabin doors.
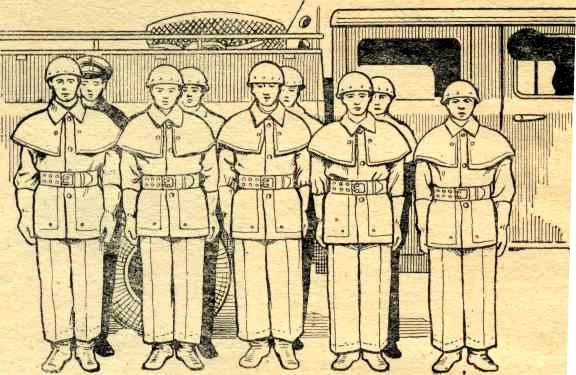

Rice. 3. Building a department at the pump truck, tank truck.
In this case, firefighters stand along the right (left) side of the car, with their backs to it, in the order of the numbers of the combat crew, the driver - on the left flank.
At the command "To the cars" ("Squad - stand up!"), the combat crew leaves the car and stands in two lines at the car on the right side (left) with its back to it.
Development of the second stage. The second stage includes gathering on alert, putting on combat clothing and equipment, getting into the car, getting a ticket, opening the gate, leaving the garage. do the exercise.
Gathering and leaving on alarm are learned after practicing the exercise - putting on combat clothing and equipment.
On a signal or command "Alarm", firefighters, regardless of location, run to the garage, while they are not allowed to throw clothes and household items on the way, stop in the aisles,
When using the descent column, each firefighter is obliged to maintain the necessary interval, watch those descending in front and not touch them with their feet. Having touched the mat at the base of the trigger column with your feet, you need to slightly push off the column and quickly move away from it.
Firefighters put on combat clothing and equipment, get into the cab, the driver starts the engine, the squad leader receives a ticket, firefighters No. 1, 2 open the garage door (if they do not open automatically), get into the cab and close the doors. The commander, taking a seat in the cab, announces the address of the fire, gives the command "March" to the driver, the driver takes the car out of the garage.
The procedure for boarding the personnel of departments and guards in fire trucks (in the garage or outside the garage) is established by the head of the fire department based on safety conditions and local characteristics.
It is prohibited to give a command to follow the cars to the place of the call before the end of boarding in the vehicles of the personnel. The landing is considered completed only when the personnel of the combat crew take their places in the car and close the cabin doors. When landing outside the garage, the exit of personnel to the site is allowed only after the vehicle has left.
The head car leaves first, the rest in the order of the established sequence.
During the movement of the vehicle, the personnel of the combat crew are prohibited from smoking, leaning out of windows, opening doors, standing on the steps, etc.
On command "Stop" the driver stops the car. When returning from a fire at the command "Sentry squad, stand up!" the personnel of the combat crew leaves the cab and line up at the car in accordance with the established procedure, after which the necessary instructions are given on preparing the car for the next departure.
According to this instruction, the combat crew, if necessary, replaces wet sleeves with dry ones, cleans technical equipment, wash cars and other work.
At the command "Car to the garage - put" the driver puts the car in its place, turns off the engine, firefighters No. 1 and 2 close the gates, the squad leader checks the refueling of combat clothing and equipment, sums up the lesson.
Communication training. Having built the students, the leader of the lesson explains the requirements for a liaison. A messenger must be literate, have good eyesight, hearing, memory and be able to navigate in a fire situation. The liaison officer must have a telephone directory, fire report forms, a notebook with clean paper and a pencil, an electric flashlight, a bag with a handset, a key to fire detectors (at facilities), a rescue rope, an oxygen insulating gas mask and a white armband with the letter C on the left sleeve . "
The leader tells the duties of a liaison on a fire. The messenger must follow all the orders of the commander at whose disposal he is, be able to establish communication by telephone from the fire detector of the radio station, call for additional help, know the procedure for submitting increased call numbers to a fire, transmitting information from a fire.
Then the head of the lesson talks about the procedure for transmitting orders to the senior, "commander to the junior. The training of messengers in the correct transmission of orders consists of various practical exercises. The head of the classes appoints two or three squad commanders from among the students, who are placed in different rooms (floors) at 15-20 m from each other. Then he announces to the messengers standing in the ranks that he (the leader) will act as the head of the fire extinguishing (RTP). After that, the commander moves away 6-7 meters from the messengers and calls them in turn to him For example: "Messenger No. 1, to me", "Messenger No. 1 arrived at your order". The head of the classes gives the order, adhering to the following order, where, to whom, what to convey. For example, to convey to the squad leader, "Open the roof to let the fireman pass."
The transmission of the order begins with the words "Comrade sergeant, the RTP ordered the roof to be opened to allow the fireman to pass." After the transfer of the order, having received permission from the squad leader, “to return, the messenger should run to the RTP and report to him: “Your order to the squad leader Sidorov (repeats the order) has been transmitted.”
Alternately calling the messengers out of action, the head of the lesson gives them orders. Then he replaces the commanders of departments and liaisons. In the process of learning, orders must be complicated and diversified.
Training and training of liaison officers in transmitting information about a fire should be carried out on existing telephones. The head announces the content and purpose of the lesson, tells the procedure for calling the Central Fire Communications Station (CPPS), announces a connected one - an approximate scheme for transmitting the first information about the lodge. Then one of the messengers is sent to the telephone to perform the duties of a telephone operator, who receives information about the fire. The rest are in service. Transmits an order to all liaisons to transmit information and in turn force it to transmit,
During the lesson, the leader complicates the content of the information, including the submission of an increased call number. Having received an order, the messenger transmits information by telephone, adhering to the following questions: who reports, the address of the fire (where it burns), whether additional assistance is required, what is burning, what forces and means are put into action, the phone number.
Standards for fire drill and tactical and special training- these are temporary, quantitative and qualitative indicators of the performance of certain tasks, methods and actions by employees (employees), cadets and students (hereinafter referred to as personnel) of the federal fire service, departments, duty guards (shifts), divisions of the federal fire service (hereinafter referred to as divisions of the FPS), educational institutions EMERCOM of Russia, in compliance with the sequence (order) set forth in the collection of standards.
Accounting for conditions, performing normalized exercises
| Group | Conditions | Correction values |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Terrain: | |
| - for mountainous terrain | 1,3 | |
| - ground area terrain | 1,1 | |
| - desert-sandy area | 1,2 | |
| - soils of the far north | 1,15 | |
| - in off-road conditions (thickness, blizzard, ice, heavy fog) | 1,2 | |
| 2 | At night without lighting | 1,6 |
| At night under moonlight (street) lighting | 1,1 | |
| 3 | Weather conditions: | |
| - compacted snow, sleet | 1,2 | |
| - in winter time hard (paved) terrain | 1,1 | |
| - at low temperatures over -20°C | 1,1 | |
| - at wind speed from 10 to 20 m/s | 1,2 | |
| - at wind speeds over 20 m/s | 1,3 | |
| 4 | Age and service life: | |
| - for performers of the first year of service | 1,1 | |
| - for performers under the age of 30 | 1,0 | |
| 31-35 | 1,1 | |
| 36-40 | 1,3 | |
| 41-45 | 1,4 | |
| 46-50 | 1,5 | |
| 51 and over | 1,8 | |
| - when acting as part of a group consisting of performers different ages, the coefficient is taken for the average age of all performers | ||
| 5 | Other conditions: | |
| - during actions in RPE (except for exercises, the implementation of which is provided for in RPE) | 1,5 | |
| - when performing exercises in a combined arms protective kit (special protective clothing) | 1,25 | |
| - when performing exercises in filtering gas masks (except for exercises that are provided for in gas masks) | 1,1 | |
| - when performing exercises with the release of water, for each sleeve of one main and one working line, 5 seconds are added to the standard time | ||
| - when performing an exercise when installing a mobile fire extinguishing equipment on a reservoir with filling the pump cavity with water, the standard time increases: | ||
| - for the standard "excellent" - for 60 seconds | ||
| - for the standard "good" - for 70 seconds | ||
| - for the standard "satisfactory" - for 80 seconds | ||
| - when performing an exercise with the installation of a mobile fire extinguishing equipment with a front and side suction pipe on the water source, the standard time increases: | ||
| - without water intake - for 2 seconds | ||
| - with water intake - for 5 seconds |
The time spent on eliminating the shortcomings made by the trainee (tested) is added to the time for fulfilling the standard, overall score is set according to the total time.
When the standards are met by a subdivision of the Federal Border Guard Service in a reduced composition, the time increases (decreases) by the corresponding percentage of absent personnel, unless this is indicated in the conditions for fulfilling the standard.
When working out the standards on the ground, the routes (directions) for the actions of the FPS units are not designated in advance and are not laid.
The procedure for determining the assessment
The standards are checked during inspections, final inspections of the activities of the territorial bodies of the Ministry of Emergency Situations of Russia, divisions of the FPS, as well as during scheduled and control classes and exercises.
If the standard is fulfilled several times (no more than three), then the mark for the fulfillment of the standards is determined by the last result shown.
The assessment for the fulfillment of the standard by personnel, squad, shift, guard is determined by:
- "excellent" if the standard is fulfilled correctly, in in full to the mark "excellent";
- "good", if the standard is fulfilled correctly, in full for the assessment of "good";
- "satisfactory", if the standard is fulfilled correctly, in full for the assessment of "satisfactory";
- "unsatisfactory" if the standard is fulfilled below the time for a positive assessment.
- "excellent" if more than half of the tested standards are met with an "excellent" rating, and the rest - with a "good" rating;
- "good" if more than half of the tested standards are met with a rating of at least "good", and the rest - with a rating of "satisfactory";
- "satisfactory" if at least 70% of the tested standards are met with a positive assessment, and when assessed according to three standards, two are met, while one of them is rated at least "good".
- "excellent", if at least 100% of employees (employees) received positive marks, while more than 50% of employees received an "excellent" rating;
- "good" if at least 100% of employees (workers) received positive ratings, while more than 50% of employees received a rating of at least "good";
- "satisfactory" if at least 90% of employees (workers) received positive ratings.
"excellent" if the first grade is "excellent" and the second is not lower than "good";
"good" if the first grade is "good" and the second is not lower than "satisfactory";
"satisfactory" if both marks are not lower than "satisfactory".
Regulations № № 1.1, 2.1, 3.2, 4.3, 5.7, 5.8, 7.3, 9.3, 10.4, 11.2 , are mandatory for implementation during inspections, final inspections of the activities of the territorial bodies of the Ministry of Emergency Situations of Russia, divisions of the Federal Border Guard Service, as well as in control classes.
List of standards
Below is a "standard" list of standards for fire drill and tactical and special training for employees of the FPS, according to the list1. Putting on combat and special clothing and equipment
1.1. Putting on combat clothes and equipment1.2. Putting on a heat reflective suit
1.3. Putting on the heat-reflective suit TK-800
2. Collection and departure on alarm with landing in the car outside the garage gate
2.1. Collection and departure on alarm (with landing in the car outside the garage gate)3. Actions with pressure fire hoses
3.1. Delivery of the RS-50 barrel at a distance of 40 m from the column installed on the hydrant3.2. Laying of the main hose line with a diameter of 77 mm by one performer for: n hoses
3.3. Laying of the main hose line with a diameter of 77 mm, calculated from 2 performers for n hoses
3.4. Laying of the main hose line with a diameter of 77 mm with a calculation of 3 performers for n hoses
4. Actions with means of rescue
4.1. Knitting a double rescue loop without putting it on the rescued4.2. Knitting a double rescue loop with putting it on the rescued
4.3. Attaching a rescue rope to a building structure (one of four methods)
4.4. Coiling the lifeline into a ball
4.5. Self-rescue from the 4th floor of the training tower using the device “Trigger kit standard (KSS-1)” 4.6. Self-rescue from the 4th floor of the training tower using a portable emergency self-rescue kit (KP-1(3))
4.7. Self-rescue from the 4th floor of the training tower using the fire and rescue system "SLIP-EVACUATOR" model "Compact"
4.8. Self-rescue with the help of the evacuation kit "Samospas"
4.9. Bringing in working position pneumatic jump rescue device PPSU-20 (life cube)
4.10. Bringing the tension rescue canvas (NSP) into working position.
5. Actions with fire escapes
5.1. Climbing a fixed ladder to a given height.5.2. Climbing a stationary ladder with a dry pressure-hose line with an attached trunk RS-50 to a predetermined height
5.3. Climbing an auto-ladder extended to a predetermined height
5.4. Climbing on a ladder with a dry hose line with an attached shaft RS-50 to a predetermined height
5.5. Carrying and hanging the assault ladder in the window of the second floor of the training tower
5.6. Climbing the suspended assault ladder to the 4th floor of the training tower
5.7. Climbing the assault ladder to the 4th floor of the training tower
5.8. Climbing the installed retractable ladder to the 3rd floor of the training tower
5.9. Installation of a retractable ladder in the window of the 3rd floor of the training tower using an AC vehicle on the chassis of ZIL, KAMAZ, URAL vehicles, foreign-made vehicles.
5.10. Installation of a retractable ladder in the window of the 3rd floor of the training tower without the use of AC.
5.11. Installing and climbing a retractable ladder to the window of the 3rd floor of the training tower using an AC vehicle on the chassis of ZIL, KAMAZ, URAL vehicles, foreign-made vehicles.
5.12. Installing and climbing a retractable ladder into the window of the 3rd floor of the training tower without using the AC.
6. Overcoming a 100 meter obstacle course.
6.1. Overcoming a 100-meter obstacle course.7. Deployment of pump-hose systems.
7.1. Installing a tank truck on a fire hydrant7.2. Installing a first aid vehicle on a fire hydrant
7.3. Installation of a tank truck on a reservoir (2 sleeves x 4m)
7.4. Installation of a tank truck on a reservoir (4 sleeves x 2m)
7.5. Fire installation pumping station to the body of water
7.6. Installation of a motor pump MP-600 (MP-800) on a pond
7.7. Installation of motor pump MP-1600 on a reservoir
7.8. Combat deployment from a tank truck with the supply of one barrel "B"
7.9. Combat deployment from a tank truck with its installation on a reservoir (hydrant) and the supply of one barrel "B" from one main line
7.10. Combat deployment from a tank truck with its installation on a reservoir (hydrant) and the supply of two barrels "B" from one main line
7.11. Combat deployment from a tank truck with its installation on a reservoir (hydrant) and the supply of two barrels "B" from two main lines
7.12. Combat deployment from a tank truck with the supply of one barrel "B" from one main line to the window of the 3rd floor of the training tower along the installed retractable ladder
7.13. Combat deployment from a tanker truck with a high pressure pump
7.14. Combat deployment from a powder extinguishing vehicle with a single barrel feed
7.15. Combat deployment from a powder extinguishing vehicle with two barrels
7.16., 7.17, 7.18 Combat deployment from a carbon dioxide extinguishing vehicle
7.19. Water supply from a tank truck using a hydraulic elevator
8. Deployment of primary fire fighting equipment.
8.1. Elimination of a simulated fire from a fire hydrant.8.2. Elimination of the source of fire with the help of a felt mat.
8.3. Putting out the fire with a fire extinguisher.
8.4. Extinguishing a fire with water from a fire barrel or reservoir using fire buckets.
9. Deployment of fire and rescue equipment.
9.1. Installation of an electric smoke exhauster with deployment of a cable line for 60 m and installation of a power distribution box9.2. Preparation of GASI for work
9.3. Cutting steel reinforcement d 18 mm using GASI
9.4. cutting metal profiles and reinforcing steel in reinforced concrete structures grinder
9.5. Deployment, start-up of the motor pump and filling the vehicle tank with water
10. Radiation, chemical and biological protection.
10.1. Checking insulating gas masks and preparing them for use10.2. Putting on a filtering gas mask or respirator
10.3. Use of a defective filtering gas mask in a contaminated atmosphere
10.4. Putting on a combined arms protective kit and a filtering gas mask individually
10.5. Putting on a special protective clothing and gas mask
10.6. Actions for the outbreak of a nuclear explosion
10.7. Actions on the signal "Radiation danger"
10.8. Actions on the signal "Chemical alarm". When operating on the ground
10.9. Assessment of the chemical situation in the event of destruction (accidents) of objects with hazardous chemicals
10.10. Preparation of devices for radiation, chemical, non-specific bacteriological (biological) reconnaissance and radiation monitoring for operation and verification of their performance
10.11. Preparation of devices for radiation, chemical, non-specific bacteriological (biological) reconnaissance and radiation monitoring for work and checking their performance.
10.12. Preparing the dosimeter-radiometer DRBP-01 for operation
10.13. Preparation for operation of the PASSPORT gas analyzer
10.14. Determination of toxic substances in the air with instruments
10.15. Partial special treatment for contamination with radioactive substances
10.16. Degassing, decontamination, disinfection of fire and rescue equipment
11. First aid
11.1. Deployment of an individual dressing package11.2. Primary dressing
11.3. The imposition of a rubber tourniquet on the thigh (shoulder)
11.4. Applying a twist with a scarf and other improvised means on the thigh (shoulder).
11.5. Overlay splints from improvised material
11.6. Putting on a helmet - a gas mask on the victim.
11.7. Using a syringe - a tube from an individual first aid kit (AI).
Sources
- Standards for fire drill and tactical and special training for personnel of the Federal Fire Service. approved 05/10/2011.
This page has no curators!





