How is RAM decrypted on a computer. What is RAM and why is RAM required in a computer
Now, having learned what it is and why and how it serves, many of you are probably thinking about getting a more powerful and productive RAM for your computer. After all, increasing computer performance with the help of additional memory RAM is the simplest and cheapest (unlike a video card, for example) method of upgrading your pet.
And ... Here you are standing at the showcase with packages of RAM. There are many and they are all different. Questions arise: And what RAM to choose?How to choose the right RAM and not miscalculate?What if I buy a RAM, and then it will not work? These are perfectly reasonable questions. In this article, I will try to answer all these questions. As you already understood, this article will take its rightful place in the series of articles in which I wrote about how to choose the right individual computer components i.e. iron. If you haven't forgotten, the articles included:
—
—
—
This cycle will continue further, and at the end you will be able to assemble a perfect super computer for yourself in every sense 🙂 (if finances allow, of course :))
In the meantime learning how to choose the right RAM for your computer.
Go!
RAM and its main characteristics.
When choosing RAM for your computer, you must definitely build on your motherboard and processor, because RAM modules are installed on the motherboard and it also supports certain types of RAM. Thus, the relationship between the motherboard, processor and RAM is obtained.

Find out about What RAM does your motherboard and processor support? you can visit the manufacturer's website, where you need to find the model of your motherboard, as well as find out which processors and RAM it supports for them. If this is not done, it will turn out that you bought a super modern RAM, but it is not compatible with your motherboard and will gather dust somewhere in your closet. Now let's go directly to the main technical characteristics of RAM, which will serve as a kind of criteria when choosing RAM. These include:
Here I have listed the main characteristics of RAM, which you should pay attention to first of all when buying it. Now let's open each of them in turn.
RAM type.
Today, the most preferred type of memory in the world are memory modules. DDR(double data rate). They differ in time of release and of course technical parameters.
- DDR or DDR SDRAM(translated from English. Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory - synchronous dynamic memory with random access and double the data transfer rate). Modules of this type have 184 contacts on the bar, are powered by a voltage of 2.5 V and have a clock frequency of up to 400 megahertz. This type of RAM is already obsolete and is used only in old motherboards.
- DDR2- a type of memory that is widely used at this time. It has 240 contacts on the printed circuit board (120 on each side). Consumption, unlike DDR1, is reduced to 1.8 V. The clock frequency ranges from 400 MHz to 800 MHz.
- DDR3- the leader in performance at the time of this writing. It is no less common than DDR2 and consumes 30-40% less voltage than its predecessor (1.5 V). Has a clock frequency up to 1800 MHz.
- DDR4- a new, super modern type of RAM, ahead of its counterparts both in performance (clock frequency) and voltage consumption (which means less heat dissipation). Announced support for frequencies from 2133 to 4266 MHz. At the moment, these modules have not yet entered mass production (they promise to release them into mass production in mid-2012). Officially, fourth-generation modules operating in the DDR4-2133 at a voltage of 1.2 V were presented at CES by Samsung on January 04, 2011.
The amount of RAM.
I will not write much about the amount of memory. Let me just say that it is in this case that size matters 🙂
All a few years ago, 256-512 MB of RAM satisfied all the needs of even cool gaming computers. Currently, for the normal functioning of the windows 7 operating system alone, 1 GB of memory is required, not to mention applications and games. There will never be an extra RAM, but I'll tell you a secret that 32-bit windows uses only 3.25 GB of RAM, even if you install all 8 GB of RAM. You can read more about this.
The dimensions of the slats or the so-called Form Factor.
Form-factor- these are the standard sizes of RAM modules, the type of design of the RAM strips themselves.
DIMM(Dual InLine Memory Module - double-sided type of modules with contacts on both sides) - mainly designed for desktop stationary computers, and SODIMM used in laptops.
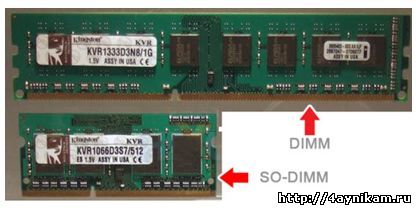
Clock frequency.
This is a pretty important technical parameter of RAM. But the motherboard also has a clock frequency, and it is important to know the operating bus frequency of this board, since if you bought, for example, a RAM module DDR3-1800, and the slot (connector) of the motherboard supports the maximum clock frequency DDR3-1600, then the RAM module as a result will operate at a clock frequency of 1600 MHz. In this case, all sorts of failures, errors in the operation of the system and are possible.

Note: Memory bus speed and processor speed are completely different concepts.

From the above tables, you can understand that the bus frequency, multiplied by 2, gives the effective memory frequency (indicated in the “chip” column), i.e. gives us the data transfer rate. The title tells us the same. DDR(Double Data Rate) - which means double the data rate.
For clarity, I will give an example of decoding in the name of the RAM module - Kingston/PC2-9600/DDR3(DIMM)/2Gb/1200MHz, where:
— Kingston- manufacturer;
— PC2-9600— the name of the module and its throughput;
- DDR3(DIMM)- type of memory (form factor in which the module is made);
— 2GB is the volume of the module;
- 1200MHz— effective frequency, 1200 MHz.
throughput.
Bandwidth- a characteristic of memory, on which the performance of the system depends. It is expressed as the product of the system bus frequency and the amount of data transmitted per clock cycle. Bandwidth (peak data rate) is a composite measure of the capability RAM, it takes into account baud rate, bus width and the number of memory channels. The frequency indicates the potential of the memory bus per clock - at a higher frequency, more data can be transferred.
The peak indicator is calculated by the formula: B=f*c, where:
B is the bandwidth, f is the transmission frequency, c is the bus width. If you use two channels for data transmission, multiply everything received by 2. To get a figure in bytes / s, you need to divide the result by 8 (because there are 8 bits in 1 byte).
For better performance memory bus bandwidth And processor bus bandwidth must match. For example, for an Intel core 2 duo E6850 processor with a 1333 MHz system bus and a bandwidth of 10600 Mb / s, you can install two modules with a bandwidth of 5300 Mb / s each (PC2-5300), in total they will have a system bus bandwidth (FSB) equal to 10600 Mb/s.
Bus frequency and bandwidth are denoted as follows: " DDR2-XXXX" And " PC2-YYYY". Here "XXXX" indicates the effective memory frequency, and "YYYY" indicates the peak bandwidth.
Timings (latency).
Timings (or latency)- these are the time delays of the signal, which, in the technical characteristics of the RAM, are written as " 2-2-2 " or " 3-3-3 " etc. Each digit here expresses a parameter. In order, it's always CAS Latency” (cycle time), “ RAS to CAS Delay” (full access time) and “ RAS Precharge Time» (precharge time).
Note
So that you can better understand the concept of timings, imagine a book, it will be our RAM, which we access. Information (data) in a book (RAM) is divided into chapters, and chapters consist of pages, which in turn contain tables with cells (like in Excel tables). Each cell with data on the page has its own vertical (columns) and horizontal (rows) coordinates. The RAS (Raw Address Strobe) signal is used to select a row, and the CAS (Column Address Strobe) signal is used to read a word (data) from the selected row (i.e., to select a column). A complete reading cycle begins with the opening of the "page" and ends with its closing and reloading, because. otherwise, the cells will be discharged and the data will be lost. This is how the algorithm for reading data from memory looks like:
- the selected "page" is activated by the RAS signal;
- data from the selected row on the page is transmitted to the amplifier, and the data transfer requires a delay (called RAS-to-CAS);
- a CAS signal is given to select (column) a word from that row;
- data is transferred to the bus (from where it goes to the memory controller), while there is also a delay (CAS Latency);
- the next word goes already without a delay, since it is contained in the prepared line;
- after the row access is completed, the page is closed, the data is returned to the cells, and the page is recharged (the delay is called RAS Precharge ).
Each digit in the designation indicates how many bus cycles the signal will be delayed. Timings are measured in nano-seconds. The numbers can have values from 2 to 9 . But sometimes a fourth one is added to these three parameters (for example: 2-3-3-8 ), called " DRAM Cycle Time Tras/Trc” (characterizes the performance of the entire memory chip as a whole).
It happens that sometimes a cunning manufacturer indicates only one value in the characteristics of the RAM, for example " CL2” (CAS Latency), the first timing is equal to two cycles. But the first parameter does not have to be equal to all timings, and maybe less than others, so keep this in mind and don't fall for the manufacturer's marketing ploy.
An example to illustrate the impact of timings on performance: a system with 100 MHz memory with 2-2-2 timings has about the same performance as the same system at 112 MHz, but with 3-3-3 delays. In other words, depending on latency, the performance difference can be as high as 10%.
So, when choosing, it is better to buy memory with the lowest timings, and if you want to add a module to an already installed one, then the timings of the purchased memory must match the timings of the installed memory.
Memory modes.
RAM can work in several modes, unless of course such modes are supported by the motherboard. This single channel, two-channel, three-channel and even four-channel modes. Therefore, when choosing RAM, you should pay attention to this parameter of the modules.
Theoretically, the speed of the memory subsystem in the dual-channel mode increases by 2 times, in the three-channel mode - by 3 times, respectively, etc., but in practice, in the dual-channel mode, the performance increase, in contrast to the single-channel mode, is 10-70%.
Let's take a closer look at the types of modes:
- Single channel mode(single-channel or asymmetric) - this mode is enabled when only one memory module is installed in the system or all modules differ from each other in terms of memory size, frequency of operation, or manufacturer. It does not matter in which slots and which memory to install. All memory will run at the speed of the slowest memory installed.
- dual mode(dual-channel or symmetrical) - the same amount of RAM is installed in each channel (and theoretically there is a doubling of the maximum data transfer rate). In dual-channel mode, memory modules work in pairs 1st with 3rd and 2nd with 4th.
- Triple Mode(three-channel) - the same amount of RAM is installed in each of the three channels. Modules are selected by speed and volume. To enable this mode, modules must be installed in slots 1, 3, and 5/or 2, 4, and 6. In practice, by the way, this mode is not always more productive than dual-channel, and sometimes even loses to it in data transfer speed.
- Flex Mode(flexible) - allows you to increase the performance of RAM when installing two modules of different sizes, but the same frequency. As in the dual-channel mode, memory boards are installed in the same-named connectors of different channels.
Usually the most common option is dual-channel memory mode.
To work in multichannel modes, there are special sets of memory modules - the so-called Kit memory(Kit-set) - this kit includes two (three) modules, from the same manufacturer, with the same frequency, timings and memory type.
Appearance of KIT-sets:
for dual channel mode

for 3-channel mode

But the most important thing is that such modules are carefully selected and tested by the manufacturer to work in pairs (triples) in two- (three-) channel modes and do not imply any surprises in operation and configuration.
Module manufacturer.
Now on the market RAM well-established manufacturers such as: Hynix, amsung, Corsair, Kingmax, Transcend, Kingston, OCZ…
Each company has its own for each product. marking number, by which, if you decipher it correctly, you can find out for yourself a lot of useful information about the product. For example, let's try to decipher the module marking Kingston families ValueRAM(see image):

Decryption:
- KVR– Kingston ValueRAM i.e. manufacturer
- 1066/1333 – operating/effective frequency (Mhz)
- D3- type of memory (DDR3)
- D (Dual) - rank / rank. A dual-rank module is two logical modules soldered on the same physical one and using the same physical channel in turn (required to achieve the maximum amount of RAM with a limited number of slots)
- 4 – 4 DRAM memory chips
- R-Registered, indicates stable operation without failures and errors for as long as possible a continuous period of time
- 7 – signal delay (CAS=7 )
- S– temperature sensor on the module
- K2- a set (kit) of two modules
- 4G- the total volume of the whale (both bars) is 4 GB.
I will give another example of marking CM2X1024-6400C5:
It can be seen from the label that this DDR2 module volume 1024 MB standard PC2-6400 and delays CL=5.
Stamps OCZ, Kingston And Corsair recommended for overclocking, i.e. have overclocking potential. They will be with low timings and a clock frequency margin, plus they are equipped with heatsinks, and some even coolers to remove heat, because. during acceleration, the amount of heat increases significantly. The price for them will naturally be much higher.
I advise you not to forget about fakes (there are a lot of them on the shelves) and buy RAM modules only in serious stores that will give you a guarantee.
Finally:
That's all. With the help of this article, I think you will not be mistaken when choosing RAM for your computer. Now you can choose the right operator for the system and improve its performance without any problems. Well, for those who buy RAM (or have already bought it), I will dedicate the next article, in which I will describe in detail how to properly install RAM into the system. Do not miss…
Best RAM 2019
Corsair Dominator Platinum

The best memory among classmates with high performance and innovation in RGB technology. Standard DDR4, speed 3200MHz, default timings 16.18.18.36, two modules of 16 gigabytes. The bars have bright Capellix RGB LEDs, an advanced iCUE program, and Dominator DHX heatsinks. The only problem is that the height of the module may not fit.
Corsair, as always, surpasses itself with each new model, Dominator Platinum is no exception. Today it is the favorite set of DDR4 memory for gamers and owners of powerful workstations. The appearance of the modules is sleek and stylish, appealing to gamers, DHX cooling works efficiently, and the performance of the bars is already ready to become a legend. In any case, for many years it will provide the user with flagship parameters. Now the memory has a new design, a new, brighter Corsair Capellix 12 LED backlight. Software (proprietary) iCUE provides flexible memory configuration for maximum performance. If you have changed the motherboard or processor, and maybe the graphics accelerator, you can configure the memory for any new component as native.
The price tag of the memory is slightly higher than that of other manufacturers, but this is offset by the highest quality and amazing performance.
The abbreviation RAM stands for Random Access Memory. In the world of computers, laptops, tablets and smartphones, random access memory (RAM) is a special device designed to store and change information while the computer is running. What is she for? I will try to explain the principle of operation of the RAM "on the fingers". Let's say you turn on your computer and run a program. First, it will be read from the hard disk of a computer or laptop, and then transferred to RAM. Here it will hang until the application terminates and, if necessary, it will change, erase, append, rewrite the values of the used parameters and variables necessary for the program to function.
But why is this necessary if the application is already written in read-only memory (ROM), that is, on the hard disk?! But why. RAM works at a very fast speed, many times the speed of reading and changing data on a computer's hard drive. That is why, in order for the software to work quickly, the operating system transfers it to RAM. The main feature of its work is that information is lost after turning off the power of the PC.
Structurally, this type of memory is made in the form of a small board with pads with memory cells soldered onto it in a row. Cells can be located on one or both sides of the microcircuit. In the slang of system administrators, one such board is called a "bank" or "die".
Abbreviation used abroad RAM- Random Access Memory - which means "Random Access Memory".
The main characteristics of the work of RAM - baud rate(Gbps) and memory bus clock frequency (MHz).
With the speed of information transfer, I think it's understandable. And what is the "frequency of RAM" ?! In simple words, this is the speed of operations. More complex language is the speed of signal exchange between the PC central processor and the RAM module. The higher the frequency, the faster the RAM runs. In this case, it is worth considering also the so-called "Timings". Timing is the time delay of a signal. Another name is Latency. Imagine that two completely identical memory modules in terms of speed and frequency can have completely different bandwidth. And the whole point is just in the timings, which show how many clock cycles of the processor the chip manages to perform a certain operation. The lower the timings, the faster the RAM works.
DIMM, SDRAM, DDR - what is it?!
These are abbreviations used to label RAM sticks and indicate the manufacturing technology used and the type of chips used.
DIMM- This is a double-sided board, where the contacts to the RAM cells are located on both sides of the module - Dual In-Line Memory Module. They came to replace SIMM, which is currently not used. There were also modules. RIMM, which Intel tried to promote with its Pentium 4 processor, but they never caught on.
SDRAM- This is the type of RAM that is currently used on all computers and laptops. It stands for "Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory", which translated into great and mighty means: "synchronous dynamic random access memory."
DDR, DDR2, DDR3, DDR4 is the type of SDRAM sticks used. The abbreviation means "Double Data Rate", that is, "Double Data Rate". To date, there are already 4 types, the most modern of them today is DDR4 with a frequency of 2800 MHz (PC22400). This type has just appeared on the market, but it is planned that by the end of 2016 it will completely dominate the market.
GDDR- a type of RAM for video cards, which differs from conventional DDR used on computers and laptops by a higher frequency of operation, as well as lower power consumption and heat dissipation. The most modern type of RAM for video cards is GDDR5.
To see the amount of installed RAM on a computer or laptop, it is absolutely not necessary to disassemble it. This information can be viewed in the information from the operating system. In particular, in Windows 7, 8 or Windows 10, just go to "System Properties" through the "Toolbar" or press the key combination win+pause. The following window will open:
In the "System" section, we look at the line "Installed memory (RAM)", it just indicates how much RAM costs.
If you need to find out more advanced information - how many RAM modules are installed, what volume, timings and frequency of sticks - use one of the special diagnostic utilities - Aida64, Everest, SiSoft Sandra etc. Their interface is about the same. We go into the summary of information on the installed equipment "Summary" and look at the section "Motherboard" (Motherboard), line "System Memory" (System Memory):
How to increase the amount of RAM?!
Here the answer is very simple - we go to the store and buy. But before you hit the road - run one of the above programs and see how many modules are already installed on the motherboard and if there are free spaces. Then, write down the name, brand, model, and frequency of the RAM sticks you are using. Well, or just take a picture of the information window on your phone and show it to the sales assistant in the store. Next, he will already offer a choice of available goods.
When buying a flash drive, many people ask themselves the question: "how to choose the right flash drive." Of course, choosing a flash drive is not so difficult if you know exactly for what purposes it is purchased. In this article I will try to give a complete answer to the question posed. I decided to write only about what to look for when buying.
A flash drive (USB drive) is a drive designed to store and transfer information. The flash drive works very simply without batteries. You just need to connect it to the USB port of your PC.
1. Flash drive interface
At the moment there are 2 interfaces: USB 2.0 and USB 3.0. If you decide to buy a USB flash drive, then I recommend taking a USB 3.0 USB flash drive. This interface was made recently, its main feature is a high data transfer rate. We'll talk about speeds a little later.
This is one of the main parameters that you need to look at first. Now flash drives are sold from 1 GB to 256 GB. The cost of a flash drive will directly depend on the amount of memory. Here you need to immediately decide for what purpose a flash drive is bought. If you are going to store text documents on it, then 1 GB is enough. For downloading and transferring movies, music, photos, etc. you need to take the more, the better. To date, the most popular are flash drives with a capacity of 8GB to 16GB.
3. Body material

The body can be made of plastic, glass, wood, metal, etc. Flash drives are mostly made of plastic. There is nothing I can advise here, it all depends on the preferences of the buyer.
4. Transfer rate
Earlier I wrote that there are two standards USB 2.0 and USB 3.0. Now I will explain how they differ. The USB 2.0 standard has a read speed of up to 18 Mbps and a write speed of up to 10 Mbps. The USB 3.0 standard has a read speed of 20-70 Mbps, and a write speed of 15-70 Mbps. Here, I think, nothing needs to be explained.

Now in stores you can find flash drives of different shapes and sizes. They can be in the form of jewelry, fancy animals, etc. Here I would advise taking flash drives that have a protective cap.
6. Password protection
There are flash drives that have a password protection feature. Such protection is carried out using a program that is located in the flash drive itself. The password can be set both on the entire flash drive, and on part of the data in it. Such a flash drive will primarily be useful to people who transfer corporate information in it. According to the manufacturers, if you lose it, you don't have to worry about your data. Not so simple. If such a flash drive falls into the hands of an understanding person, then hacking it is just a matter of time.
Such flash drives look very beautiful, but I would not recommend buying them. Because they are very fragile and often break in half. But if you are a neat person, then feel free to take it.
Output
Nuances, as you noticed, a lot. And this is just the tip of the iceberg. In my opinion, the most important parameters when choosing: the standard of a flash drive, the volume and speed of writing and reading. And everything else: design, material, options - this is just a personal choice of everyone.Good afternoon my dear friends. In today's article, I want to talk about how to choose the right mouse pad. When buying a rug, many do not attach any importance to this. But as it turned out, this moment needs to be given special attention, because. mat determine one of the indicators of comfort while working at a PC. For an avid gamer, choosing a rug is a completely different story. Consider what options for mouse pads have been invented today.

Mat options
1. Aluminum2. Glass
3. Plastic
4. Rubberized
5. Double sided
6. Helium
And now I would like to talk about each species in more detail.
1. First, I want to consider three options at once: plastic, aluminum and glass. These mats are very popular with gamers. For example, plastic mats are easier to find commercially. On such mats, the mouse glides quickly and accurately. And most importantly, these mats are suitable for both laser and optical mice. Aluminum and glass mats will be a little more difficult to find. And yes, they will cost a lot. The truth is for what - they will serve for a very long time. Rugs of these types have small flaws. Many people say that they rustle and feel a little cool when used, which may cause discomfort for some users.

2. Rubberized (rag) mats have a soft glide, but the accuracy of their movements is worse. For ordinary users, such a rug will be just right. Yes, and they are much cheaper than the previous ones.

3. Double-sided mousepads are, in my opinion, a very interesting kind of mousepads. As the name implies, these rugs have two sides. As a rule, one side is high-speed, and the other is high-precision. It happens that each side is designed for a certain game.

4. Helium pads have a silicone cushion. She allegedly supports her hand and relieves tension from it. For me personally, they were the most uncomfortable. By appointment, they are designed for office workers, since they sit at the computer all day. For ordinary users and gamers, these mats are not suitable. The mouse slides very poorly on the surface of such rugs, and their accuracy is not the best.

Mat sizes
There are three types of rugs: large, medium and small. It all depends on the taste of the user. But as is commonly believed, large rugs are well suited for games. Small and medium ones are taken mainly for work.Rugs design
In this regard, there are no restrictions. It all depends on what you want to see on your rug. The blessing now on rugs that only do not draw. The most popular are the logos of computer games such as DotA, Warcraft, ruler, etc. But if it happened that you could not find a rug with the pattern you need, do not be upset. Now you can order a print on the rug. But such rugs have a minus: when printing is applied to the surface of the rug, its properties deteriorate. Design for quality.
 On this I want to end the article. From myself I wish you to make the right choice and be happy with it.
On this I want to end the article. From myself I wish you to make the right choice and be happy with it.
Who does not have a mouse or wants to replace it with another, I advise you to look at the article:.
Monoblocks from Microsoft have replenished with a new monoblock model called Surface Studio. Microsoft presented its new product recently at an exhibition in New York.

On a note! I wrote an article a couple of weeks ago where I reviewed the Surface monoblock. This monoblock was presented earlier. Click on to view the article.
Design
Microsoft calls its new product the thinnest monoblock in the world. With a weight of 9.56 kg, the thickness of the display is only 12.5 mm, the other dimensions are 637.35x438.9 mm. The display dimensions are 28 inches with a resolution greater than 4K (4500x3000 pixels), aspect ratio 3:2.
On a note! The display resolution of 4500x3000 pixels corresponds to 13.5 million pixels. This is 63% more than 4K resolution.
The monoblock display itself is touch-sensitive, enclosed in an aluminum case. On such a display, it is very convenient to draw with a stylus, which ultimately opens up new possibilities for using a monoblock. In my opinion, this monoblock model will appeal to creative people (photographers, designers, etc.).

On a note! For people of creative professions, I advise you to look at an article where I considered monoblocks of similar functionality. Click on the selected one: .
To everything written above, I would add that the main feature of the monoblock will be its ability to instantly turn into a tablet with a huge work surface.

On a note! By the way, Microsoft has another amazing candy bar. To find out about it, go to.
Specifications
I will present the characteristics in the form of a photograph.
From the periphery, I note the following: 4 USB ports, a Mini-Display Port connector, an Ethernet network port, a card-reader, a 3.5 mm audio jack, a 1080p webcam, 2 microphones, a 2.1 Dolby Audio Premium audio system, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth 4.0. It also supports Xbox wireless controllers.



Price
When buying a monoblock, it will be installed with Windows 10 Creators Update. This system should be released in the spring of 2017. This operating system will have updated Paint, Office, etc. The price of a monoblock will be from $ 3,000.Dear friends, write in the comments what you think about this monoblock, ask your questions. I'll be glad to chat!
OCZ has demonstrated new VX 500 SSDs. These drives will be equipped with Serial ATA 3.0 interface and are made in 2.5-inch form factor.

On a note! For those who are interested in how SSD drives work and how long they live, you can read in an article I wrote earlier:.The novelties are made using 15-nanometer technology and will be equipped with Tochiba MLC NAND flash memory microchips. The controller in SSD drives will be used by Tochiba TC 35 8790.
The VX 500 drive lineup will consist of 128GB, 256GB, 512GB and 1TB. According to the manufacturer, the sequential read speed will be 550 Mb/s (this is for all drives in this series), but the write speed will be from 485 Mb/s to 512 Mb/s.

The number of input / output operations per second (IOPS) with data blocks of 4 KB in size can reach 92,000 when reading, and 65,000 when writing (this is all arbitrary).
The thickness of OCZ VX 500 drives will be 7 mm. This will allow them to be used in ultrabooks.


Prices of new products will be as follows: 128 GB - $ 64, 256 GB - $ 93, 512 GB - $ 153, 1 TB - $ 337. I think in Russia they will cost more.
Lenovo has unveiled its new IdeaCentre Y910 gaming all-in-one at Gamescom 2016.

On a note! Earlier, I wrote an article where I already considered gaming monoblocks from different manufacturers. This article can be viewed by clicking on this one.

The novelty from Lenovo received a 27-inch frameless display. The display resolution is 2560x1440 pixels (this is QHD format), the refresh rate is 144 Hz, and the response time is 5 ms.

The monoblock will have several configurations. The maximum configuration includes a 6th generation Intel Core i7 processor, a hard drive up to 2 TB or 256 GB. The amount of RAM is 32 GB DDR4. The video card NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1070 or GeForce GTX 1080 with Pascal architecture will be responsible for the graphics. Thanks to such a video card, it will be possible to connect a virtual reality helmet to the monoblock.
From the periphery of the monoblock, I would single out the Harmon Kardon audio system with 5-watt speakers, the Killer DoubleShot Pro Wi-Fi module, a webcam, USB 2.0 and 3.0 ports, and HDMI connectors.

In the basic version, the IdeaCentre Y910 monoblock will be available in September 2016 at a price of 1800 euros. But the monoblock with the version of "VR-ready" will appear in October at a price of 2200 euros. It is known that this version will have a GeForce GTX 1070 graphics card.
MediaTek has decided to upgrade its Helio X30 mobile processor. So now the developers from MediaTek are designing a new mobile processor called Helio X35.

I would like to briefly talk about Helio X30. This processor has 10 cores, which are combined into 3 clusters. Helio X30 has 3 variations. The first - the most powerful - consists of Cortex-A73 cores with a frequency of up to 2.8 GHz. There are also blocks with Cortex-A53 cores with a frequency of up to 2.2 GHz and Cortex-A35 with a frequency of 2.0 GHz.

The new Helio X35 processor also has 10 cores and is being created using 10nm technology. The clock frequency in this processor will be much higher than that of its predecessor and ranges from 3.0 Hz. The novelty will allow you to use up to 8 GB LPDDR4 RAM. The Power VR 7XT controller will most likely be responsible for the graphics in the processor.
The station itself can be seen in the photographs in the article. In them we can observe the drive bays. One bay with a 3.5" jack and the other with a 2.5" jack. Thus, both a solid state disk (SSD) and a hard disk drive (HDD) can be connected to the new station.

The dimensions of the Drive Dock station are 160x150x85mm, and the weight is no less than 970 grams.
Many people probably have a question about how the Drive Dock connects to a computer. The answer is: this happens through a USB 3.1 Gen 1 port. According to the manufacturer, the sequential read speed will be 434 Mb / s, and in write mode (serial) 406 Mb / s. The novelty will be compatible with Windows and Mac OS.

This device will be very useful for people who work with photo and video materials at a professional level. You can also use Drive Dock to back up files.
The price for a new device will be acceptable - it is $ 90.
On a note! Previously, Renduchinthala worked at Qualcomm. And since November 2015, he moved to a competing company Intel.

In his interview, Renduchintala did not talk about mobile processors, but only said the following, and I quote: "I prefer to talk less and do more."
Thus, the top manager of Intel made an excellent intrigue with his interview. We just have to wait for more announcements in the future.
And again, hello everyone! Today we will talk about RAM. What is working memory? What is it for? How it works? What types of RAM are there? What characteristics should you pay attention to when choosing it? You will find answers to these questions below in this article. And let's start in order.
What is working memory?
Random access memory - it is also RAM (Random Access Memory), RAM (random access memory), memory, RAM - a volatile part of a computer memory system in which executable machine code (programs) is stored during computer operation, as well as input, output and intermediate data processed by the processor.
Physically, the RAM module is embodied in the form of such strips that are inserted into a special slot on:

Here, in principle, I answered the first two questions. Although no, little is clear from this definition to the average person. But now we will analyze everything in detail. So.
There are several types of memory in a computer: energy NOT dependent and volatile or temporary.
Non-volatile memory is any memory device that can store data whether it is powered or not. In a computer, this is . You can save a file on it, disconnect your computer from the network, and the next time you turn it on again, everything will remain in place.
Volatile memory is computer memory that needs constant power to store information. Such in a computer is RAM. Which means that if you turn off the power from it (turn off the computer), all the information stored in it will disappear. That is, every time you turn on the computer, its RAM is empty.
I think this is understandable. The next part of the definition answers our next question.
What is RAM for?
A fair question would be: why in addition to a hard drive on which data is stored regardless of whether power is supplied to it or not, why does a computer need an additional, so unreliable thing like RAM?
The fact is that in comparison with the speed of work, the speed of reading and writing to the hard disk is very small. And if the processor directly worked with it, then the performance of the computer would be very low.
RAM is much faster than a hard drive. If you do not take into account the various caches, then the RAM will be the fastest element in a computer device, after the central processing unit.
Thus, RAM is needed to increase the performance of the computer, due to the fact that it allows the latter to quickly receive the necessary data.
How does it all work?
When you start the computer, all the necessary data: the operating system kernel, drivers, various services and startup programs are loaded from the hard disk into RAM and from there the CPU takes them for processing. The processor also returns the results of its work to RAM and not to the hard disk. Every program, every window you open in any program on your computer resides in RAM. The central processor also works with it. And only when you save some results of your work, they are written to the hard disk.
To better understand, let's look at a simple example of creating a text document in Word.
When you click on the shortcut to launch the program, all the files necessary for its operation are loaded into RAM and after that the editor window appears on the computer monitor. When you start writing text, it is also in RAM, you just won’t find it on your hard drive. In order for the result of your work to be saved on it, it must be saved by clicking the button of the same name in Word. Everyone at least once had such that you write, write some text and suddenly closed the program or the computer turned off, and after turning it on again, your text disappeared. Precisely because the RAM has been reset to zero, and you have never bothered to save your creativity.
I think now you already understand what RAM is, why it is needed and how it works. Now let's move on to more practical things. Namely, we will consider the types of RAM and its main characteristics.
Types (types) of RAM
Nowadays, RAM can be of two types: static (SRAM) and dynamic (DRAM). Static RAMs are faster than dynamic RAMs due to their manufacturing technology, but at the same time more expensive. This type is often used as a processor cache. DRAM technology is used for mass production of RAM modules. And there are several types of such memory. The ones you can see right now:
- DDR SDRAM- synchronous dynamic memory with random access and double data rate ( D double D ata R ate S synchronous D dynamic R andom A ccess M emory) of the first generation;
- DDR2 SDRAM- second generation DDR SDRAM;
- DDR3 SDRAM- third generation DDR SDRAM;
- DDR4 SDRAM- fourth generation DDR SDRAM;
As you might guess, DDR SDRAM is the oldest type of RAM, which is now very difficult to find. DDR4 is the newest. By far the most common is DDR3. These types of memory differ in performance and appearance.
In order to inadvertently not be able to insert a bar with one type of RAM into a slot designed for another type, there is a special key (sawed) on the bar, and a protrusion in the slot on the motherboard in the same place. And each type of memory is different.

In addition, with this key, you will not be able to insert the RAM module in reverse.
The main characteristics of RAM
- RAM type. You need to know what type of RAM your motherboard supports: DDR, DDR2, DDR3 or DDR4. And move on from that.
- RAM. Here you need to build on your needs. As I wrote above, all running programs will be placed in RAM. Accordingly, the more RAM you have on your computer, the more programs you can use at the same time. However, I'll give you a little hint. For simple homemade or office computer will be enough 2 GB. For home multimedia can be installed from 4 GB of memory. If you have game computer or you often use "heavy" professional programs You can install from 8 or more GB of RAM.
- Clock frequency. The bigger, the better. But here you also need to make sure that the motherboard and processor support this frequency. Otherwise, if the RAM frequency is higher than that supported by the motherboard, the RAM will operate at lower frequencies, which will mean an overpayment for unnecessary performance for you.
- Timings. This is the delay between accessing the memory and until it issues the necessary data. Accordingly, the lower the delays, the faster the RAM will work.
On this I will finish. I tried to present the basic information on the RAM of a computer, which will be enough for an ordinary user to understand what RAM is, what it is for and how it works, its main characteristics. Feel free to ask me questions in the comments if you don't understand something.
New generations of processors stimulated the development of faster SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory) with a clock frequency of 66 MHz, and memory modules with such chips were called DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module).
For use with Athlon processors, and later with Pentium 4, the second generation of SDRAM chips was developed - DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate SDRAM). DDR SDRAM technology allows data to be transferred on both edges of each clock pulse, providing the opportunity to double the memory bandwidth. With the further development of this technology in DDR2 SDRAM chips, it was possible to transfer 4 portions of data in one clock pulse. Moreover, it should be noted that the increase in performance occurs due to the optimization of the process of addressing and reading / writing memory cells, but the clock frequency of the memory matrix does not change. Therefore, the overall performance of the computer does not increase by two or four times, but only by tens of percent. On fig. the frequency principles of operation of SDRAM chips of different generations are shown.

There are the following types of DIMMs:
- 72-pin SO-DIMM (Small Outline Dual In-line Memory Module) - used for FPM DRAM (Fast Page Mode Dynamic Random Access Memory) and EDO DRAM (Extended Data Out Dynamic Random Access Memory)

- 100-pin DIMM - used for SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory) printers

- 144-pin SO-DIMM - used for SDR SDRAM (Single Data Rate...) in laptops

- 168-pin DIMM - used for SDR SDRAM (less often for FPM/EDO DRAM in workstations/servers

- 172-pin MicroDIMM - used for DDR SDRAM (Double date rate)

- 184-pin DIMM - used for DDR SDRAM

- 200-pin SO-DIMM - used for DDR SDRAM and DDR2 SDRAM


- 214-pin MicroDIMM - used for DDR2 SDRAM

- 204-pin SO-DIMM - used for DDR3 SDRAM

- 240-pin DIMM - used for DDR2 SDRAM, DDR3 SDRAM and FB-DIMM (Fully Buffered) DRAM



- 244-pin Mini-DIMM - for Mini Registered DIMM

- 256-pin SO-DIMM - used for DDR4 SDRAM

- 284-pin DIMM - used for DDR4 SDRAM

To prevent the installation of an unsuitable type of DIMM module, several slots (keys) are made in the textolite board of the module among the contact pads, as well as on the right and left in the zone of the module fixing elements on the system board. For mechanical identification of various DIMM modules, a shift in the position of two keys in the textolite board of the module, located among the contact pads, is used. The main purpose of these keys is to prevent the installation of a DIMM module with an unsuitable supply voltage for memory chips into the slot. In addition, the location of the key or keys determines the presence or absence of a data buffer, etc.

DDR modules are labeled PC. But unlike SDRAM, where PC denoted the frequency of operation (for example, PC133 - the memory is designed to operate at a frequency of 133 MHz), the PC indicator in DDR modules indicates the maximum achievable bandwidth, measured in megabytes per second.
DDR2 SDRAM
| Name of the standard | Memory type | Memory frequency | Bus frequency | Data transfer per second (MT/s) | |
| PC2-3200 | DDR2-400 | 100 MHz | 200 MHz | 400 | 3200 MB/s |
| PC2-4200 | DDR2-533 | 133 MHz | 266 MHz | 533 | 4200 MB/s |
| PC2-5300 | DDR2-667 | 166 MHz | 333 MHz | 667 | 5300 MB/s |
| PC2-5400 | DDR2-675 | 168 MHz | 337 MHz | 675 | 5400 MB/s |
| PC2-5600 | DDR2-700 | 175 MHz | 350 MHz | 700 | 5600 MB/s |
| PC2-5700 | DDR2-711 | 177 MHz | 355 MHz | 711 | 5700 MB/s |
| PC2-6000 | DDR2-750 | 187 MHz | 375 MHz | 750 | 6000 MB/s |
| PC2-6400 | DDR2-800 | 200 MHz | 400 MHz | 800 | 6400 MB/s |
| PC2-7100 | DDR2-888 | 222 MHz | 444 MHz | 888 | 7100 MB/s |
| PC2-7200 | DDR2-900 | 225 MHz | 450 MHz | 900 | 7200 MB/s |
| PC2-8000 | DDR2-1000 | 250 MHz | 500 MHz | 1000 | 8000 MB/s |
| PC2-8500 | DDR2-1066 | 266 MHz | 533 MHz | 1066 | 8500 MB/s |
| PC2-9200 | DDR2-1150 | 287 MHz | 575 MHz | 1150 | 9200 MB/s |
| PC2-9600 | DDR2-1200 | 300 MHz | 600 MHz | 1200 | 9600 MB/s |
DDR3 SDRAM
| Name of the standard | Memory type | Memory frequency | Bus frequency | Data transfers per second(MT/s) | Peak Data Rate |
| PC3-6400 | DDR3-800 | 100 MHz | 400 MHz | 800 | 6400 MB/s |
| PC3-8500 | DDR3-1066 | 133 MHz | 533 MHz | 1066 | 8533 MB/s |
| PC3-10600 | DDR3-1333 | 166 MHz | 667 MHz | 1333 | 10667 MB/s |
| PC3-12800 | DDR3-1600 | 200 MHz | 800 MHz | 1600 | 12800 MB/s |
| PC3-14400 | DDR3-1800 | 225 MHz | 900 MHz | 1800 | 14400 MB/s |
| PC3-16000 | DDR3-2000 | 250 MHz | 1000 MHz | 2000 | 16000 MB/s |
| PC3-17000 | DDR3-2133 | 266 MHz | 1066 MHz | 2133 | 17066 MB/s |
| PC3-19200 | DDR3-2400 | 300 MHz | 1200 MHz | 2400 | 19200 MB/s |
The tables indicate exactly the peak values, in practice they may be unattainable.
For a comprehensive assessment of the capabilities of RAM, the term memory bandwidth is used. It also takes into account the frequency at which data is transmitted and the bus width and the number of memory channels.
Bandwidth = Bus frequency x channel width x number of channels
For all DDRs, the number of channels = 2 and the width is 64 bits.
For example, when using DDR2-800 memory with a 400 MHz bus frequency, the bandwidth will be:
(400 MHz x 64 bits x 2)/ 8 bits = 6400 MB/s
Each manufacturer gives each of its products or parts its internal production marking, called P / N (part number) - part number.
For memory modules from different manufacturers, it looks something like this:
- Kingston KVR800D2N6/1G
- OCZ OCZ2M8001G
- Corsair XMS2 CM2X1024-6400C5
On the website of many memory manufacturers, you can learn how their Part Number is read.
| Kingston Part Number | Description |
| KVR1333D3D4R9SK2/16G | 16GB 1333MHz DDR3 ECC Reg CL9 DIMM (Kit of 2) DR x4 w/TS |






