God of temptation in Greek mythology. ancient mythology
Hades - God is the ruler of the realm of the dead.
Antey- the hero of myths, a giant, the son of Poseidon and the Earth of Gaia. The earth gave her son strength, thanks to which no one could cope with him.
Apollo- the god of sunlight. The Greeks portrayed him as a beautiful young man.
Ares- god of perfidious war, son of Zeus and Hera
Asclepius- the god of medical art, the son of Apollo and the nymph Coronis
Boreas- the god of the north wind, the son of the titanides Astrea (starry sky) and Eos (morning dawn), brother of Zephyr and Nota. Depicted as a winged, long-haired, bearded, powerful deity.
Bacchus One of the names of Dionysus.
Helios (Helium ) - the god of the Sun, brother of Selena (goddess of the moon) and Eos (morning dawn). In late antiquity, he was identified with Apollo, the god of sunlight.
Hermes- the son of Zeus and Maya, one of the most ambiguous Greek gods. The patron of wanderers, crafts, trade, thieves. Possessing the gift of eloquence.
Hephaestus- the son of Zeus and Hera, the god of fire and blacksmithing. He was considered the patron saint of artisans.
Hypnos- deity of sleep, son of Nikta (Night). He was depicted as a winged youth.
Dionysus (Bacchus) - the god of viticulture and winemaking, the object of a number of cults and mysteries. He was depicted either as a fat elderly man, or as a young man with a wreath of grape leaves on his head.
Zagreus God of fertility, son of Zeus and Persephone.
Zeus- the supreme god, the king of gods and people.
Zephyr- god of the west wind.
Iacchus- the god of fertility.
Kronos - titan , the youngest son of Gaia and Uranus, the father of Zeus. He ruled the world of gods and people and was overthrown from the throne by Zeus ..
Mom- the son of the goddess of the Night, the god of slander.
Morpheus- one of the sons of Hypnos, the god of dreams.
Nereus- the son of Gaia and Pontus, meek sea god.
Note- the god of the south wind, depicted with a beard and wings.
Ocean - titan , son of Gaia and Uranus, brother and husband of Tethys and father of all the rivers of the world.
Olympians- the supreme gods of the younger generation of Greek gods, led by Zeus, who lived on the top of Mount Olympus.
Pan- the forest god, the son of Hermes and Dryopa, a goat-legged man with horns. He was considered the patron saint of shepherds and small livestock.
Pluto- the god of the underworld, often identified with Hades, but unlike from him, who owned not the souls of the dead, but the riches of the underworld.
Plutus- the son of Demeter, the god who gives people wealth.
Pont- one of the older Greek deities, the offspring of Gaia, the god of the sea, the father of many titans and gods.
Poseidon- one of the Olympian gods, brother of Zeus and Hades, ruling over the sea element. Poseidon was also subject to the bowels of the earth,
he commanded storms and earthquakes.
Proteus- sea deity, son of Poseidon, patron of seals. Possessed the gift of reincarnation and prophecy.
satires- goat-footed creatures, demons of fertility.
Thanatos- the personification of death, the twin brother of Hypnos.
Titans- the generation of the Greek gods, the ancestors of the Olympians.
Typhon- a hundred-headed dragon, born of Gaia or a Hero. During the battle of the Olympians and the Titans, he was defeated by Zeus and imprisoned under the volcano Etna in Sicily.
Triton- the son of Poseidon, one of the sea deities, a man with a fish tail instead of legs, holding a trident and a twisted shell - a horn.
Chaos- an endless empty space from which at the beginning of time arose the most ancient gods of the Greek religion - Nikta and Erebus.
Chthonic gods - deities of the underworld and fertility, relatives of the Olympians. These included Hades, Hecate, Hermes, Gaia, Demeter, Dionysus, and Persephone.
cyclops - giants with one eye in the middle of the forehead, children of Uranus and Gaia.
Evre (Eur) god of the southeast wind.
aeolus- lord of the winds.
Erebus- the personification of the darkness of the underworld, the son of Chaos and the brother of the Night.
Eros (Eros)- god of love, son of Aphrodite and Ares. In ancient myths - a self-arisen force that contributed to the ordering of the world. Depicted as a winged youth (in the Hellenistic era - a boy) with arrows, accompanying his mother.
Ether- deity of the sky
Goddesses of ancient Greece
Artemis- Goddess of hunting and nature.
Atropos- one of the three moira, cutting the thread of fate and cutting off human life.
Athena (Pallas, Parthenos) - the daughter of Zeus, born from his head in full combat weapons. One of the most revered Greek goddesses, the goddess of just war and wisdom, the patroness of knowledge.
Aphrodite (Kythera, Urania) - Goddess of love and beauty. She was born from the marriage of Zeus and the goddess Dione (according to another legend, she came out of the sea foam)
Hebe- daughter of Zeus and Hera, goddess of youth. Sister of Ares and Ilithyia. She served the Olympian gods at feasts.
Hecate- the goddess of darkness, night visions and sorcery, the patroness of sorcerers.
Hemera- the goddess of daylight, the personification of the day, born of Nikto and Erebus. Often identified with Eos.
Hera- the supreme Olympic goddess, sister and third wife of Zeus, daughter of Rhea and Kronos, sister of Hades, Hestia, Demeter and Poseidon. Hera was considered the patroness of marriage.
Hestia- Goddess of the hearth and fire.
Gaia- mother earth, mother of all gods and people.
Demitra- Goddess of fertility and agriculture.
Dryads- lower deities, nymphs who lived in trees.
Diana-goddess of the hunt
Ilithyia- patron goddess of childbirth.
Irida- winged goddess, assistant to Hera, messenger of the gods.
calliope- the muse of epic poetry and science.
Kera- demonic creatures, children of the goddess Nikta, bringing misfortune and death to people.
Clio- one of the nine muses, the muse of history.
Clotho ("spinner") - one of the moira, spinning the thread of human life.
Lachesis- one of the three moira sisters, who determines the fate of each person even before birth.
Summer- Titanide, mother of Apollo and Artemis.
Mayan- a mountain nymph, the eldest of the seven pleiades - the daughters of Atlanta, the beloved of Zeus, from whom Hermes was born to her.
Melpomene- muse of tragedy.
Metis- the goddess of wisdom, the first of the three wives of Zeus, who conceived Athena from him.
Mnemosyne- mother of nine muses, goddess of memory.
moira- the goddess of fate, the daughter of Zeus and Themis.
Muses- patron goddess of the arts and sciences.
naiads- nymphs-guardians of waters.
Nemesis- the daughter of Nikta, the goddess, personifying fate and retribution, punishing people in accordance with their sins.
Nereids- fifty daughters of Nereus and the oceanides of Dorida, sea deities.
Nika- the personification of victory. Often she was depicted with a wreath, a common symbol of triumph in Greece.
nymphs- the lowest deities in the hierarchy of the Greek gods. They personified the forces of nature.
Nikta- one of the first Greek deities, the goddess - the personification of the primordial Night
Orestiades- mountain nymphs.
Ory- the goddess of the seasons, tranquility and order, the daughter of Zeus and Themis.
Peyto- the goddess of persuasion, the companion of Aphrodite, often identified with her patroness.
Persephone- daughter of Demeter and Zeus, goddess of fertility. The wife of Hades and the queen of the underworld, who knew the secrets of life and death.
polyhymnia- the muse of serious hymn poetry.
Tethys- the daughter of Gaia and Uranus, the wife of the Ocean and the mother of the Nereids and Oceanids.
Rhea- the mother of the Olympian gods.
Sirens- female demons, half-woman half-birds, capable of changing the weather at sea.
Waist- muse of comedy.
Terpsichore- Muse of dance art.
Tisiphone- one of the Erinyes.
quiet- the goddess of fate and chance among the Greeks, companion of Persephone. She was depicted as a winged woman standing on a wheel and holding a cornucopia and ship's steering wheel in her hands.
Urania- one of the nine muses, the patroness of astronomy.
Themis- Titanide, goddess of justice and law, second wife of Zeus, mother of mountains and moira.
Charites- the goddess of female beauty, the embodiment of a kind, joyful and eternally young beginning of life.
Eumenides- another hypostasis of the Erinyes, revered as goddesses of benevolence, preventing misfortunes.
Eris- daughter of Nikta, sister of Ares, goddess of discord.
Erinyes- goddesses of vengeance, creatures of the underworld, who punished injustice and crimes.
Erato- Muse of lyrical and erotic poetry.
Eos- Goddess of the dawn, sister of Helios and Selena. The Greeks called it "pink-fingered".
Euterpe- the muse of lyrical chanting. Depicted with a double flute in her hand.
Rhea, christened by Kron, bore him light children, - the Virgin - Hestia, Demeter and the golden-shod Hera, the glorious power of Hades, who lives under the earth, And the providence - Zeus, the father of both immortals and mortals, whose thunders tremble the wide earth. Hesiod "Theogony"
Greek literature originated from mythology. Myth- this is the idea of an ancient person about the world around him. Myths were created at a very early stage in the development of society in various areas of Greece. Later, all these myths merged into a single system.
With the help of myths, the ancient Greeks tried to explain all natural phenomena, presenting them in the form of living beings. At first, experiencing a strong fear of the elements, people portrayed the gods in a terrible animal form (Chimera, Gorgon Medusa, Sphinx, Lernean Hydra).
Later, however, the gods become anthropomorphic, that is, they have a human appearance and they have a variety of human qualities (jealousy, generosity, envy, generosity). The main difference between the gods and people was their immortality, but with all their greatness, the gods communicated with mere mortals and even often entered into love relationships with them in order to give birth to a whole tribe of heroes on earth.
There are 2 types of ancient Greek mythology:
- cosmogonic (cosmogony - the origin of the world) - ends with the birth of Kronos
- theogonic (theogony - the origin of gods and deities)
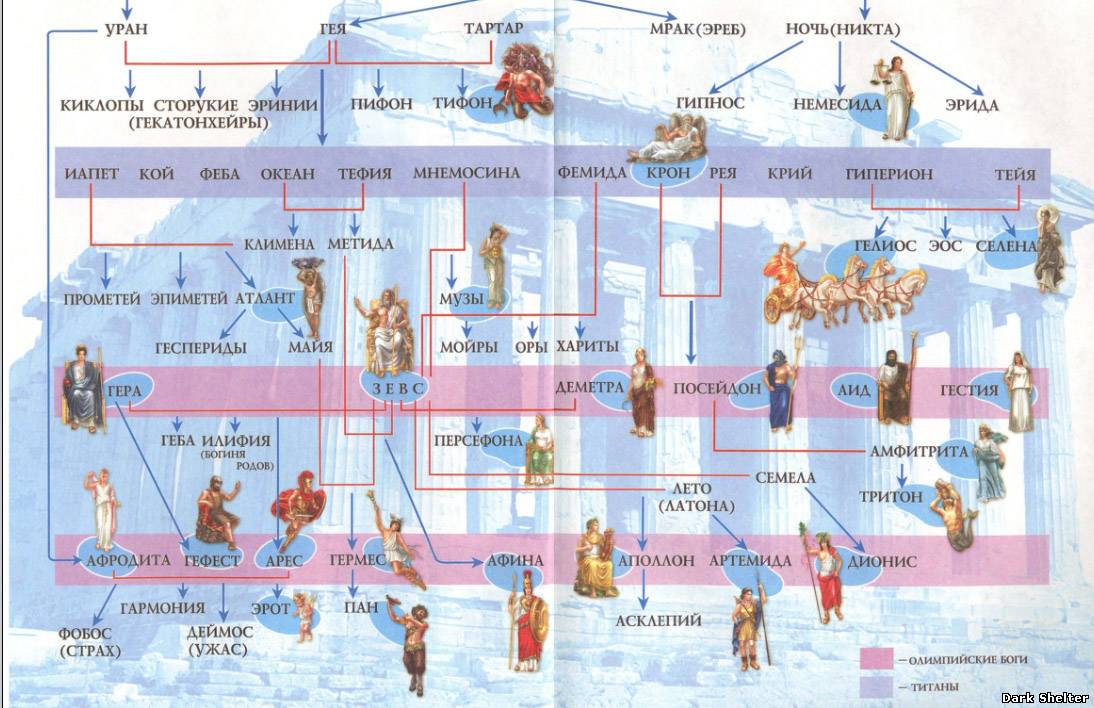
The mythology of Ancient Greece went through 3 main stages in its development:
- pre-Olympic- this is basically a cosmogonic mythology. This stage begins with the idea of the ancient Greeks that everything came from Chaos, and ends with the murder of Kron and the division of the world between the gods.
- Olympic(early classic) - Zeus becomes the supreme deity and with a retinue of 12 gods settles on Olympus.
- late heroism- heroes are born from the gods and mortals, who help the gods in establishing order and in the destruction of monsters.
On the basis of mythology, poems were created, tragedies were written, and lyricists dedicated their odes and hymns to the gods.

There were two main groups of gods in Ancient Greece:
- titans - gods of the second generation (six brothers - Oceanus, Kei, Crius, Gipperion, Iapetus, Kronos and six sisters - Thetis, Phoebe, Mnemosyne, Teia, Themis, Rhea)
- olympic gods - Olympians - gods of the third generation. The Olympians included the children of Kronos and Rhea - Hestia, Demeter, Hera, Hades, Poseidon and Zeus, as well as their descendants - Hephaestus, Hermes, Persephone, Aphrodite, Dionysus, Athena, Apollo and Artemis. The supreme god was Zeus, who deprived the power of his father Kronos (the god of time).
The Greek pantheon of the Olympian gods traditionally included 12 gods, but the composition of the pantheon was not very stable and sometimes consisted of 14-15 gods. Usually they were: Zeus, Hera, Athena, Apollo, Artemis, Poseidon, Aphrodite, Demeter, Hestia, Ares, Hermes, Hephaestus, Dionysus, Hades. The Olympic gods lived on the sacred Mount Olympus ( Olympos) in Olympia, off the coast of the Aegean Sea.

Translated from ancient Greek, the word pantheon means "all gods". Greeks
divided the deities into three groups:
- Pantheon (great Olympian gods)
- Inferior deities
- monsters
Heroes occupied a special place in Greek mythology. The most famous of them:
v Odysseus
Supreme gods of Olympus
|
Greek gods |
Functions |
roman gods |
|
god of thunder and lightning, sky and weather, law and fate, attributes - lightning (three-pronged pitchfork with notches), scepter, eagle or chariot drawn by eagles |
||
|
goddess of marriage and family, goddess of the sky and starry skies, attributes - diadem (crown), lotus, lion, cuckoo or hawk, peacock (two peacocks drove her wagon) |
||
|
Aphrodite |
"foam-born", the goddess of love and beauty, Athena, Artemis and Hestia were not subject to her, attributes - a rose, an apple, a shell, a mirror, a lily, a violet, a belt and a golden bowl that bestows eternal youth, a retinue - sparrows, doves, a dolphin, satellites - Eros, charites, nymphs, ororas. |
|
|
god of the underworld of the dead, "generous" and "hospitable", attribute - magic cap of invisibility and three-headed dog Cerberus |
||
|
the god of insidious war, military destruction and murder, he was accompanied by the goddess of discord Eris and the goddess of violent war Enyo, attributes - dogs, a torch and a spear, there were 4 horses in the chariot - Noise, Horror, Shine and Flame |
||
|
god of fire and blacksmithing, ugly and lame on both legs, attribute - blacksmith's hammer |
||
|
the goddess of wisdom, crafts and art, the goddess of just war and military strategy, the patroness of heroes, the “owl-eyed”, used male attributes (helmet, shield - aegis from the skin of the goat amalthea, decorated with the head of Medusa Gorgon, spear, olive, owl and snake), was accompanied by Nicky |
||
|
god of invention, theft, trickery, trade and eloquence, patron of heralds, ambassadors, shepherds and travelers, invented measures, numbers, taught people, attributes - a winged rod and winged sandals |
Mercury |
|
|
Poseidon |
god of the seas and all water bodies, floods, droughts and earthquakes, patron of sailors, attribute - a trident that causes storms, breaks rocks, knocks out springs, sacred animals - a bull, a dolphin, a horse, a sacred tree - a pine |
|
|
Artemis |
goddess of hunting, fertility and female chastity, later - goddess of the moon, patroness of forests and wild animals, forever young, she is accompanied by nymphs, attributes - hunting bow and arrows, sacred animals - doe and bear |
|
|
Apollo (Phoebus), Kifared |
“golden-haired”, “silver-armed”, god of light, harmony and beauty, patron of arts and sciences, leader of the muses, predictor of the future, attributes - silver bow and golden arrows, golden cithara or lyre, symbols - olive, iron, laurel, palm tree, dolphin , swan, wolf |
|
|
goddess of the hearth and sacrificial fire, virgin goddess. was accompanied by 6 priestesses - vestals who served the goddess for 30 years |
||
|
"Mother Earth", the goddess of fertility and agriculture, plowing and harvest, attributes - a sheaf of wheat and a torch |
||
|
god of fruitful forces, vegetation, viticulture, winemaking, inspiration and fun |
Bacchus, Bacchus |
Minor Greek gods
|
Greek gods |
Functions |
roman gods |
|
Asclepius |
"opener", god of healing and medicine, attribute - a staff entwined with snakes |
|
|
Eros, Cupid |
the god of love, the “winged boy”, was considered the product of a dark night and a bright day, Heaven and Earth, attributes - a flower and a lyre, later - arrows of love and a flaming torch |
|
|
"the sparkling eye of the night", the goddess of the moon, the queen of the starry sky, has wings and a golden crown |
||
|
Persephone |
goddess of the realm of the dead and fertility |
Proserpina |
|
the goddess of victory, depicted winged or in a pose of rapid movement, attributes - a bandage, a wreath, later - a palm tree, then - a weapon and a trophy |
Victoria |
|
|
goddess of eternal youth, depicted as a chaste girl pouring nectar |
||
|
“pink-fingered”, “beautiful-haired”, “golden-throned” goddess of the dawn |
||
|
goddess of happiness, chance and good luck |
||
|
god of the sun, owner of seven herds of cows and seven herds of sheep |
||
|
Kronos (Chronos) |
god of time, attribute - sickle |
|
|
goddess of furious war |
||
|
Hypnos (Morpheus) |
||
|
goddess of flowers and gardens |
||
|
god of the west wind, messenger of the gods |
||
|
Dike (Themis) |
goddess of justice, justice, attributes - scales in the right hand, blindfold, cornucopia in the left hand; The Romans put a sword into the hand of the goddess instead of a horn |
|
|
god of marriage |
Thalassium |
|
|
Nemesis |
winged goddess of revenge and retribution, punishing for violation of social and moral norms, attributes - scales and bridle, sword or whip, chariot drawn by griffins |
Adrastea |
|
golden-winged goddess of the rainbow |
||
|
earth goddess |
In addition to Olympus, in Greece there was a sacred mountain Parnassus, where muses - 9 sisters, Greek deities who personified poetic and musical inspiration, patrons of the arts and sciences.
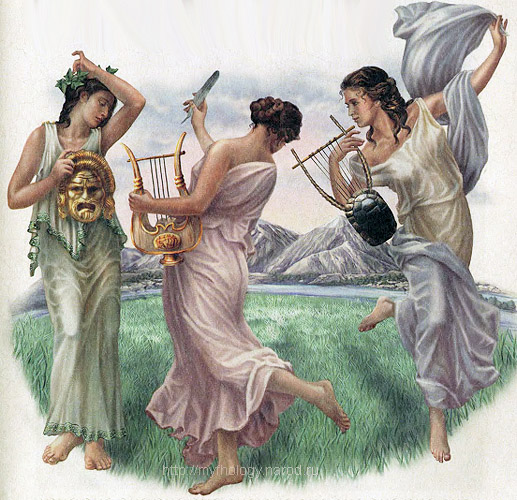

Greek Muses
|
What patronizes |
Attributes |
|
|
Calliope ("beautiful") |
muse of epic or heroic poetry |
wax tablet and stylus (bronze rod for writing) |
|
("glorifying") |
muse of history |
papyrus scroll or scroll case |
|
("pleasant") |
muse of love or erotic poetry, lyrics and marriage songs |
kifara (stringed musical instrument, a kind of lyre) |
|
("beautiful") |
muse of music and lyric poetry |
avlos (a wind musical instrument similar to a pipe with a double tongue, the predecessor of the oboe) and syringa (a musical instrument, a kind of longitudinal flute) |
|
("celestial") |
muse of astronomy |
spotting scope and leaf with celestial signs |
|
Melpomene ("singing") |
muse of tragedy |
wreath of vine leaves or ivy, theatrical mantle, tragic mask, sword or club. |
|
Terpsichore ("delightful dancing") |
muse of dance |
head wreath, lyre and plectrum (mediator) |
|
polyhymnia ("multi-singing") |
muse of sacred song, eloquence, lyric, chant and rhetoric |
|
|
("blooming") |
muse of comedy and bucolic poetry |
comic mask in hands and wreath ivy on the head |
Inferior deities in Greek mythology, these are satyrs, nymphs and ororas.
satires - (Greek satyroi) - these are forest deities (the same as in Russia goblin), demons fertility, retinue of Dionysus. They were depicted as goat-legged, hairy, with horse tails and small horns. Satyrs are indifferent to people, mischievous and cheerful, they were interested in hunting, wine, pursued forest nymphs. Their other hobby is music, but they only played wind instruments that make sharp, piercing sounds - flutes and pipes. In mythology, they personified a rough, base beginning in nature and man, therefore they were represented with ugly faces - with blunt, wide noses, swollen nostrils, disheveled hair.

nymphs - (the name means "source", among the Romans - "bride") the personification of living elemental forces, noticed in the murmur of a stream, in the growth of trees, in the wild charms of mountains and forests, spirits of the earth's surface, manifestations of natural forces acting in addition to man in the solitude of grottoes , valleys, forests, away from cultural centers. They were portrayed as beautiful young girls with wonderful hair, with a dress of wreaths and flowers, sometimes in a dancing pose, with bare legs and arms, with loose hair. They are engaged in yarn, weaving, sing songs, dance in the meadows to the flute of Pan, hunt with Artemis, participate in the noisy orgies of Dionysus, and are constantly fighting with annoying satyrs. In the view of the ancient Greeks, the world of nymphs was very extensive.
The azure pond was full of flying nymphs,
Dryads animated the garden,
And the bright water spring was sparkling from the urn
Laughing naiads.
F. Schiller
Nymphs of the mountains oreads,
nymphs of forests and trees - dryads,
spring nymphs - naiads,
nymphs of the oceans oceanides,
nymphs of the sea nerids,
nymphs of the valleys sing,
meadow nymphs - limeades.

Ory - the goddess of the seasons, they were in charge of order in nature. Guardians of Olympus, now opening, then closing its cloudy gates. They are called gatekeepers of heaven. Harness the horses of Helios.

In many mythologies, there are numerous monsters. In ancient Greek mythology, there were also many of them: Chimera, Sphinx, Lernean Hydra, Echidna and many others.
In the same vestibule, the shadows of monsters crowd around:
Scylla biform here and herds of centaurs live,
Here Briares the hundred-handed lives, and the dragon from Lerna
The swamp hisses, and the Chimera intimidates enemies with fire,
Harpies fly in a flock around the three-bodied giants ...
Virgil, "Aeneid"
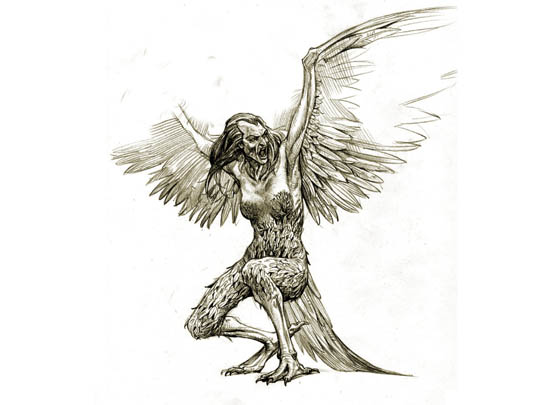
Harpies - these are evil kidnappers of children and human souls, suddenly flying in and just as suddenly disappearing like the wind, terrifying people. Their number ranges from two to five; depicted as wild, half-female, half-birds of a hideous appearance with wings and paws of a vulture, with long sharp claws, but with the head and chest of a woman.

Gorgon Medusa - a monster with a woman's face and snakes instead of hair, whose gaze turned a person to stone. According to legend, she was a beautiful girl with beautiful hair. Poseidon, seeing Medusa and falling in love, seduced her in the temple of Athena, for which the goddess of wisdom in anger turned the hair of the Gorgon Medusa into snakes. The Gorgon Medusa was defeated by Perseus, and her head was placed on the auspices of Athena.

Minotaur - a monster with a human body and a bull's head. He was born from the unnatural love of Pasiphae (wife of King Minos) and a bull. Minos hid the monster in the labyrinth of Knossos. Every eight years, 7 boys and 7 girls descended into the labyrinth, intended for the Minotaur as victims. Theseus defeated the Minotaur, and with the help of Ariadne, who gave him a ball of thread, got out of the labyrinth.

Cerberus (Cerberus) - this is a three-headed dog with a snake tail and snake heads on its back, guarding the exit from the kingdom of Hades, not allowing the dead to return to the kingdom of the living. He was defeated by Hercules during one of the labors.

Scylla and Charybdis - These are sea monsters located at the distance of an arrow flight from each other. Charybdis is a sea whirlpool that absorbs and spews water three times a day. Scylla ("barking") - a monster in the form of a woman, whose lower body was turned into 6 dog heads. When the ship passed the rock where Scylla lived, the monster, opening all its mouths, abducted 6 people from the ship at once. The narrow strait between Scylla and Charybdis was a mortal danger to all who sailed through it.

Also in ancient Greece, there were other mythical characters.
Pegasus - a winged horse, a favorite of the muses. Flying at the speed of the wind. To ride a Pegasus meant to receive poetic inspiration. He was born at the origins of the Ocean, therefore he was named Pegasus (from the Greek "stormy current"). According to one version, he jumped out of the body of the Gorgon Medusa after Perseus cut off her head. Pegasus delivered thunder and lightning to Zeus on Olympus from Hephaestus, who made them.

From the foam of the sea, from the azure wave,
Faster than an arrow and more beautiful than a string,
An amazing fairytale horse is flying
And easily catches heavenly fire!
He likes to splash in colored clouds,
And often walks in magic verses.
So that the ray of inspiration in the soul does not go out,
I saddle you, snow-white Pegasus!
Unicorn - a mythical creature symbolizing chastity. Usually depicted as a horse with one horn coming out of his forehead. The Greeks believed that the unicorn belonged to Artemis, the goddess of the hunt. Subsequently, in medieval legends, there was a version that only a virgin could tame him. Having caught a unicorn, it can only be held by a golden bridle.

centaurs - wild mortal creatures with the head and torso of a man on the body of a horse, inhabitants of mountains and forest thickets, accompany Dionysus and are distinguished by their violent temper and intemperance. Presumably, centaurs were originally the embodiment of mountain rivers and turbulent streams. In heroic myths, centaurs are the educators of heroes. For example, Achilles and Jason were raised by the centaur Chiron.
The main gods in Ancient Hellas were those that belonged to the younger generation of celestials. Once upon a time, it took power over the world from the older generation, which personified the main universal forces and elements (see about this in the article The Origin of the Gods of Ancient Greece). The gods of the older generation are usually called titans. Having defeated the titans, the younger gods, led by Zeus, settled on Mount Olympus. The ancient Greeks honored 12 Olympian gods. Their list usually included Zeus, Hera, Athena, Hephaestus, Apollo, Artemis, Poseidon, Ares, Aphrodite, Demeter, Hermes, Hestia. Hades is also close to the Olympian gods, but he does not live on Olympus, but in his underworld.
- the main deity of ancient Greek mythology, the king of all other gods, the personification of the boundless sky, the lord of lightning. In Roman religions Jupiter corresponded to it.



P
oseidon - the god of the seas, among the ancient Greeks - the second deity in importance after Zeus. like olithe creation of a changeable and stormy water element Poseidon was closely associated with earthquakes and volcanic activity. In Roman mythology, he was identified with Neptune.Hades - the lord of the gloomy underground kingdom of the dead, inhabited by the incorporeal shadows of the dead and terrible demonic creatures. Hades (Hades), Zeus and Poseidon made up the triad of the most powerful gods of Ancient Hellas. As ruler of the depths of the earth, Hades was also associated with agricultural cults, with whom his wife, Persephone, was closely associated. The Romans called it Pluto.
Hera - the sister and wife of Zeus, the main female goddess of the Greeks. The patroness of marriage and conjugal love. Jealous Hera severely punishes the violation of marriage bonds. The Romans corresponded to Juno.
Apollo - originally the god of sunlight, whose cult then received a wider meaning and connection with the ideas of spiritual purity, artistic beauty, medical healing, retribution for sins. As a patron of creative activity, he is considered the head of the nine muses, as a healer - the father of the god of doctors Asclepius. The image of Apollo among the ancient Greeks was formed under the strong influence of Eastern cults (the Asia Minor god Apelun) and carried refined, aristocratic features. Apollo was also called Phoebus. Under the same names, he was revered in ancient Rome.


Artemis - sister of Apollo, virgin goddess of forests and hunting. Like the cult of Apollo, the veneration of Artemis was brought to Greece from the East (the Asia Minor goddess Rtemis). The close connection of Artemis with forests comes from her ancient function as the patroness of vegetation and fertility in general. The virginity of Artemis also contains a dull echo of the ideas of birth and sexual relations. In ancient Rome, she was revered in the person of the goddess Diana.
Athena is the goddess of spiritual harmony and wisdom. She was considered the inventor and patroness of most of the sciences, arts, spiritual pursuits, agriculture, and crafts. With the blessing of Pallas Athena, cities are being built and state life is going on. The image of Athena as a defender of the fortress walls, a warrior, a goddess who, at her very birth, came out of the head of her father, Zeus, armed, is closely connected with the patronage functions of cities and the state. Among the Romans, Athena corresponded to the goddess Minerva.
Hermes is the most ancient pre-Greek god of roads and field boundaries, all borders separating one from the other. Due to his primordial connection with the roads, Hermes was later revered as a messenger of the gods with wings on his heels, the patron of travel, merchants and trade. His cult was also associated with ideas about resourcefulness, cunning, subtle mental activity (skillful differentiation of concepts), knowledge of foreign languages. The Romans have Mercury.
Ares is the wild god of war and battle. In ancient Rome, Mars.
Aphrodite is the ancient Greek goddess of sensual love and beauty. Her type is very close to the Semitic-Egyptian veneration of the productive forces of nature in the form of Astarte (Ishtar) and Isis. The famous legend about Aphrodite and Adonis was inspired by the most ancient oriental myths about Ishtar and Tammuz, Isis and Osiris. The ancient Romans identified with Venus.


Eros - the son of Aphrodite, a divine boy with a quiver and a bow. At the request of his mother, he shoots well-aimed arrows that kindle incurable love in the hearts of people and gods. In Rome - Cupid.
Hymen Companion of Aphrodite, god of marriage. According to his name, wedding hymns were also called hymens in ancient Greece.
Hephaestus - a god whose cult in the era of hoary antiquity was associated with volcanic activity - fire and roar. Later, thanks to the same properties, Hephaestus became the patron of all crafts associated with fire: blacksmithing, pottery, etc. In Rome, the god Vulcan corresponded to him.
Demeter - in Ancient Greece personified the productive force of nature, but not wild, as Artemis once did, but “ordered”, “civilized”, the one that manifests itself in regular rhythms. Demeter was considered the goddess of agriculture, who rules the annual natural cycle of renewal and decay. She also led the cycle of human life - from birth to death. This last aspect of the cult of Demeter was the content of the Eleusinian mysteries.
Persephone Daughter of Demeter, kidnapped by the god Hades. The inconsolable mother, after a long search, found Persephone in the underworld. Hades, who made her his wife, agreed that she would spend part of the year on earth with her mother, and the other with him in the bowels of the earth. Persephone was the personification of the grain, which, being "dead" sown in the ground, then "comes to life" and comes out of it into the light.
Hestia - patron goddess of the hearth, family and community ties. Altars to Hestia stood in every ancient Greek house and in the main public building of the city, all citizens of which were considered one big family.
Dionysus - the god of winemaking and those violent natural forces that bring a person to insane delight. Dionysus was not one of the 12 "Olympic" gods of Ancient Greece. His orgiastic cult was borrowed comparatively late from Asia Minor. The popular veneration of Dionysus was opposed to the aristocratic service of Apollo. From frenzied dances and songs at the feasts of Dionysus later came the ancient Greek tragedy and comedy.
The most interesting and instructive stories, fascinating stories and adventures gave the world Greek mythology. The narrative immerses us in a fairy-tale world where you can meet heroes and gods, scary monsters and unusual animals. The myths of Ancient Greece, written many centuries ago, are currently the greatest cultural heritage of all mankind.
What are myths
Mythology is an amazing separate world in which people opposed the deities of Olympus, fought for honor and resisted evil and destruction.
However, it is worth remembering that myths are works created exclusively by people using fantasy and fiction. These are stories about gods, heroes and exploits, unusual natural phenomena and mysterious creatures.
The origin of legends is no different from the origin of folk tales and legends. The Greeks invented and retold unusual stories that mixed truth and fiction.
It is possible that there was some truth in the stories - a life case or an example could be taken as a basis.
Source of the myths of ancient Greece
How do modern people know the myths and their plots for certain? It turns out that Greek mythology was preserved on the tablets of the Aegean culture. They were written in Linear B, which was deciphered only in the 20th century.
The Crete-Mycenaean period, to which this type of writing belongs, knew most of the gods: Zeus, Athena, Dionysus, and so on. However, due to the decline of civilization and the emergence of ancient Greek mythology, mythology could have its gaps: we know it only from the latest sources.

Various plots of the myths of Ancient Greece were often used by writers of that time. And before the onset of the Hellenistic era, it became popular to create their own legends based on them.
The largest and most famous sources are:
- Homer, Iliad, Odyssey
- Hesiod "Theogony"
- Pseudo-Apollodorus, "Library"
- Gigin, "Myths"
- Ovid, "Metamorphoses"
- Nonnus, "Acts of Dionysus"
Karl Marx believed that the mythology of Greece was a vast repository of art, and also created the ground for it, thus fulfilling a dual function.
ancient greek mythology
Myths did not appear overnight: they took shape over several centuries, passed from mouth to mouth. Thanks to the poetry of Hesiod and Homer, the works of Aeschylus, Sophocles and Euripides, we can get acquainted with the stories at the present time.

Each story has value, keeping in itself the atmosphere of antiquity. Specially trained people - mythographers - began to appear in Greece in the 4th century BC.
These include the sophist Hippias, Herodotus of Heracles, Heraclitus of Pontus and others. Dionysius of Samoia, in particular, was engaged in compiling genealogical tables and studied tragic myths.
There are many myths, but the most popular are stories related to Olympus and its inhabitants.
However, the complex hierarchy and history of the origin of the gods can confuse any reader, and therefore we propose to understand this in detail!
With the help of myths, it becomes possible to recreate the picture of the world in the view of the inhabitants of Ancient Greece: the world is inhabited by monsters and giants, among which are giants - one-eyed creatures and Titans.
Origin of the gods
Eternal, boundless Chaos enveloped the Earth. It contained the world source of life.
It was believed that it was Chaos that gave birth to everything around: the world, the immortal gods, the goddess of the Earth, Gaia, who gave life to everything growing and living, and the mighty force that animates everything - Love.
However, a birth also took place under the Earth: the gloomy Tartarus was born - an abyss of horror filled with eternal darkness.
In the process of creating the world, Chaos gave birth to the Eternal Darkness, called Erebus, and the dark Night, named Nikta. As a result of the union of Nikta and Erebus, Ether was born - the eternal Light and Hemera - the bright Day. Thanks to their appearance, the light filled the whole world, and day and night began to replace each other.
Gaia, a powerful and gracious goddess, created the immense blue Sky - Uranus. Spread over the Earth, he reigned throughout the world. High Mountains proudly stretched towards him, and the noisy Sea spread over the whole Earth.

Goddess Gaia and her Titan children
After Mother Earth created the Sky, Mountains and Sea, Uranus decided to take Gaia as his wife. From the divine union came 6 sons and 6 daughters.
Titan Ocean and the goddess Thetis created all the rivers that rolled their waters to the sea, and the goddesses of the seas, called oceanides. Titan Gipperion and Theia gave the world Helios - the Sun, Selena - the Moon and Eos - the Dawn. Astrea and Eos gave birth to all the stars and all the winds: Boreas - the north, Eurus - the east, Notus - the south, Zephyr - the west.
The overthrow of Uranus - the beginning of a new era
The goddess Gaia - the mighty Earth - gave birth to 6 more sons: 3 cyclops - giants with one eye in the forehead, and 3 fifty-headed hundred-armed monsters called Hekantocheirs. They possessed boundless power that knew no limits.
Struck by the ugliness of his giant children, Uranus renounced them and ordered them to be imprisoned in the bowels of the Earth. Gaia, being a Mother, suffered, weighed down by a terrible burden: after all, her own children were imprisoned in her bowels. Unable to stand it, Gaia called her children-titans, persuading them to rebel against their father - Uranus.

Battle of the gods with the titans
Being great and powerful, the titans were still afraid of their father. And only Kronos, the youngest and most treacherous, accepted his mother's offer. Having outwitted Uranus, he overthrew him, seizing power.
As a punishment for the deed of Kronos, the goddess Night gave birth to death (Tanat), discord (Eris), deceit (Apata),

Kronos devouring his child
destruction (Ker), nightmare (Hypnos) and vengeance (Nemesis) and other terrible gods. All of them brought horror, discord, deceit, struggle and misfortune to the world of Kronos.
Despite his cunning, Kronos was afraid. His fear was built on personal experience: after all, the children could overthrow him, as he once overthrew Uranus - his father.
Fearing for his life, Kronos ordered his wife Rhea to bring him born children. To Rhea's horror, 5 of them were eaten: Hestia, Demeter, Hera, Hades, and Poseidon.
Zeus and his reign
Heeding the advice of her father Uranus and her mother Gaia, Rhea fled to the island of Crete. There, in a deep cave, she gave birth to her youngest son, Zeus.
Hiding the newborn in it, Rhea tricked the hard Kronos into swallowing a long stone wrapped in swaddling clothes instead of her son.
As time went. Kronos did not figure out his wife's deceit. Zeus grew up while in Crete. His nannies were nymphs - Adrastea and Idea, instead of mother's milk, he was fed with the milk of the divine goat Amalthea, and industrious bees carried honey to baby Zeus from Mount Dikta.
If Zeus began to cry, the young Curetes, who stood at the entrance to the cave, struck their shields with their swords. Loud sounds drowned out the crying so that Kronos would not hear it.

The myth of the birth of Zeus: feeding the milk of the divine goat Amalthea
Zeus grew up. Having defeated Kronos in battle with the help of the Titans and the Cyclopes, he became the supreme deity of the Olympian Pantheon. The lord of heavenly forces commanded thunders, lightnings, clouds and showers. He dominated the universe, giving people laws and protecting order.
Views of the Ancient Greeks
The Greeks believed that the gods of Olympus are like people, and the relationship between them is comparable to human. Their lives were also filled with quarrels and reconciliations, envy and interference, resentment and forgiveness, joy, fun and love.

In the views of the ancient Greeks, each deity had its own occupation and sphere of influence:
- Zeus - lord of the sky, father of gods and people
- Hera - the wife of Zeus, the patroness of the family
- Poseidon - the sea
- Hestia - family hearth
- Demeter - agriculture
- Apollo - light and music
- Athena - wisdom
- Hermes - trade and messenger of the gods
- Hephaestus - fire
- Aphrodite - beauty
- Ares - war
- Artemis - hunting
From the earth, people each turned to their god, according to their destiny. Temples were built everywhere to propitiate them, and gifts were offered instead of sacrifices.
In Greek mythology, not only Chaos, the Titans and the Olympian Pantheon mattered, there were other gods.
- Nymphs Naiads who lived in streams and rivers
- Nereids - nymphs of the seas
- Dryads and Satyrs - nymphs of the forests
- Echo - nymph of mountains
- Goddesses of fate: Lachesis, Clotho and Atropos.

The rich world of myths was given to us by ancient Greece. It is filled with deep meaning and instructive stories. Thanks to them, people can learn ancient wisdom and knowledge.
How many different legends exist at the moment, do not count. But believe me, every person should get acquainted with them after spending time with Apollo, Hephaestus, Hercules, Narcissus, Poseidon and others. Welcome to the ancient world of the ancient Greeks!
The life of the ancient Greek gods on Mount Olympus seemed to people a continuous fun and a daily holiday. Myths and legends of those times are a storehouse of philosophical and cultural knowledge. Having considered the list of the gods of Ancient Greece, you can plunge into a completely different world. Mythology surprises with its uniqueness, it is important because it pushed humanity to the development and emergence of many sciences, such as mathematics, astronomy, rhetoric, and logic.
First generation
Initially, there was Mist, and Chaos arose from it. From their union came Erebus (darkness), Nikta (night), Uranus (sky), Eros (love), Gaia (earth) and Tartarus (abyss). All of them played a gigantic role in the formation of the pantheon. All other deities are related to them in one way or another.
Gaia is one of the first deities on earth, which arose along with the sky, sea and air. She is the great mother of everything on earth: heavenly gods were born from her union with her son Uranus (heaven), sea gods from Pontos (sea), giants from Tartaros (hell), and mortal beings were created from her flesh. Depicted as a fat woman, half rising from the ground. We can assume that it was she who came up with all the names of the gods of Ancient Greece, a list of which can be found below.
Uranus is one of the primeval gods of Ancient Greece. He was the original ruler of the universe. He was overthrown by his son Kronos. Born to one Gaia, was also her husband. Some sources call his father Akmon. Uranus was depicted as a bronze dome covering the world.
List of gods of Ancient Greece born by Uranus and Gaia: Oceanus, Kous, Hyperion, Crius, Thea, Rhea, Themis, Iapetus, Mnemosyne, Tethys, Kronos, Cyclopes, Brontes, Steropes.
Uranus did not feel much love for his children, more precisely, he hated them. And after their birth he imprisoned them in Tartarus. But during their rebellion he was defeated and castrated by his son Kronos.
Second generation
The Titans, born of Uranus and Gaia, were the six gods of time. The list of titans of ancient Greece includes:
Ocean - tops the list of gods of Ancient Greece, titanium. It was a large river surrounding the earth, was the reservoir of all fresh water. Oceanus' wife was his sister, the titanide Tethys. Their union gave birth to rivers, streams and thousands of oceanids. They did not take part in the Titanomachy. The ocean was depicted as a horned bull with a fish tail instead of legs.
Kay (Koy/Keos) - Phoebe's brother and husband. Their union gave birth to Leto and Asteria. Depicted in the form of a celestial axis. It was around her that the clouds revolved and Helios and Selena walked across the sky. The couple were thrown by Zeus into Tartarus.
Kriy (Krios) - an ice titan that can freeze all living things. He shared the fate of his brothers and sisters, thrown into Tartarus.
Iapetus (Iapetus / Iapetus) - the most eloquent, commanded the titans during the attack on the gods. Also sent by Zeus to Tartarus.
Hyperion - lived on the island of Trinacria. He did not take part in the Titanomachy. The wife was the titinide Thea (she was thrown into Tartarus along with her brothers and sisters).

Kronos (Chronos/Kronus) is the temporary ruler of the world. He was so afraid of losing the power of the supreme god that he devoured his children so that none of them would claim the throne of the ruler. He was married to his sister Rhea. She managed to save one child and hide him from Kronos. Deposed by his only rescued heir, Zeus, and sent to Tartarus.
Closer to people
The next generation is the most famous. They are the main gods of Ancient Greece. The list of their exploits, adventures and legends with their participation is very impressive.
They not only became closer to people, descending from heaven and emerging from chaos to the top of the mountain. The gods of the third generation began to contact people more often and more willingly.

This was especially boasted by Zeus, who was very partial to earthly women. And the presence of the divine wife Hera did not bother him at all. It was from his union with a man that the familiar hero of myths, Hercules, was born.
third generation
These gods lived on Mount Olympus. From its name they got their title. There are 12 gods of Ancient Greece, the list of which is known to almost everyone. All of them performed their functions and were endowed with unique talents.

But more often they talk about fourteen gods, the first six of which were the children of Kronos and Rhea:
Zeus - the main god of Olympus, the ruler of the sky, personified power and strength. God of lightning, thunder and creator of people. The main attributes of this god were: Aegis (shield), Labrys (double-sided ax), Zeus' lightning (two-pointed pitchfork with notches) and an eagle. Distributed good and evil. Was in alliance with several women:
- Metis - the first wife, the goddess of wisdom, was swallowed by her husband;
- Themis - the goddess of justice, the second wife of Zeus;
- Hera - the last wife, the goddess of marriage, was the sister of Zeus.
Poseidon is the god of rivers, floods, seas, drought, horses and earthquakes. His attributes were: a trident, a dolphin and a chariot with white-maned horses. Wife - Amphitrite.
Demeter is the mother of Persephone, the sister of Zeus and his lover. She is the goddess of fertility and patronizes farmers. Demeter's attribute is a wreath of ears of corn.
Hestia is the sister of Demeter, Zeus, Hades, Hera and Poseidon. The patroness of the sacrificial fire and the family hearth. I took a vow of chastity. The main attribute was a torch.
Hades is the ruler of the underworld of the dead. Husband of Persephone (goddess of fertility and queen of the kingdom of the dead). The attributes of Hades were a bident or a wand. Depicted with an underground monster Cerberus - a three-headed dog, who stood guard at the entrance to Tartarus.
Hera is the sister and wife of Zeus. The most powerful and wise goddess of Olympus. She was the patroness of family and marriage. A mandatory attribute of Hera is a diadem. This decoration is a symbol of the fact that she is the main one on Olympus. She obeyed (sometimes reluctantly) all the main gods of ancient Greece, the list of which she headed.
Other Olympians
Although these gods did not have such powerful parents, almost all of them were born from Zeus. Each of them was talented in their own way. And he did his job well.
Ares is the son of Hera and Zeus. God of battles, war and masculinity. He was a lover, then the husband of the goddess Aphrodite. Ares' companions were Eris (goddess of discord) and Enyo (goddess of violent war). The main attributes were: a helmet, a sword, dogs, a burning torch and a shield.
Apollo - the son of Zeus and Leto, was the twin brother of Artemis. The god of light, the leader of the muses, the god of medicine and the predictor of the future. Apollo was very loving, he had many mistresses and lovers. The attributes were: a laurel wreath, a chariot, a bow with arrows and a golden lyre.
Hermes is the son of Zeus and the Pleiades Maya or Persephone. God of trade, eloquence, dexterity, intelligence, animal husbandry and roads. Patron of athletes, merchants, artisans, shepherds, travelers, ambassadors and thieves. He is the personal messenger of Zeus and the escort of the dead to the kingdom of Hades. He taught people writing, trade and accounting. Attributes: winged sandals that allow him to fly, an invisibility helmet, a caduceus (a wand adorned with two intertwined snakes).

Hephaestus is the son of Hera and Zeus. God of blacksmithing and fire. He limped on both legs. Wives of Hephaestus - Aphrodite and Aglaya. The attributes of the god were: bellows, tongs, a chariot and a pilos.
Dionysus is the son of Zeus and the mortal woman Semele. God of vineyards and winemaking, inspiration and ecstasy. Theater patron. He was married to Ariadne. Attributes of God: a cup of wine, a vine wreath and a chariot.
Artemis is the daughter of Zeus and the goddess Leto, the twin sister of Apollo. The young goddess is a hunter. Being the first to be born, she helped her mother give birth to Apollo. Chaste. Attributes of Artemis: doe, quiver with arrows and chariot.
Demeter is the daughter of Kronos and Rhea. Mother of Persephone (wife of Hades), sister of Zeus and his lover. Goddess of agriculture and fertility. Demeter's attribute is a wreath of ears.
Athena, the daughter of Zeus, completes our list of the gods of Ancient Greece. She was born from his head after he swallowed her mother Themis. Goddess of war, wisdom and craft. Patroness of the Greek city of Athens. Her attributes were: a shield with the image of the Gorgon Medusa, an owl, a snake and a spear.
Born in foam?
I want to talk about the next goddess separately. She is not only to this day a symbol of female beauty. In addition, the history of its origin is hidden in mystery.
There is a lot of controversy and speculation about the birth of Aphrodite. The first version: the goddess was born from the seed and blood of Uranus castrated by Kronos, which fell into the sea and formed foam. The second version: Aphrodite originated from a sea shell. The third hypothesis: she is the daughter of Dione and Zeus.
This goddess was in charge of beauty and love. Spouses: Ares and Hephaestus. Attributes: chariot, apple, rose, mirror and dove.
How they lived on the great Olympus
All the Olympic gods of Ancient Greece, the list of which you see above, had the right to live and spend all their free time from miracles on the great mountain. The relationship between them was not always rosy, but few of them dared to open hostility, knowing the power of their opponent.

Even among the great divine beings, there was no permanent peace. But everything was decided by intrigues, secret conspiracies and betrayals. It is very similar to the human world. And this is understandable, because humanity was created by the gods, so they all look like us.
Gods who do not live on Mount Olympus
Not all deities had a chance to reach such heights and climb Mount Olympus to rule the world there, feasting and having fun. Many other gods either failed to deserve such a high honor, or were modest and content with an ordinary life. If, of course, you can call the existence of a deity that way. In addition to the Olympic gods, there were other gods of Ancient Greece, a list of their names is here:
- Hymen is the god of marriage bonds (the son of Apollo and the muse Calliope).
- Nike is the goddess of victory (daughter of Styx and the titan Pallas).
- Irida is the goddess of the rainbow (daughter of the sea god Tawmant and the oceanid Electra).
- Ata is the goddess of obscuration of the mind (daughter of Zeus).
- Apata is the mistress of lies (heiress of the goddess of night darkness Nyukta).
- Morpheus is the god of dreams (the son of the lord of dreams Hypnos).
- Phobos - the god of fear (a descendant of Aphrodite and Ares).
- Deimos - the lord of horror (the son of Ares and Aphrodite).
- Ora - the goddess of the seasons (daughters of Zeus and Themis).
- Eol - the demigod of the winds (the heir of Poseidon and Arna).
- Hekate is the mistress of darkness and all monsters (the result of the union of the titan Perse and Asteria).
- Thanatos is the god of death (son of Erebus and Nyukta).
- Erinyes - goddesses of revenge (daughters of Erebus and Nyukta).
- Pontus is the ruler of the inland sea (heir to Ether and Gaia).
- Moira - the goddess of fate (daughter of Zeus and Themis).

These are not all the gods of Ancient Greece, the list of which can be continued even further. But to get acquainted with the main myths and legends, it is enough to know only these characters. If you want to read more stories about each, we are sure that the ancient storytellers came up with a lot of interweaving of their destinies and details of the divine life, in which you will gradually get to know more and more new heroes.
Meaning of Greek mythology
There were also muses, nymphs, satyrs, centaurs, heroes, cyclops, giants and monsters. This whole vast world was not invented in one day. Myths and legends have been written for decades, with each retelling acquiring other details and characters that have never been seen before. All the new gods of ancient Greece appeared, the list of names of which grew from one storyteller to another.
The main goal of these stories was to teach future generations the wisdom of the elders, to tell in an understandable language about good and evil, about honor and cowardice, about loyalty and lies. And besides, such a huge pantheon made it possible to explain almost any natural phenomenon, the scientific justification of which was not yet available.





