How to make a basement under the house. Is it possible to make a basement in an already built house
Our distant ancestors had no idea that the basement could be used as a dwelling.
However, with the development of technological progress, building materials have appeared that can make the basement habitable.
It is for this reason that the owners of country houses, interested in increasing the usable area of their own home, use the basement for a variety of purposes.
Basements built in compliance with all technological features can perform a variety of functions - it all depends on the needs of the homeowner. In any case, this corner will not become a useless room, and it certainly will not be empty.
Types of basements by purpose
By way of use basements are divided into several types:
- cellar for storing vegetables, fruits and various homemade preparations. Today, many residents of country houses are happy to grow vegetables and fruits. Now they will have the opportunity to take a separate corner for the harvest.
- Basement workshop. In this room, you can make a full-fledged workplace, put comfortable tables and place all the necessary tools on the basement shelves.
- Basement as an additional room. Most often, original living rooms or cozy mini-bars with a wine cellar are arranged here. However, in the basement there may be a bedroom, a lounge, and a billiard room.
- underground garage This is a great idea for small lot owners who can't build a free standing garage for car storage and maintenance.
- Basement with bath, sauna and swimming pool. With proper design and construction of this room, it will be a great place for the whole family to relax.
- Basement as a technical room. Here you can place a boiler room or various communications, for example, a gas boiler for heating a house.
Materials and tools
To the choice materials necessary for the construction of the basement should be approached with special attention, since not only the quality of the structure, but also the process of waterproofing (protecting building structures from moisture penetration) will depend on them.
The best solution for building a basement would be silicate brick. When building walls and ceilings, it is better to use waterproof concrete, which will protect the basement from the pressure of groundwater.
As for the tools, you will need:
- mixer for the preparation of concrete composition;
- several clean buckets;
- welding machine;
- shovel, as well as bayonet-shovel;
- trowel (in other words, "trowel", a tool that is a polished spatula on a curved handle);
- hammers of various sizes;
- saw;
- plane;
- hacksaw;
- axe.
Basement building step by step
Before starting the construction of the basement, it is necessary to carry out all the necessary calculations and compose blueprints future building. In this case, the depth of soil freezing should be taken into account, as well as the negative destructive effect of groundwater.

Groundwater can make the basement unsuitable for full use. Prolonged exposure to groundwater leads to foundation destruction and then the entire building.
Laying the foundation for a country house with a basement
 It is clear that the basement will be below the ground surface, so it is necessary to dig a foundation pit of the required depth. (1.5 - 2 m) and then arrange it properly.
It is clear that the basement will be below the ground surface, so it is necessary to dig a foundation pit of the required depth. (1.5 - 2 m) and then arrange it properly.
The trench walls should compact to keep the soil from sinking. Several layers of crushed stone and sand are laid at the bottom of the pit, which are carefully compacted.
Basement floor construction
 It should be noted: if you make the floor after the walls, then the concrete mixture is poured air bag, and the construction of formwork is not required.
It should be noted: if you make the floor after the walls, then the concrete mixture is poured air bag, and the construction of formwork is not required.
Basement floor construction technology:
- First of all, it is checked pit depth, if necessary, remove excess soil.
- Next stage - basement waterproofing. This procedure can be carried out in different ways, but the simplest way is to use a special thick film for waterproofing, it is sold in specialized stores. This material is durable and does not lose its properties for many years.
- After waterproofing on the base of the floor is mounted thermal insulation layer consisting of extruded polystyrene, expanded polystyrene, etc. Sheets of thermal insulation material are laid directly on the surface of the film.
- Another one is mounted waterproofing layer and then set reinforcement mesh. The thickness of the wire of such a grid should be at least 3 mm.
- The last step in the formation of the base for the floor will be pouring concrete mortar. The optimum thickness of the concrete layer is 8 - 10 cm.
Advice! In order to keep the heat in the basement better, it is necessary that the thermal insulation layer be at least 5 cm thick.
After the concrete base has completely hardened, you can proceed to floor finishing in the basement. For this you can use ceramic tiles, flooring etc.
Construction of monolithic walls in the basement
 If technology is chosen for a house with a basement strip foundation, then the walls will turn out to be reliable and durable.
If technology is chosen for a house with a basement strip foundation, then the walls will turn out to be reliable and durable.
The procedure is as follows:
- initially mounted stationary wooden form, which corresponds to the height of the walls;
- Further reinforced monolithic walls. For this, a reinforcing cage is knitted, the distance between the cells is 25x25 cm, reinforcing mesh diameter not less than 12 mm;
- poured concrete. It is important to fill immediately, and not in several stages. To do this, you must first take care of the availability of the required amount of concrete mortar.
Advice! The thickness of the concrete walls in the basement should be 20 - 40 cm. It may vary depending on the characteristics of the soil and the number of floors in the residential building.
Basement waterproofing
 In order for water not to accumulate in the basement, you need to think about it. waterproofing.
In order for water not to accumulate in the basement, you need to think about it. waterproofing.
If the basement was built from foam blocks or bricks, all seams should be covered with a special waterproofing mastic and then gently plaster the walls.
Also on the floor all available joints treated with mastic. This procedure should only be carried out on a dry surface.
Another mandatory step will be the production drainage(a method of collecting and subsequent removal of groundwater from a building structure), which will protect the basement from flooding, as well as from the accumulation of moisture.
To do this, even at the stage of building walls, specially dug trenches at the base of the foundation (the lower part that is in contact with the ground) are installed drainage pipes. Products are mounted at an angle of approximately 3 degrees. Water from them will leave naturally.
How to make ventilation in the basement
 Most often, to create comfortable conditions in the basement, they use supply and exhaust ventilation system providing a natural supply of fresh air.
Most often, to create comfortable conditions in the basement, they use supply and exhaust ventilation system providing a natural supply of fresh air.
It consists of:
- supply pipe supplying fresh air from the street;
- hood that brings air outside from the room.
exhaust pipe mounted along the ceiling, and then displayed on the roof. If there is a fireplace channel in the basement, then the hood is installed next to it. This allows you to significantly improve the efficiency of basement ventilation. The exhaust pipe should be located higher than all buildings that are located near the house.
supply pipe is installed on the opposite side of the exhaust, and is located approximately at a height of 50 cm from the floor. This pipe is also displayed on the roof.
How to insulate a basement
 The basement is the coldest and most uncomfortable place in the whole house, so you should take care of it, which will not create condensation in the heat and keep warm in the cold.
The basement is the coldest and most uncomfortable place in the whole house, so you should take care of it, which will not create condensation in the heat and keep warm in the cold.
After the waterproofing mastic dries, you can begin the process of floor insulation.
For this, it is used polystyrene foam, which can be glued to the floor surface using bitumen (tarry or solid product - a mixture of hydrocarbons with sulphurous, nitrogenous, metal-containing derivatives).
Styrofoam sheets are covered from above asbestos-cement slabs.
Suitable for the ceiling surface:
- polystyrene foam is glued to the ceiling using liquid nails or universal synthetic adhesives;
- mineral wool is mounted in a crate, which is pre-made from boards or metal profiles;
- foam is glued to the surface of the ceiling using a special adhesive.
Basement design
 Basement design completely depends on the needs and desires of the owner of the house.
Basement design completely depends on the needs and desires of the owner of the house.
So, lovers of entertainment and fun parties can arrange there stylish bar, and lovers of family holidays will like living room with soft sofas, a fireplace and a large TV.
Finishing the basement depends only on the preferences of the owner of the house, elements are often used brickwork, arches, and aged furniture and accessories. Be sure to take care of grounding outlets, without which safety is out of the question.
As a rule, the basement is connected to the house with a small hatch. For convenience, you can build a staircase or buy a finished structure.
Estimated cost of building a basement
 If the basement is built with your own hands, then the cash costs will go only to materials and the necessary tools. Everything will depend on room dimensions and, of course, from the professionalism of the performers.
If the basement is built with your own hands, then the cash costs will go only to materials and the necessary tools. Everything will depend on room dimensions and, of course, from the professionalism of the performers.
If you involve professionals with special construction equipment in the work, then the prices vary from 500 thousand to 2 million rubles.
You can learn the features of building a basement with your own hands from laying the foundation to building walls and ceilings from this video.
Basement not: if the latter is necessarily located away from the house, then the basement is under it or in close proximity; most often, the basement as a building structure is also the foundation of the house. The basement is necessarily buried below the standard freezing depth of the soil (NGP); the cellar can also be bulk surface. The basement floor is often located below the groundwater level (GWL). All this makes the basement and the house on it especially sensitive to ground movements and the action of groundwater. Moreover, the basement can exacerbate the influence of both of these factors. All this makes the construction of the basement almost the most difficult and responsible task of the entire cycle of construction work. When built to order on a turnkey basis, a house with a basement costs 30-100% more than the same baseless one. However, the basement in the house provides a lot of conveniences and benefits, and it is quite possible to build a basement with your own hands and save a large amount. Let's try to figure out how.
What does the basement provide?
The traditional use of the basement as food storage is already more useful than cellars: the microclimate in it is more stable, easier to regulate, and it is much more difficult for pests to get into the basement than into the cellar. The basement is also more suitable for a workshop and other utility rooms: it is electrified, gasified and heated along with the house.
The basement in a private house is especially beneficial as a center for the concentration of life support systems (LSS): all equipment can be located safely, compactly and conveniently for current maintenance and repair, on the left in Fig. And that's not all: a boiler or heating stove with a water circuit, transferred in the same house from the boiler room (furnace) upstairs to the basement, it turns out, they begin to consume 3-5% less fuel due to the same stable basement microclimate. The savings for the heating season in material terms are quite tangible.

Another advantage of a house with a basement in our area is still little known, but in the countries of Southern Europe the demand for houses with a residential basement (on the right in the figure) steadily exceeds supply. The point here is survival, but not in case of war or some fantastic cataclysms. There are also enough real ones: due to global warming, the Sahara will “spit” hot air every summer for a long time to come. Surcharges, special or "environmental" tariffs, penalties, etc. requisitions for overexpenditure of electricity in countries that are provided with their own energy resources - mother, do not worry! When it stays + (40-45) in the yard for weeks and months, it is impossible to live normally, and energy bills for air conditioning the whole house come in such that ... think better about democratic values, they are enduring. Moving to a residential basement for the summer either reduces the cost of air conditioning to an acceptable level, or allows you to do without it altogether.
Waterproofing: the beginning
The basement under the house will only be a boon when it is dry and does not violate the stability of the entire structure. Both of these factors are interrelated, because. a house with a basement often begins to lean and / or settle just as a result of a violation of the underground flow by a rigid box deeply buried in the ground: the natural movement of groundwater is disturbed, see Fig .:

As a consequence, the mobility and bearing properties of the soil also change. There are cases when a house with a basement, built on dry dense loam, had to be abandoned - a quicksand crawled under it due to the influence of an improperly built basement.

There are various ways for soil moisture to penetrate into the basement, and there are no 100% effective ways to drain a moldy basement. Basement dampness and the whole house will make uncomfortable and unhealthy. But you also need to think about the effect of the basement on the underground runoff. The only way to prevent such a Gordian knot from tying is the correct design of the basement and its reliable external waterproofing. The choice of design is directly related to the properties of the structural material. Therefore, in order to properly build a house with a basement, its development must be carried out in the following sequence:
- Choice of construction material;
- Choice of power circuits in plan and section;
- The choice of method and scheme of waterproofing;
- Determining the composition of the basement arrangement;
- Choice of construction technique.
Note: if the basement gets wet, but the house with it still stands, then there are ways to dry the basement, see below. Such a basement will not be suitable for housing and stationary electrification, drying will have to be repeated every 3-5 years, but it will serve as a food storage and / or a location for non-volatile heating devices.
materials
It is possible to make a basement from materials capable of withstanding a lateral soil pressure of 20 bar (2 kgf / sq. cm or 20 tf / sq. m) and a pressure of formation water of 10 bar (1 kgf / sq. cm or 10 tf / sq. m) .m). These conditions correspond to the strength grade from M200 and the water resistance grade from W10. Of course, the greater the margin for both parameters, the more reliable the basement will be.
Independent developers usually build basements with reinforced concrete monolithic (pos. 1 in the figure), prefabricated from concrete foundation blocks with a monolithic base (pos. 2), brick (pos. 3), monolithic with a brick plinth (pos. 4) or from cinder blocks, pos. 5.

The “brick on concrete” option is durable enough if the base is made of burnt iron brick or clinker brick: the front outer brick is not designed to carry the weight load from the building; its service life is up to 40 years, and a house with a basement is built for generations. The red working brick in the immediate vicinity of the ground begins to crumble within 25 years, and completely loses its load-bearing properties in 50-60 years. Iron ore and clinker will stand in the plinth of the century, but they are not aesthetic. In general, the basement at pos. 4 is not an option. For beauty, it would be easier, more reliable and cheaper to fill in a monolith and veneer it to taste.
The suitability of certain materials for building a basement is shown in the figure:

As you can see, they can be divided into 3 groups:
- Unsuitable.
- Conditionally suitable for structured soils (dense sandy loam, light loam), if the GWL does not rise closer than 0.2 m to the bottom of the basement floor.
- Suitable.
I group
Unambiguous "losers" - foam and aerated concrete, and their low bearing capacity is not the most important thing here. Let's say the natural wear of concrete is 0.01 mm per year. This is an insignificant amount; in the ground it is much more. The minimum layer of concrete over the reinforcement is 40 mm. In order for the reinforcement to begin to be massively exposed and thus the structure required a major overhaul, in the absence of other destructive factors, 4000 years must pass. We also assume that the bridges between the pores of foam and aerated concrete are thick, 1 mm; they are usually thinner. With the same wear in 25 years, the material will lose 50% of its strength (the lintels are destroyed from 2 sides) - major repairs are impossible, the structure has become unusable. After another 10-15 years, it will begin to spontaneously collapse without the possibility of recovery. For this reason, in Southern Europe (most of all in Spain), thousands of houses, once built for seasonal rental, are now being sold “for how much they will give”. Their appearance is still chic, but their lifespan is ending, and there is no way to restore it.
This also includes silicate brick and expanded clay concrete. The first one in the ground crumbles literally before our eyes, it is expensive and requires quite high skills to work with it. The second one is cheap, it is easier to work with it, but, alas, it gets wet through, and it is impossible to isolate it reliably, there are no such methods and compositions.
II group
From this group, it is better not to use red brick and poor concrete for the foundation under the house: they crumble in the ground and repair is often impossible. Clinker bricks are quite reliable, durable up to 150 years or more, easily insulated, but expensive. Burnt brick-iron ore is a little inferior to it and is cheap, but it does not go on sale regularly, because. is a manufacturing defect. But a cinder block basement, due to its cheapness and ease of working with it, is quite common, see video:
Video: building a “box” of a cinder block basement
An important advantage of the cinder block basement is that it is light and the house with it gives a normal draft on rather weak soils with a bearing capacity of> 0.7 kgf / sq. see It is possible to build a basement from a cinder block not only on dry ground. It can be quite suitable for economic purposes if the soil water is above the level of the basement floor for no more than 6 months. per year, and the formation pressure does not exceed 10 bar; in most cases of self-building, these conditions are met. But, firstly, measures for waterproofing the walls of the basement must begin to be carried out already at the stage of their construction, steadily observing all the rules of cinder block masonry, see the video:
Video: cinder block masonry basics
Secondly, waterproofing must be done the same as for walls made of bricks or foundation blocks, but reinforced: both paint with bituminous compounds, and pasting, see below. And instead of gluing materials on a textile basis, use roofing paper on cellulose (cardboard). Looking ahead, the principle of operation of insulation based on natural bitumen is as follows: if, after many years, the structure isolated by it is dismantled, not a trace of the original insulator is found. Bitumen from it is pressed into concrete, on which a waterproof crust has formed. The pores of the cinder block are much wider than in concrete, and the cellulose fibers from the base of the roofing sheet will become a reinforcing filling for the bitumen in them.
How to isolate cinder block

How the cinder block basement waterproofing is arranged is shown in fig. on right. Since there is no and cannot be any guarantee for the level of standing groundwater, it is better to replace backfilling with soil with a clay castle (highlighted in color) with a removal at the top of 0.5 m beyond the contour of the blind area. Its presence around the house, as well as heels with a removal of 0.4 m under the foundation tape, is an indispensable condition for the reliability of waterproofing a cinder block basement.
Pasting (sheet) insulation in this case is applied in the reverse order to the generally accepted one - from top to bottom. It is more convenient to work this way, using a device in the form of a tragus with a stick or a piece of pipe laid in it, on which a roll of roofing is put on. The tragus is placed on the foundation tape, and then:
- A section of the wall is painted over to a width of a roll + (15-20) cm with liquid bituminous mastic-prime (primary) on a gasoline thinner. It is better to apply prime mastic with a wide, hard brush, pressing into the wall material;
- They smear the same area with bituminous mastic on anthracene oil - it is thicker, stickier and dries more slowly than on gasoline. Layer - 3-4 mm;
- A piece of roofing sheet is wound from the roll to the bottom with a small margin;
- The insulator is rolled to the coating, going from bottom to top and squeezing out bubbles;
- The cut is cut with some margin;
- The tragus is rearranged so that the overlap of the cuts is 20-25 cm;
- Repeat paragraphs. 1-6 on a new section of the wall with an offset of 15-20 cm beyond the width of the roofing strip;
- The joint of the sheets is heated with a gas burner and rolled according to clause 4;
- Repeat paragraphs. 1-8 until they reach the corner;
- At the corner, they paint over and coat the adjacent wall, the removal of the roofing around the corner is cut across at the top and bottom;
- The wing of the insulator is not very warm from the outside and softly wrapped around the corner;
- The wrapping is heated and rolled according to clause 4;
- Repeat the work cycle until the entire building is bypassed;
- Apply the 2nd layer of adhesive insulation in a similar way;
- An external safety layer of paint insulation is applied from the same mastic;
- They backfill the soil or put a clay castle.
To a beginner, this whole procedure will seem very laborious, but any reliable pressure-proof insulation is no easier to do. But a cinder block basement will cost 1.5-2.5 times cheaper than concrete or brick.
At the same time about the brick
The insulation described above does not provide 100% protection of the brick basement from dampness - the pores of the brick are thinner than the cinder block, and the bitumen is pressed into them poorly. It is better to insulate the walls of a brick basement with modern penetrating materials with a deep penetration effect (see below). A typical scheme for insulating a brick wall with them is given in Fig.:

Plastering a wall on a grid for insulation is mandatory: penetrates reliably fill cracks up to 0.4 mm, and wider cracks can form in a brick wall. The role of a clay lock, which does not let capillary moisture into the concrete-brick seam, is played by plugs from Penekrit in a strobe 25x50 mm and Penekrit with Penetron in the holes of the concrete heel. The disadvantage of this scheme is that penetrates are not eternal, like natural bitumen; after 10-30 years, the insulation will have to be replaced.

Repair of a damp concrete basement with deep penetration compounds
Note 2: if a previously dry concrete basement began to dampen with a drop on the walls and floor (the underground drain has changed), it can be repaired with Penekrit with Penetron for 5-20 years, see fig. on right. Shtroba - 25X25 mm. The insulation is plastered with moisture-resistant plaster in 2 layers of 15-20 mm each with a reinforcing mesh (see above) to avoid swelling of the insulating layer by capillary pressure. Work is carried out during the driest time of the year. The basement is pre-dried, see below, and immediately before applying the insulation it is wetted twice with a wide soft brush.
III group
In the materials of group III, high-strength moisture-resistant concrete stands by a wide margin. Only from it can you build a dry basement on watered soil, without doing such a complex and technically not always feasible thing as site drainage. It is enough to apply inexpensive (and very durable) bituminous insulation, see next. fig., and the basement will not dampen the generations of residents, no matter how the groundwater “walks”.

A big minus of the concrete basement is the emergency work on pouring and technical breaks for the monolith to gain strength; building on your own, you can simply not be in time for the season. In addition, concrete M400 W>10 is not cheap, and the concrete truck will not arrive exactly at the time you set. Most likely, it will be assigned to you, and even you will have to wait.
The way out is the construction of a basement from ready-made foundation blocks. 2-3% by volume of liquid glass is added to the water for masonry mortar. It is better to buy ready-made blocks, they are already M (400-600) W (20-3). Block 200x200x400 is turned by one person. The laying is then carried out in 2 blocks with dressing of the seams and alternating spoon rows with bonder rows, like a brick wall. Corner "semi-blocks" are not chipped or cut off - let them stick out half into the ground, the whole structure will only be more stable. If there are 2-3 strong assistants and at least a hoist, it is even better to purchase blocks of 400x400x800 - they are with a tooth and the masonry will be very strong. In this case, it is led into one block with dressing of the seams in rows.
Foundation blocks on reinforced concrete structures undergo steaming, which is not feasible at home. But, let it be known to you that the exposure is from 3 months. blocks that have gained 25% strength in a stack under the film completely replaces it. The rows in the stack must be shifted with pieces of wood so that there are gaps of 20-30 mm between them; in hot, dry weather, the stack is wrapped in damp burlap. And do-it-yourself high-strength concrete can also be prepared by hand kneading, see the plot:
Video: manual concrete production
The construction of a basement, especially in an existing house, can generally be considered the third thing that does not tolerate haste. Then - the first year we are preparing slowly the required number of blocks; next summer we are building again without rush work. Blocks can be cast not typical, within one's strength and with a tooth - the finished masonry will withstand a pressure of more than 30 bar. What about W? In production, liquid glass is mixed into the concrete mass in special devices, which, again, cannot be done at home. But self-builders successfully prepare moisture-resistant concrete at W (10-15) with the well-known repair compound Dehydrol, see the video:
Video: how to make hydraulic concrete
Note: self-made hydroconcrete does not guarantee against the penetration of capillary moisture, therefore, external anti-pressure insulation must be supplemented with internal anti-capillary insulation from the same Dehydrol, see fig. Also inside the entire basement is plastered with armoring insulation made of cement-sand plaster, see above.
Power Circuits
The basement waterproofing scheme is tied to its general power (carrier) scheme. It is also developed depending on local conditions, first in a section, and then in a plan.
Possible power circuits of makeshift basements in the context are given in the figure:

A basement on a slab is built on weak homogeneous soils: a large bearing area gives a low specific pressure on the soil and distributes the weight load more evenly over it. In fact, the entire building in this case stands on a deeply buried slab foundation. The removal of the slab along the contour is needed no less than the thickness of the basement walls (foundation tape), otherwise weight loads will be concentrated on the edge of the slab, it will crumble over time, and the whole house will sag crookedly. Also, basements on soft soils float more easily, see below; "side hook" counteracts this. The slab is poured with the onset of stable warm weather, withstands up to 50% strength (at least 20 days) and is built on it from any other suitable material. If the seasonal standing of groundwater is possible above 0.6 m above the level of the sole (not the floor!) Of the basement, the slab is poured one and a half thickness (from 300 mm) with a tooth a third of the height, see below.

A basement on a tape is built, on the contrary, on dense, well-bearing (from 1.7 kgf / sq. Cm), and, possibly, heterogeneous soils: a slab from a boulder that fell at an angle to it during precipitation will dangerously tilt; the tape will either push it down or push it to the side. On dense homogeneous non-rocky or slightly heaving soils, if the house has been established without disturbance for at least 3-5 years, it is possible to build a foundation on a tape in an existing house. A typical scheme is given in fig. on the right, but in each case the construction is carried out according to an individual project based on on-site research.
If the basement on the tape is being built at the same time as the house, then the emergency concreting cycles are not tied to each other: the pouring of the permanent floor can and even needs to be (see below) postponed until next year. In any case, the removal of the heel of the tape to the side must be at least 0.6 m in order to "disperse" the load from the force of soil resistance to the settling building (shown in red dotted line), otherwise the floor can simply be squeezed up.
Temporary floor
It is advisable to leave the basement on the tape without a floor for a year, if the groundwater level does not rise above 0.2 m under the basement base, so that the building gives an initial draft and the permanent floor does not exactly kick out. In the meantime, you can lay a temporary floor, like laying floors on the ground.
Schemes for flooring on the ground are given on the left in the figure:

Pos. A is applicable if the soil water does not rise above 0.6 m to the basement basement; pos. B - if they reach 0.2 m below it. In the case when the utility cellar on the tape remains dry for more than 3 years, a warm dirt floor is often laid in it, on the right in rice: this way vegetables and fruits are stored longer and spoil less. Plant products in storage release ethylene, which stimulates their ripening; without ethylene, products "sleep". Ethylene is slightly heavier than air and is not completely removed by normal basement ventilation (see below); there are many cases of ethylene poisoning of people who have been in food cellars for a long time. Ethylene soil, on the contrary, eagerly absorbs, you just need to make the bins ventilated and on stands from 15-20 cm. In addition, homemade kvass, liqueurs, wine, beer, mead in a basement with a dirt floor ripen better and turn out to be much tastier.
Note: basements on slab and tape are suitable for installation of boiler equipment and electrification for housing only after at least 3 years after the completion of the construction of the entire house, if during this time there were no signs of dampness of the basement and / or uneven settlement of the building.
A basement-caisson made of moisture-resistant concrete with external anti-pressure insulation will be dry on any soil, even if it floats in water - during the Second World War, even sea ships were built from reinforced concrete. The coffered basement is also compatible with any building, see below. But its construction is a continuous complex emergency job, see below. And on light, loose, heavily watered soils, the basement-caisson can suddenly emerge. Basements on the slab and the tape let you know about the troubles of the underground runoff by dampening despite any insulation - the working and masonry seams are torn - and the caisson can literally float up and fall on its side along with the house in just a week. Therefore, caisson basements are not recommended to be built at the highest groundwater level of more than 0.6 m above the basement floor, and the box should be taken out from 0.6 m on medium and dense soils and from 0.8 m on light ones.
The power scheme of the basement in the plan is already linked not only with the ground, but also with the structure of the building. Its possible options for self-building are shown in Fig. below. The basement floor (pos. 1) is the only one that allows you to immediately equip a boiler room and a house communications wiring unit in the basement (on the left in the figure at the beginning); in this case, it is built coffered. The important thing here is that there must be a window in the boiler room, and the walls of the caisson and the basement of the building are a single monolith.

An incomplete basement floor is built less frequently - savings on earthworks are more than eaten up by an excess of concrete. Typical justified cases are heavy, complex and expensive soil to develop (pos. 1a) or a light loose spot is found on heavy soil, suitable in size for a basement, pos. 1b. In this case, on the contrary, it is in no way possible to build a basement-caisson or on a slab, only on a tape! The caisson is not recommended for pos. 1a, so you will have to wait several years before moving the boiler house to the basement or equipping it for housing.
Note: an incomplete basement floor and a basement mezzanine are two different things. In the basement mezzanine, it is possible to install an external entrance door, buried in the pit by no more than 3-4 steps.
Even less often, basements are built adjacent to the foundation of an existing house (item 2 in the figure above) - there is a high risk of a new uneven settlement of the building. If the pros are building according to the project, then the owner and operator give a subscription that the damage from all possible consequences is assumed. In an existing house, it is better to build a “floating” basement, at least 1 m away from the foundation tape of the house, pos. 3. Its power circuit in the section is possible in any way, however, you will have to spend money on a separate basement floor, between which and the floor floor of the house you need a free clearance of 0.3 m, i.e. and the basement pit needs to be dug deeper. The reason is the difference in the speed and magnitude of the draft of 2 separate buildings nested one into the other.
You can get by with a smaller total volume of earthwork and concrete work, as well as a general overlap, by building a connected basement - connected to the foundation of the house with rigid reinforced concrete lintels the width of the foundation tape. They are deepened, like the tape of the foundation of the house, but the norm, > 0.6 m below the standard freezing depth (NGP), and the basement walls - as needed so that you can walk in it to your full height (1.9-2.2 m + floor thickness + cushion thickness under the floor). As a result, the difference in specific pressures on the soil of the foundation of the house and the walls of the basement turns out to be a value that jumpers up to 1-1.5 m long can accept.
The T-shaped scheme (pos. 4) is used on light pliable homogeneous soils; H-shaped (pos. 5) on light heterogeneous and medium, and cellular (pos. 6) - on medium heterogeneous and heavy homogeneous. In any case, a connected basement is built only and only on a tape - on a slab or a caisson, it will tear the lintels and destroy the foundation of the building. Typical mistakes in the development of foundation and basement connection diagrams are as follows:
- The corners of the basement adjacent to the connected corners are left hanging (pos. 7).
- The connection scheme is made asymmetrical with respect to both axes of the foundation plan (pos. 8) or centrally symmetrical (pos. 9).
- The corner of the basement box is connected to the corner of the foundation, pos. 10.
The latter is especially dangerous for the integrity and stability of the entire structure. In the case, as in pos. 10, it would be necessary either to change the layout of the house with a basement to symmetry at least along one axis, pos. 11, or, better, without changing the plan, tie the inner corners of the foundation with a jumper, and complete the basement with an incomplete basement, pos. 12.
Waterproofing
In the process of developing basement waterproofing, its scheme is first selected in relation to a given structure in given specific conditions, and then suitable materials are selected. Water is an insidious element and it is impossible to protect yourself from its penetration for decades with a single obstacle. A typical case in individual construction is when, at the seasonal peak of dryness, the GWL drops below the basement floor by 0.2 m or more, and at the peak of moisture rises to the level of the humus layer; the most fertile soil layer is considered to be constantly moistened, but does not create any significant flow and pressure of moisture on the structure.
Under these conditions, the only reliable is the external anti-pressure waterproofing. Non-pressure only from surface runoff does not guarantee the dryness of the basement, because, firstly, in rainy years, the pressure of surface water can become significant. Secondly, the most underground flow under the building may change, see above. Internal anti-capillary insulation and armor holding it may be required with a stable lower standing of the groundwater level at the level of the basement floor and above, see below.
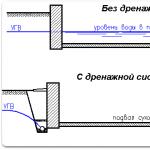
External waterproofing of the basement is carried out in general in 2 ways: cut-off (cut-off), on the left in the figure, and diverting (outlet), on the right:

If a building with a basement stands on permeable soil (pebbles, gravel, cartilage, sand, sandy loam, loose loam), then cut-off insulation can be made without drainage; in this case, the clay castle is continued down to a level of -(0.25-0.3) m below the base of the basement floor cushion. This is its great advantage - it does not need an expensive and time-consuming drainage system. If the basement is built of hydroconcrete, then the walls are plastered on the outside with cement-sand plaster for insulation, and instead of a clay castle, backfilling is carried out with excavated soil. This is the second advantage of cut-off insulation - self-digging clay is not suitable for a lock, you need to buy construction, and a lot.
Disadvantages of cut-off insulation, firstly, a large amount of excavation. Secondly, they are not always technically feasible - nearby buildings may not allow choosing a pit of the desired profile (see below). Thirdly, clay is an obstacle for moisture, but not a deaf barrier. It reduces the flow and pressure of water on the wall, but does not stop it completely. Therefore, external insulation is needed full-fledged (prime + coating + flooring), and if the basement is cinder block or brick, then reinforced, see above. Fourthly, cut-off insulation is applied only in its entirety, at least within the wall, since the joints of the flooring sheets need to be glued and heated, so arranging it on an existing house is very problematic - it is impossible to dig out any of its walls completely without risking the stability of the entire structure.
Drainage insulation works only in conjunction with drainage: its basis is a membrane with a reverse capillary effect that collects moisture and removes it to the drainage. The membrane itself is glued to the wall instead of the cut-off insulation sheeting and is protected from rapid soil clogging with geotextiles. The main advantage of diversion insulation is minimal or no impact on the underground runoff under the house; cut-off insulation even with drainage changes it, therefore it is recommended to isolate the basements of houses on soils with complex unstable hydrology with a membrane. Additional, firstly, a pit for cut-off insulation is needed with a width less than the removal of the blind area (practically 0.6-0.8 m is enough, if only the worker could squeeze into it). Secondly, it is possible to isolate in pieces with a width of about 1.5 membrane panels. Therefore, the basements of existing houses can almost always be insulated only by a diversion method.
The disadvantages of drainage waterproofing are also very serious. The first is an even greater volume and complexity of earthworks, only related. Building a site drainage is a serious matter, and finding a place under the drainage discharge field is also far from always possible. Second, the best membranes last up to 20 years; more often - 10-12 years, and on heavily watered loose soils for 3-7 years. If you intend to insulate the basement with a membrane, be prepared to dig the house and change it at such intervals.
When needed inside
If UGV is more than 3 months. in a year it is flush with the basement floor or rises higher, the external anti-pressure waterproofing is supplemented by the internal anti-capillary. Concrete, not to mention brick, is not a solid monolith. Its microstructure is the smallest grains of cement, similar to sea urchins, the needles of which are silicate crystals. These “needles” cement grains are linked together, and the gaps are filled with sand and, in hydro concrete, hardened liquid glass (which is also silicate), and in moisture-resistant polymer additives. In both cases, micropores remain; the polymer also decomposes in 3-15 years, and under pressure, concrete passes moisture a little. It is imperceptible in the hydroelectric dam, but very much in the basement.

Options for internal anti-capillary waterproofing of the basement are shown in fig. on pos. In and D, external insulation is conditionally not shown, but it is needed here as well. Seam insulation on pos. B - at least 4 layers of roofing material, glued with prime liquid mastic and heated with a burner. It is impossible to isolate the seam with a thin solution - it will leak. Tolem or roofing bituminous insulation (hydrobutyl, etc.) is also impossible - the wall will squeeze and squeeze out of it. Steklorubit, etc. based on fiberglass, the weight of the wall, on the contrary, will not crush - the base will remain uncrushed and capillary moisture will go through it, so it’s also impossible. Pressure wall on pos. B - plastering on the grid with a cement-sand mortar, see above.
Insulating materials
Roof and wall waterproofers are not suitable for the basement - they are not designed to withstand the pressure of the soil and the pressure of formation waters. According to the method of application and purpose, materials for basement waterproofing are divided into:
- Primary, or primes, or impregnating - liquid mastics applied to the prepared surface (see below) to create a base for coating with other materials.
- Painting or coating - more viscous adhesive compositions, used either separately, or as a base holding overhead sheet insulation, or, again together with prime, for anti-capillary lubrication inside. In the latter case, after plastering, the walls are plastered over the mesh with any moisture-resistant plaster in one layer.
- Cement-filled thick-layer mastics - designed for coating up to 20 mm thick only on the sides facing the pressure. They are used instead of overhead materials in cases where the groundwater level does not reach the basement floor for more than 9 months. in a year.
- Overhead or pasting - sheet flexible or soft materials on a woven or fibrous base, impregnated with the insulator itself. The most versatile and most reliable insulator. They are also superimposed only on the sides facing the pressure water.
- Capillary membranes - a special coating with a reverse capillary effect is applied to the waterproof plastic base, see above.
The insulating beginning of these materials, except for membrane ones, can be as follows:
- Bitumen - still unsurpassed in durability, but difficult to work with. How bituminous waterproofing works, see above. It is produced in the form of primary mastics on a gasoline diluent (primes), coating mastics, thick-layer mastics and overhead materials. Armor insulation is almost never required; if yes, then cement-sand plaster. Holds on any wall (concrete, brick). Penetration into concrete up to 30 mm (more often - 7-15 mm), so the treated surface loses its water resistance in case of mechanical damage.
- Bitumen-nairite mastics are frost-resistant, can be applied at temperatures down to -(15-25) degrees. Layer - up to 6 mm. Tighten cracks up to 30-50 mm wide, because they foam in the air, so the opened package must be worked out within the period indicated on it (or in the instructions). The coating retains plasticity up to -(45-60) degrees. Service life - 10-25 years. A specific material for northern construction or complex repairs of very dilapidated buildings.
- Epoxy, epoxy-tar and epoxy-furan mastics are an even more specific material for waterproofing building structures that are regularly flooded up to full immersion in water, freezing and icing unheated. Fragile, after 3-5 years require a complete replacement. In the work are complex, toxic, carcinogenic.
- Natural elastomers (liquid rubber) - they are easy to work with, but are only applicable as repairs to internal insulation. Only brick and cinder block fit well. The term for updating waterproofing with natural elastomers is 1-5 years, depending on local conditions. Mandatory armor insulation of at least 2 layers of cement-sand plaster on the grid, because. easily swell and exfoliate by capillary pressure. In general, an ambulance to a damp basement, until the hands and wallet reach a more serious repair.
- Synthetic elastomers - polyurethane, silicone, MS-plastics. They act similarly to bitumen, but penetrate deeper into concrete, up to 100 mm. After 7-20 years, the insulation needs to be renewed. For repairs from the inside, they are applied to a dried and abundantly moistened surface immediately before processing, see below.
- Penetrating (deeply penetrating) compositions - synthetic elastomers + cement + polymer additives. Produced in the form of mastics for painting with a thick layer. The work is simple. They are used for external insulation only. They are pressed into gaps up to 0.4 mm (polyurethane) or up to 10 mm (on silicone or MS) to a depth of 100 mm and clog them with cement that recrystallizes under the action of moisture. The surface to be applied must be leveled to +/-(2 mm) and thoroughly free from dust. Bituminous pasting materials do not hold on to themselves. Reservation insulation, if required - cement-sand plaster on the grid. Service life - 10-30 years. Capillary moisture is not cut off 100%, therefore, bituminous anti-capillary insulation inside is almost always needed.
What if he got wet?
Since we are talking about repairing an existing damp basement, it would be appropriate to mention sets of compositions for it. Their components are prepared, as a rule, on a different basis, but are coordinated with each other in terms of physicochemical properties. Therefore, the repair of a damp basement from the inside must be done with compositions from one reputable manufacturer.
For an example in fig. it is shown how basements of various designs are insulated inside with compounds from the well-known Dehydrol kit. Shtroba wherever needed - 25x25 mm. Surface preparation - according to the instructions for acc. composition. Dehydrol 10-2 is also successfully used to make homemade waterproof concrete, see above.

How to dry a basement
Bituminous waterproofing mastics are applied to a dry surface. When they write that penetrating compounds must be applied to wet, this is correct. But when they add that it is better for freshly poured concrete, this is fundamentally wrong. Capillary moisture in the wall, prepared for processing with penetrates, should go deep into the dry mass and, as it were, pull the insulator along with it. If the mass of concrete is saturated with water, it will flow out through the capillaries and, conversely, squeeze out the insulator. The depth of its penetration into the wall will be, at best, much less than the calculated one; resp. the service life will also decrease, tk. the destruction of the composition is outside under the action of air.
A damp basement must be thoroughly dried before repair, and immediately before processing, moisten the walls and floor several times with water using a soft plaster brush. Wetting with a roller gives the worst effect, and spraying is even worse, because. the air is excessively moistened and capillary moisture no longer actively seeks to go into the concrete mass.
It is useless to dry the basement with a stream of warm air - it will not dry out until it starts to “sweat” again in the fall. It is necessary to dry with thermal (infrared, IR) radiation. But not “far” from an electric fireplace or a nichrome “goat” (which is dangerous), but “nearby” - it is given in excess by incandescent lamps, which is why they are becoming obsolete. Near infrared penetrates deeply into concrete and brick, almost not being absorbed in the air. Bulbs need to be hung with more garlands at the rate of 60-100 W per 1 cubic meter. m basement. If a control pit is hammered near its wall, then most often after 10-12 days of continuous drying of the IR, it turns out that the soil around has already begun to dry. In any case, after a week it is already possible to apply penetrates or smear with bitumen. In no case will it hurt to dry longer - how much patience is enough to watch how the electricity meter winds.
Repair not for your hands

Sometimes it is possible to dry a damp basement only by injecting special compounds into the surrounding soil, see fig. on right. For example, if a quicksand crawled under the house, then the whole structure must be saved. But in this case, an irregularly shaped body is formed in the ground, and it is definitely impossible to predict the further settlement of the structure. Therefore, only specialized organizations are engaged in injections into the soil based on the results of on-site research, and they take a subscription from the customer and the owner of the building that they take on any consequences.
Arrangement
This section is not about 3D wallpaper, bar, HD TV, jacuzzi or 3-bed under a mirror on the ceiling. All this and more is up to you. Mandatory and, for residential and technical, desirable arrangement of the basement consists of:
- Ventilation is a must.
- Entrance with stairs is a must.
- Entrance hatch - if the staircase is steep.
- Insulation - for residential and technical basement.
- Surface drainage - in areas with heavy rainfall in the warm season.
Ventilation
Ventilation is vital for any basement. almost all harmful, poisonous and many explosive gases are heavier than air and flow down. For the same reason, basements are built with non-volatile natural supply and exhaust ventilation.
The basement ventilation device under the house is quite simple, pos. 1 and 2 in Fig.:

The cross-sectional area of the lumen of the branch pipes is 5 sq. cm for each cubic meter of basement volume, but its diameter in any case is from 60 mm. Instead of a mesh from rodents, it is better to put a filter on the inlet pipe, on the right in Fig. Flow-through with filter media (pos. 3) protects, in addition to dust, from insects, but requires regular inspection and replacement of the media. Aerodynamic (pos. 4) is cleaned as needed, you only need to attach a strip of newsprint, etc., to the mouth of the inlet pipe in the basement. flow indicator: when the air filter is clogged, the air flow stops very abruptly. But especially harmful and cunning mosquitoes with flies make their way through it.

If the basement is near the house, then making a high exhaust pipe is difficult and not always possible. In this case, the basement ventilation is built according to the scheme in Fig. on right. Minimum nozzle diameter 100 mm; for a basement of more than 10 cubic meters, a cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200b10 square meters. see per cubic meter of volume. In the basement, between the supply and exhaust pipes, there should be no obstacles to the movement of air. The upper ends of the pipes are bent with a goose from rain and snow.
Ladder
The staircase to the basement is one of the most common causes of domestic injuries, so the most careful attention should be paid to its design. From this point of view, stairs are divided into ascending and steeply inclined. On the first one, you can climb / descend with a load in your hands, without holding on to the railing, and it’s generally undesirable to walk along steeply inclined ones - awkwardly stepping or swaying, you can crash, leaning back. With a load in one hand, they generally climb a steeply inclined staircase, grabbing the railing or upper steps with the other.
The design of the stairs can be any of those shown on the left in Fig. The most convenient in terms of saving usable space are highlighted in color:

On the right in fig. calculated ratios for them are given, and here there is a nuance: since the height of the ascent and descent into the basement is small, a staircase with a slope of up to 50 degrees will be quite comfortable. tg 50 is almost exactly equal to 1.2, which makes it easier to calculate, based on the fact that the minimum width of the tread of a ladder step is 180 mm, and its maximum allowable height is 230 mm. Let's say the height of the descent to the basement is 2.2 m, counting from the top of the ceiling (see below). At this height, an integer number of steps should fit, we take 10. The height of the step is then 220 mm. Divide by 1.2, we get 183 mm - suitable. The removal of the stairs in the plan will be 183x10 = 1.83 m, which is also not bad. The area under the stairs, with a minimum allowable width of 0.8 m - 1.83X0.8 = 1.464 sq. m.
About erroneous stairs
What you don’t have to be smart with the basement staircase is, firstly, to do it on a string (one stringer) with hanging steps, pos. 1 in the figure, such stairs are extremely traumatic:

Secondly, pour the concrete stairs in place, pos. 2. Ready-made concrete stairs are a real monolith, they are poured entirely into a detachable form. There are no working concreting joints in them, and when pouring with a “self-made” they are inevitable: the upper stage cannot be poured until the lower one has seized. The seams are weak, in the basement they soon crack, and as a result, a home-made concrete staircase to the basement serves less than a wooden one.
Basement stairs
In a dry basement, a wooden staircase serves no less than himself. A properly made wooden staircase does not suddenly collapse, and before the steps begin to rot, it lets you know about the violation of the structure by creaking.
The device of a wooden ladder for the basement is shown in the figure:

Instead of cutouts in the inner bowstring, you can fill it with fillies from a board or, better, thick plywood under the treads of steps, pos. A. However, the collapse of rotten wooden basement stairs in a damp basement is also common in domestic injuries, so it is better to attach the treads to steel or concrete stringer beams. The cross-sectional dimensions of the concrete stringer are from 100 mm wide and from 150 mm high. Steel - channel from 100 mm or I-beam from 80 mm.
Methods for attaching wooden treads to steel and concrete stringers are shown in the figure:

Dowels for fastening to concrete are made from pieces of 8-18 mm corrugated rebar. Deepening in concrete from 60 mm; in a tree from 30 mm. Holes in fillies for landing on dowels are drilled 2-2.5 mm narrower; fillies are impaled with blows of a mallet. Mounting the treads on the legs allows you to simply arrange the railing: the reinforcements are released upwards to the height of the railing, and for the supports of the treads and balusters, pipe sections are put on them; can be plastic. It is best to attach the treads to the strip - they will not rot even in a damp basement.
In the case when there is not even one and a half squares under the stairs, here in fig there are drawings of a wooden steep staircase for the basement. It will definitely need a hatch, see below.
Note: all parts of the wooden stairs to the basement before assembly into the product must be impregnated with an oily water-repellent composition (it can be worked off), and the finished staircase must be varnished with acrylic varnish for outdoor use or painted with moisture-resistant paint. Best of all - acrylic enamel for baths.
Entrance and hatch

There is often no place for a climbing staircase to the basement under a private house, and then the entrance to it is made from the outside. So it is generally necessary if a ready-made concrete staircase is purchased for the basement - they are not made with a slope of more than 40 degrees. Then, firstly, the entrance to the basement must be protected from precipitation by a canopy, see fig. on right. The overhang of the roof of the canopy should protrude forward above the edge of the upper step by less than 30 cm, and on the sides and rear - from 15 cm. Secondly, the upper step should protrude above the ground or blind area by at least 70 mm, and the basement door opening should be with a threshold of 90 mm. Both are necessary so that rain and melt water does not penetrate into the basement. It is better to make a threshold with a height of 120-130 mm, attaching ramps with a width of 400 mm or more to it on both sides.
The hatch to the basement is also a thing not so simple. “Lada” from boards with a rope now, probably, no one is doing anymore - there is a wide range of ready-made basement hatches on sale. In the ceiling (see below), they are immured with a cement-sand mortar, and the price is next. way:
- Non-automatic with a mechanical stop, sort of like the old sofa beds: pulled, raised - snapped into place. It is necessary to close - pulled up, snapped off, lowered.
- Semi-automatic in a spring-lever mechanism - pulled all the way, kept open. It is necessary to close - pushed down, sank.
- Semi-automatic with a pneumatic lift - pulled a little up, opened. It is necessary to close - pushed down, he smoothly closed.
- Automatic with a pneumatic lift - stepped firmly on the edge of the lid, removed his foot - it opened. To close, lightly push the lid down, closes.
In terms of ease of use, both semi-automatics are equivalent, but automatic ones are nothing more than a marketing gimmick without regard for safety. Let's imagine that furniture is brought into the house. The riggers (or you and an assistant) are carrying a closet. The front one steps on the hatch, it opens. The rear one does not see what is under his feet, and he is not up to it - he falls through, is crippled. If you really want to fork out for the steepness of the basement, take an auto hatch with remote control from the remote control, these are also sold.
Warming
Insulation is necessary for a residential and technical basement. The last - so that the water in the pipes does not freeze, and fuel savings are noted only in insulated bulk boilers. It is also desirable to insulate the basement storage near the house: building structures are good cold bridges in winter, and warm in summer.
The basement must be insulated with sand backfill, see Fig., So that seasonal soil movements do not tear the insulation.

Mineral wool and cellulose insulation, which is excellent in all other respects, are not suitable for basement walls: they cake and collapse under the ground. Granular foam is also bad: under the pressure of soil and formation water, it quickly crumbles into granules. Extruded polyethylene foam (EPS) is more or less stable in the ground; spray applied polyurethane coating lasts more than 10-15 years. They are insulated with one and the other in the usual ways, and before filling the sand cushion, they are protected with cement-sand plaster.
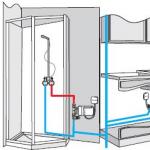
Drainage

In places with heavy rainfall in the warm season, no basement without surface contour drainage at home will always be dry. In other cases, drainage is also useful: it reduces the range of GWL fluctuations, which makes it possible to simplify basement waterproofing and / or increase its effectiveness. Equally important, the impact of a drained house with a basement on underground runoff is reduced significantly. Irregular settlement of such buildings is extremely rare as a result of gross violations of construction. The scheme of the contour surface drainage of a residential building is shown in fig. on right. The discharge field can be placed under a garden or, better, a garden: almost the same atmospheric precipitation is collected in drains, quite suitable for irrigation.
Basement under the garage
The basement in the garage is attractive in that it does not require the withdrawal of land or the complexity of the design of a newly built house. The basement under the existing garage is being built without demolishing the housing. But there are special requirements for the equipment of the basement under the garage, because. explosive vapors of fuels and oils heavier than air; much heavier - in the cold, when they thicken.
Firstly, the hood of the garage basement must be high, rising above the roof by at least 1.5 m, on the left in the figure:

It is unacceptable to display “geese” near the ground! Secondly, the exhaust duct needs an increased cross section, from 15 sq. cm per cube of basement volume or at least 120 mm in diameter. Thirdly, the hood must have an aerodynamically closed type deflector that provides some “cold” draft and in complete calm, for example. TsAGI or Khonzhenkov deflector. Fourthly, in winter, the basement should be warmer than an unheated garage, so that air is taken into the ventilation only from the outside. Therefore, they insulate the basement under the garage from above, like the attic floor of the house, on the right in Fig.
Drivers, of course, will ask: but the machine will not push through this feather bed? More and how. Therefore, in the insulation, it is necessary to provide gaps along the length and lay the ruts in them flush with the floor. It will be necessary to drive into the garage carefully so as not to move out of them. In general, the basement in the garage is not all that attractive; there is a place for a repair pit.
Construction
Building a basement on your own is possible only in dry or seasonally dry soil. In the latter case, all the work of this year must be fully completed before the rise of the GWL. Groundwater pumping is so complicated and expensive that it is rarely used in large-scale construction. The exception is the basement-caisson, which is built upstairs to the side and installed in the pit, but if it is concrete, you need a crane from 20 tons and a team of experienced slingers-riggers. There is, however, an exception to the exception, see at the end. In general, the construction of the basement includes the following. work stages:- Excavation of the pit;
- Filling the base - slabs or soles of the tape;
- Installation of communication input channels;
- Walling;
- Floor device - on dense ground when the GWL is above its level for no more than 3 months. after at least 6 months. at the end of the annual cycle of work;
- Cover installation;
- Basement equipment, see above.
foundation pit

Building a basement in a pit with vertical walls is a gross mistake - it is impossible to make high-quality waterproofing. When insulating an existing basement, the house is dug in pieces, and the finished area is covered before choosing the next one. A typical excavation profile for the construction of a basement is shown in fig. on right. The width of the passage outside of the future wall is at least 75 cm along the bottom. The slope angle is acceptable for this soil.
Base
At this stage, you need to order a concrete truck with reinforced concrete. It's not about the quality of self-mixing, it can be better than the factory one, but in its volume. The working seams of concreting on the base of the basement are highly undesirable, so you need to fill in one bay. It is also wrong to lay the reinforcing cage directly on the sand-gravel pillow - lean preparation is needed for crushed stone, see below. Before pouring, insulation is applied to the preparation with lapels on the sides of the pit 150-200 mm above the thickness of the slab / sole. Concrete is poured into the resulting bowl. Thus, direct contact of concrete with soil is excluded, which, in turn, excludes the formation of holes in the monolith. The fistula may not lead to dampness of the basement, but it will let moisture through to the fittings, and in fact keep the base of the basement on itself and the whole house. After pouring the concrete mass, it is deaerated (deaerated) by piercing each cell of the reinforcement cage in the middle with a rod. After the monolith has set, it is covered with wet burlap, which is kept moist until the base reaches 25% strength; in a typical summer in the Russian Federation, this is approx. a week.
Walls
Basement walls are built according to the usual building technology for this material. If a basement-caisson is being built (see below), the walls are built along with the base. Door and window openings are strengthened with concrete lintels from 80 mm high, laid from 120 mm into concrete walls and from 200 mm into brick and cinder block walls. It is impossible to strengthen the openings in the basement with steel or wooden mortgages! Remember again: the basement supports the whole house! When light dry spots appear on the cured drying concrete of the walls, anti-capillary insulation can be applied. On brick and block walls - after 3-4 days of erection to the top.
permanent floor
The permanent floor in the basement on the tape is immediately poured during the construction process after the walls have set at least 25% strength. Under a permanent floor, crushed stone backfill is poured over sand with a lean liquid cement mortar: cement from M400: sand 1:3 - 1:4. Pour to a level of 40-50 mm above the tops of the pebbles. When the filling sets, insulation is applied and the cement:sand:crushed stone 1:3:2 screed is poured with a layer of 70-80 mm. It is possible to lay a clean floor and finish the walls in 2 weeks - a month.
overlap
Ceilings from hollow or box-shaped ready-made slabs of the road and require for the installation of lifting mechanisms with qualified operators. Self-made monolithic overlap is laborious and technologically difficult. He, like the ceilings from hollow core slabs, has a clearly excessive bearing capacity for a private house. Is it possible, having sacrificed it within reasonable limits, to cover the basement with something moderate in price and easier to work with?
In modern individual construction, prefabricated block floors, designed specifically for such a case, are becoming more common. You can compare a monolith with a prefabricated block structure according to the figure:

Insulation of the floor of the house above the basement under the prefabricated block floor in normal climatic conditions is not required or a simplified one is required. Bearing beams are poured together with the bearing belt (see below) in grooved formwork on supports, which are much easier and simpler to make than solid hanging under a monolith.
Laying and belt
It is impossible to build a house with a “box on a box” basement: at the top of the basement walls you need a large strobe, into which a monolithic ceiling enters, slabs are laid or the bearing belt of a prefabricated block ceiling is poured. In all cases, the minimum wall thickness and the laying of the ceiling in it are different for walls made of different materials.
How much overlap is laid in a wall of concrete or brick is shown in the figure:

Waterproofing is shown conditionally, in the case when the basement ends with the basement of the building with its ceilings. For a cinder wall, the laying is the same as for a brick one, but its distance from the top is at least 2 rows of masonry.
How to build a caisson
The reinforcement cage of the basement caisson is assembled at the top as a whole and installed in the prepared pit (see below) by a crane. It is impossible to assemble the entire frame by welding - the reinforcement will weaken due to metal tempering. Therefore, the frame is first knitted with wire as usual, and then individual joints are welded: at the bottom at the corners of the cells 3x3 or 4x4 cells of the frame, and on the walls in each 3rd or 4th belt.
A pit for a caisson is prepared as for other basements, see above. Further construction goes in the following sequence (see also Fig.):


Note: the concrete walls of the basements on the slab and the tape are also poured according to paragraphs. 7 and 8. Pouring between the boards and the ground is a mistake - what kind of reliable anti-pressure insulation is there.
Couldn't it be sooner?
A very valid question. The construction of an eternally dry, reliable basement is difficult for the inexperienced to eerily in the knees, and even experienced ones have a headache. The answer is positive: you can buy a ready-made basement-caisson, put it in a pit on a sand and gravel pillow and fill a clay castle (necessarily, otherwise it will pop up). If he (the basement) is needed not under the house, not residential and not technical. Vegetables in the bins will have to be sorted out from time to time, but suppliers optionally offer delivery to the place and installation in the finished pit.

Caissons for basements are produced as steel welded insulated ones with a hatch, stairs, ventilation and fittings for concreting (optional), on the left in fig. Plastic ones are also on sale, but don’t take them - 100% pop up. Caissons for cellars are also cooked by individuals from steel from 8 mm. For a hook on the ground from floating, staples are welded from a strip of 12 mm or more (on the right in the figure), but this is less reliable, and you have to isolate the caisson from corrosion yourself.
It is possible, by the way, to do even cheaper - to make a basement-caisson from a used shipping container. If you cover it with a thick layer of bitumen-cement mastic, it will last at least 100 years in the ground. For a hook on the ground, pipes are threaded into the eyes of the rigging paws at the bottom and an anchor frame is welded to them. Container width - auto dimension 9 feet (2.7 m). Length - 12-70 feet (3.6-21 m); the most running 20 and 40 feet (6 and 12 m). It’s enough for a basement, and how savvy lovers make basements from shipping containers, see the video.
Own cellar will be useful in almost every private household. In the cellar you can store vegetables, preservation and other things. At the same time, such storage will be as convenient and high-quality as possible, because. the cellar is located underground and does not take up useful space in residential premises, and the temperature conditions in the basement ensure the longest possible storage of various food products.
The cellar can be equipped both at the stage of construction of the building, and in a ready-made private building. In the second case, the work is complicated by the fact that you will have to dig a hole for the cellar by hand and take the earth out of the room on your own. Otherwise, the procedure for arranging the cellar for both situations mentioned is practically the same.

The cellar in the underground of the house should be buried at least 150-180 cm. With a smaller depth, the temperature in the basement will exceed +8 degrees, which will not be the best effect on the conditions and shelf life of vegetables.


Before starting work, you need to establish the depth of the passage of groundwater specifically on your site. This is easiest to do at the stage of arranging the foundation of the house, because. geodetic research is included in the list of mandatory preparatory activities.
If the house has already been built, but you just now decided to start arranging your personal cellar, determine the point of passage of groundwater will have to do it yourself.
This can be done according to the following methods:
- dig a hole with a depth of 250 cm and monitor its condition for several days in terms of filling it with water;
- determine the depth of water in wells on adjacent land plots.
You can also contact a specialized well drilling company.
Checking the groundwater level should be done during the spring flood or autumn long rains. It is during these periods that the ground aquifers rise to the maximum level.
If groundwater is closer to the soil surface than 100 cm, you will have to refrain from constructing an underground basement, preferring a remote cellar in some other suitable area.
If the groundwater level is in the range of 100-150 cm, you can try to reduce it using a drainage system laid along the perimeter of the building below the floor of the future basement. In this case, the waterproofing of the basement walls will need to be given special attention.
Ideally, the underground cellar should have a depth of 200-230 cm. With such depth indicators in the underground room, it will be comfortable to go about your business, and the air temperature will be set at about + 4-5 degrees, which is the best indicator for long-term storage of conservation, vegetables, etc.
Before starting the arrangement of the cellar, you need to select suitable building materials. The walls of the room can be built from concrete, natural stone, concrete blocks, ceramic bricks. Silicate brick and cinder blocks are best not to use.

Determine the best option for entering the cellar. The simplest option is to arrange a hatch in the field of the room with the installation of a ladder for descending into the cellar. If possible, the descent can be made from full-fledged concrete steps - it's more convenient. An inclined trench for arranging the descent must be provided for even at the stage of digging the foundation pit.
A step-by-step guide to building a cellar

Independent arrangement of the cellar under the house is carried out in several simple steps. Do each one in sequence.

Video - Cellar under the house
The first stage is the definition of dimensions
Start by determining the dimensions of the cellar that are convenient for you. As a rule, the cellar area under the house is at least 5-8 m2. With such dimensions, it will be possible to place racks with preservation in jars, and containers with various root crops. Otherwise, be guided by your requirements.
Make the size of the pit at least 60 cm larger than the size of the cellar on each side. From this stock, about 30 cm will go to the walls. The rest of the place will be filled with waterproofing material and a clay castle.
Video - Cellar construction
The second stage - earthworks
Start digging a pit. If the house is just being built, use special equipment. In the case of arranging a cellar in an already finished house, you will have to dig manually. To prevent the side walls of the pit from crumbling, strengthen them with temporary supports, for example, from plywood or boards.
Make the depth of the pit such that its bottom is about 30 cm below the bottom of the future cellar under the house.

The third stage is the foundation
Fill the bottom of the pit with gravel of different fractions. Tamp the backfill and lay the reinforcing mesh on it. Pour concrete. Allow 2-5 days for the pot to dry initially. After that, you can start arranging the walls of the future cellar.
Fourth stage - walls
It is better if the walls of the cellar are made of monolithic concrete. To increase the moisture resistance of the filling, it is necessary to add a special mixture to the solution to create a penetrating moisture insulation.

Assemble formwork for pouring concrete walls. To do this, use boards, bars, ties and nails. It is better that the formwork boards are planed - they are easier to dismantle in the future. Make the formwork about 30 cm wide. Lay 2 reinforcing bars along the future walls with a connection at the joints of the walls. Use soft wire to connect the bars.
At the stage of arranging the formwork, provide places for placing ventilation pipes.
Pour the concrete into the formwork. It is best to pre-order ready-made concrete, because. it will take a very long time to prepare the required amount of solution on your own.

After pouring in several places, pierce the concrete with a metal rod to remove excess air from the material. The solution will dry for about a week and it will take another 3-4 weeks to set strength.
Let the walls dry and remove the formwork.
Fifth stage - waterproofing
Proceed to the external waterproofing of the cellar. For this, bituminous mastic is best suited. Apply 3-4 layers of waterproofing material to the outside of the basement walls with a roller, and then stick a layer of roofing material over the mastic. Let the insulation dry and fill the space around the walls with earth or make a clay castle.

If there is a risk of flooding the cellar, a clay castle must be done without fail. Mix clay, clean sand and water until a homogeneous mass resembling plasticine is obtained. Layer-by-layer fill the hole with the resulting mass and carefully tamp.

Inside, both the walls of the cellar and its floor are waterproofed. The floor is best filled with hot bitumen and pasted over with roofing material. To isolate the walls, you can use polymer mastic or penetrating waterproofing. The second option is more preferable.
During the installation of the floor, remember the required 1-2 degree slope of the surface in the direction of the technical pit. Thanks to the slope, the cellar will remain dry even during the rainy season and floods.


Stage six - finishing
At the finishing stage, you have to make a ladder, a manhole cover and ventilation.
If you decide to get by with a simple wooden ladder, pre-soak the raw materials with an antiseptic. Place the stairs with a slope that makes it easy for you to go up and down.


The hatch cover must be hinged. Otherwise, at this stage, be guided by your preferences.
Video - Ventilation in the cellar
Insert the ventilation pipes into the holes that you made at the stage of preparing the walls for pouring concrete. The exhaust opening should be located under the ceiling of the cellar above the pit, the inlet should be located almost near the floor in the opposite wall. Bring air ducts outside. Place protective grilles (nets) over the ventilation openings.

The procedure for arranging the ceiling depends on whether the cellar is created at the stage of building a house or whether it is equipped in an already finished building. In most cases, the ceiling of the cellar is an ordinary floor slab with a pre-prepared hole for the hatch. The procedure for arranging such an overlap depends, as already noted, on the circumstances under which a cellar is created under the house, so be guided by the conditions of your particular case.
This completes the construction of the cellar under the house with their own hands. Install the planned racks and shelves, and you can start using your own equipped cellar.

Successful work!
Video - Do-it-yourself cellar under the house
Building a basement in a house is a task that every land owner faces. It is almost impossible to imagine a cottage without a basement. And if you think that this constructive element is intended only for storing unnecessary things, then you are deeply mistaken. Do-it-yourself basement construction can easily solve the topical problem of lack of usable territory and get rid of many problems. Don't believe? This article will dispel your doubts!
Basement classification
The construction of a basement in a private house can have different goals, according to which the underground is divided into several types.
cellar. Great for storing fruits and vegetables, as well as preparations for the winter. However, keep in mind that in this situation, you will have to forget about heating underground spaces, and this is not entirely good for the foundation.
Basement-technical room. It will provide an opportunity to place engineering structures, for example, filters, water heaters, boilers. This will allow you to get rid of bulky appliances in the bathroom or in the kitchen and use the usable area with maximum benefit.

Basement-ground floor. Ideal for creating an office or billiard room. However, everything will depend solely on your fantasies. If you want, equip a place for a meeting of football fans in such a basement, or if you want, a gym.
Basement workshop. It will be a real salvation for those who like to make something with their own hands. You can divide the room into two functional areas: a workshop and a warehouse for storing tools.
Basement garage. One of the most popular options. But remember that the main condition for construction is convenient entry. The basement should be spacious, because you will have to worry not only about the proper conditions for storing the car, but also for carrying out minor repairs if necessary.

As for the cost of building a basement, this indicator can vary widely. In any case, the construction of a basement, the price of which suits you, is quite real.
Basement construction technology
If the basement will act as a technical structure, then the height of the walls should be in the range of 1.9-2.2 m. If this room is residential, then the optimal height is 2.6 m.
It is important!
With a surface flow of groundwater, it is better to build a basement from reinforced concrete. For greater reliability, purchase M500 concrete.
The order of work also depends on groundwater. If they are too close, then the first thing they do is form the floor, while if they are absent, you can start from the walls.
How to make a floor?
A hole is dug with a margin in width (for formwork), a sand cushion is formed with the addition of crushed stone. Then the formwork is arranged, waterproofing is laid, followed by reinforcement and concrete pouring.

If the walls were built first, then the sand cushion is simply poured with concrete mortar. A layer of waterproofing is laid between the walls, i.e. the need for formwork is eliminated automatically. The main thing here is to dig a hole to a depth similar to the depth of the walls (so that the sand cushion is at the same level).
How to make walls?
During the construction of a monolithic basement, the walls are equipped using strip foundation technology. Trenches are dug, sand is poured to the bottom, formwork is installed. After carrying out waterproofing measures, a reinforcing mesh is laid and concrete is poured.
If you decide to pour the floor first, then the formwork for forming the walls is installed only after the final hardening of the concrete. Otherwise, the formwork braces under the weight of the solution may be pressed into the floor, thereby forming unnecessary recesses.

Concrete, no doubt, is a good material, but for those who are not looking for simple solutions and want to be 100% sure of the reliability of the building, it is worth thinking about building brick walls. Yes, such work requires extreme accuracy, because. you have to monitor the horizontal and vertical walls, but the result is worth it.
Laying starts from the corner, and leads to the 7th row. If you plan to apply plaster to the walls, make sure that the solution does not get on the inner surface.
It is important!
Professionals advise laying a reinforcing mesh every half a meter. This is necessary to give the structure additional strength. To cover the frame with a solution completely, it is necessary to increase the thickness of the applied layer by 2 cm.
Be mindful of the locations of door and window openings. Jumpers can be both reinforced concrete and wooden. Wooden ones are made of bars with a section of 15 cm. Jumpers pre-treated with bitumen are laid at a distance of 25 cm on each side. Reinforced concrete is mounted in a reinforced formwork, identical in width to the walls. Reinforcement diameter - 7-8 mm.

Another option for building walls is the use of blocks. The method attracts by saving time - a basement of blocks can be built very quickly. The only thing is that you will have to align each block horizontally, vertically and wall level. To make this process not seem tedious, start laying from the corners. When planning load-bearing columns, it is recommended to fill them with concrete mortar using columnar foundation technology.
Basement waterproofing
Building a basement, even in the driest area, requires competent waterproofing. After all, torrential rains and breakthroughs of water pipes have not yet been canceled.
Internal waterproofing
If the basement is made of bricks or blocks, then the gaps between the joints should be secured. The thickness of the layer of waterproofing mastic must be at least 2 cm. After coating the joints, you can additionally process the blocks with the same mastic. Now it's time to plaster. Fix the reinforcing cage on the walls and apply a 3 cm layer of plaster.

Let's get to the floor. Coat the joints between the walls and the floor with bitumen. Ideally, penetrating waterproofing should be used, but please note that filling concrete pores is possible only if the floor is not completely dry. But waterproofing mastic is applied exclusively on a dry surface.
External waterproofing
External waterproofing is designed to provide reliable protection against moisture outside the walls and under the floor. The best way to protect the floor is clay rammed at the bottom of the pit, covered with a double layer of roofing material and smeared with bitumen.

Walls are protected in a similar way. However, first it will not be superfluous to make sure that the horizontal waterproofing protrudes 15 cm beyond the wall. Then roofing material is laid along the entire height of the walls. It should go beyond the surface by 20 cm. If there is a gap of 10 cm outside of the erected walls, then clay is laid around the entire perimeter, if more - halves of bricks.
How to insulate a basement?
Like it or not, but the basement is the coldest and dampest place in the house, which involves not only waterproofing, but also insulation. In the hot period, thermal insulation will relieve condensation, in winter - from heat loss.

Wall insulation is carried out after the waterproofing mastic has dried (on the 6th day). Extruded polystyrene boards are glued directly onto the waterproofing. Bitumen is suitable for gluing. The slabs should protrude 40 cm above the ground. Before backfilling the trench, cover the insulation with asbestos-cement sheets. But that's not all. After backfilling, horizontal insulation is performed at the site of the future blind area at a depth of 30 cm.

Floor insulation is carried out according to the same algorithm. Expanded polystyrene 10 cm thick is laid on the waterproofing. Next, the second layer of the heat insulator is laid. You can use penofol, which will reflect heat into the basement.
The ceiling also needs protection. Styrofoam, polystyrene foam, mineral wool are equally good for its insulation.
Basement ventilation
Building a basement in a finished house is impossible without designing a well-thought-out ventilation system. Most often, a supply and exhaust ventilation project is being implemented, also called natural ventilation, based on the temperature difference inside and outside the basement.

Such a ventilation system consists of two pipes: exhaust and supply. Exhaust, starting from the ceiling, goes to the roof. The supply is located on the opposite side and starts from the floor.
It is important!
The hood removes air from the room, and the supply pipe provides fresh oxygen. So natural ventilation helps maintain normal humidity in the basement.
Pipe diameter is important. The most profitable option is pipes with a total diameter of more than 10 cm. Although, if the basement is small, this figure can be slightly reduced.

Now you know how to build a basement that will be dry and warm, which means that in such a room you can easily store homemade workpieces, equip a gym or a car repair shop.
Basement construction: video
The basement in a private house is a multifunctional room and an important component in a number of utility rooms. In the building for permanent residence, not only stocks of food and drinks are stored, but also seasonal items. In the cellars and basements of country houses, blanks and conservation, seed material for the future harvest are stored. A competent basement device in the house helps to unload the kitchen and other usable space, as well as create optimal conditions for storing vegetables. The basement of a country house according to a well-thought-out project is a wine cellar, a room for sports equipment, a room for revision of communications and a boiler room.
Basement purpose
A well-equipped basement sometimes occupies a full-fledged basement, divided into separate rooms. Here you can even equip a mini-production, for example, for growing mushrooms or ripening homemade cheese. However, if during the construction a house with a basement was not planned, then you can limit yourself to arranging a small room with a height slightly higher than human height, for ease of use, equipped with shelves, niches and compartments.

A room of 3x3m (or a little more) is enough for storage:
- blanks and conservation;
- harvest of fruits and vegetables;
- garden tools;
- working tools;
- fishing gear;
- children's sledge (summer);
- bicycles (in winter);
- auto parts;
- folding garden furniture;
- seasonal and work shoes;
- a small supply of drinks.
When it is decided to equip an additional residential or residential area in the basement, a mini-pool with a sauna and a massage chair, a wine cellar with a tasting place for guests, it is important to consider the insulation of the room. A well-equipped basement provides for central or local heating. However, it is not recommended to equip living rooms in the basement of a wooden house for permanent residence - only a reserve for the time of a large influx of guests. Yes, and it is quite difficult to place standard furniture and lighting here. In the basement, it is important to consider the placement of lighting fixtures for the normal functioning of vision, especially when doing small manual work.
In private houses with stove heating in the basement, they often equip a pit for storing coal and firewood so that in frosty winter there is no need to go outside for them. For whatever purposes the basement is planned, it can successfully combine the functions of different rooms, but it is important to provide good waterproofing there and maintain a good microclimate - the basement in the house photo.

Difference between cellar and basement
When building a basement, it is important to determine its purpose, that is, it is important to decide - you need:
- cellar,
- warehouse space,
- lower semi-floor.
In many cases, they make a cellar for storing vegetables, and at the same time store other things that deteriorate from excess moisture and low temperatures. But it's important to remember that:
- a cellar in a private house is a storage of vegetables (stocks of preservation and seed);
- a basement is a storage room below ground floor level.
That is, part of the basement can be equipped as a cellar, but it is not recommended to make a cellar in the cellar, there is a difference in their construction and arrangement. A one-story house with a basement is a classic option, but sometimes cellars for vegetables are built separately. In both cases, it is desirable to impregnate the wall with an antiseptic and antifungal composition before use, which not only spoils the contents of the storage, but the underground room itself.

When trying to combine a basement and a cellar, it is important to properly equip a place for storing vegetables - compartments or piles should be low for uniform ventilation of root crops and tubers. Vegetables "breathe", they are easier to view and discard rot, which quickly spreads to good products when the height of the compartment is not more than half a meter. Undried vegetables, with clods of damp earth and signs of rot, must not be loaded into compartments and piles. It is important to think about good ventilation - vegetables will always give off some of the fumes into the air, so a small window must be made in the cellars.
Tip: Do not forget to equip the cellar or storage for vegetables with a dense mesh or fine grate - the smell of vegetables attracts rats, mice, and voles. Watch the temperature - the optimal conditions for storing vegetables range from + 6 ° C, and with high humidity and the appearance of condensate, ventilation should be increased or the cellar or part of the basement should be ventilated more often.
In a dry and properly equipped basement with a cellar, things do not deteriorate, fungi and mold do not start. If the groundwater in a given area is close to the surface of the earth, it is not worth equipping a basement or cellar, even if there have been no problems with flooding in recent years.

What is important to know about building a basement after building a house?
The stages of the basement construction process are well developed by specialized construction companies:
1. Excavation with the help of machinery.
2. Arrangement of drainage.
3. Delivery of building materials and equipment to the facility.
4. Construction of the basement floor for the arrangement of the basement.
5. Arrangement of waterproofing, summing up communications, construction of partitions and ceilings to prepare for the construction of the 1st floor.
Some stages can be entrusted to professionals, and something can be done independently, using knowledge, skills, physical strength and tools. However, construction technologies should not be violated, since deviation from the norms leads to the precariousness of the structure. The foundation and storage room inside is the base of the building, especially if it is a two-story house with a basement. It is wise to start building a basement along with laying the foundation, but sometimes they think about how to make a basement in a house after a while.

In this case, they are usually limited to a small room in a built house between the partitions of the foundation.
1. Cut an opening in the floor (entrance hall, kitchen pantry or corridor), from where it will be convenient to go down to the cellar.
2. They excavate the earth to a depth of 2m and a width of at least 2x2m.
3. They equip floors (most often it is a cement screed, but clay plus a wooden shield is better) and walls (brickwork is better), sometimes the ceiling is additionally reinforced with beams (on the other hand, the floor of the living room).
4. Equip shelves and partitions, break through the ventilation window.
5. Fix the ladder and form a floor-level ladder.
6. Supply electricity to illuminate the underground space.

Disadvantages of this construction method:
- excavation is possible only manually with simple equipment;
- the earth has to be carried out through the dwelling;
- it is difficult to competently make waterproofing, drainage and ventilation;
- Lyada should be flush with the floor, and the handle is thought out so that it does not cling to it when walking.
Tip: The ideal choice of location is a pantry with a basement, but it is better to build a regular pantry in the house and a covered vegetable cellar next to the house. Sometimes a cellar is equipped under a built house with a separate exit to the outside from the outside of the house. This is dangerous because you have to destroy a fragment of the foundation, which threatens to collapse part of the house.
How to start building a basement in a house?
If the question arose - how to make a basement under the house, even before the start of construction or at the stage of digging a foundation pit, then this is the most competent approach to resolving the issue. This is justified when, during the construction of a house, a strip foundation and a basement are made. Here the foundation itself will be more solid, and in addition there will be a usable area in the house, and the subsidence of the structure will be the least noticeable.

Before starting the construction of a basement in a house, it is important to take into account all the features of the construction, since nothing can be fixed after the construction.
1. It is important to remember the pressure on the foundation from the side of the ground, so the walls of the basement being built are made quite reliable and strong. When the pit is just being dug, it is better to make it wider than the intended foundation, and fill the gap between the wall and the ground with a mixture of greasy clay and tamp it - the basement will be drier and warmer.
2. Arrangement of waterproofing and drainage system at the same time the foundation and walls of the basement floor is a very important point, since it directly depends on whether dampness will start in the house.
3. Inside the basement, heat and vapor insulation should be made, which is often provided using a clay floor or walls. If the foundation is dug to a layer of clay, it is enough to add crushed stone and compact it with sand. Next, the floors are equipped - reinforced concrete slabs, layers of hydrostekloizol and wooden shields.
4. The walls and the lower level of the basement, in case of a threat of flooding with groundwater, are made of brick with a reinforced concrete base. But this does not always save, so waterproofing additives will always be appropriate.

5. A common way is to dig a pit, build basement walls and ceilings, equip drainage and waterproofing, and concrete the floor. However, in wet soil this is not always rational, and there is a possibility of uneven shrinkage, and even a small basement depth will not solve the issue.
6. Many construction organizations immediately lay a monolithic reinforced concrete slab at the bottom of the pit, and then erect block walls of the foundation (in the basement). But even in this case, the slab under the foundation from below is laid on several layers of waterproofing (bitumen + polyethylene film) for reliable protection against groundwater.
7. Waterlogging of the soil is removed by arranging the drainage system along the perimeter of the foundation - this is a trench, the bottom of which is covered with geotextile, on top of it there is a perforated pipe covered with crushed stone. From above, geotextiles cover crushed stone and soil, but it is important to observe the slope of the trench into the water collector, and from where excess water should sometimes be pumped out - this will save the basement from flooding.
8. A well-arranged entrance to the basement is the absence of the possibility of moisture getting in from the outside, for example, after heavy rain. This is facilitated by the threshold, under which drainage is also thought out. At the entrance, they also make a water collector (a trench with a grate), which should drain water into the groove.
9. It is important that the staircase to the basement is secure and closed with a door or a porch so that unwanted rodent guests do not enter there. Lyada is a two-layer plank shield, an insulating film is laid between them, and a tight fit will protect against a specific smell.
10. The ventilation system will provide the basement with a normal microclimate with a low level of humidity - just a pipe that opens into a barred window. There should be a small moat on the lowest side of the basement where the condensate flows.

11. The basement stairs should be made wide and comfortable, and the steps should be non-slip, so that it would be convenient to go down / up without the help of the railing, for example, when your hands are busy. However, it is desirable to equip convenient handrails, and it is better to make the steps not high.
Only a well-equipped basement will be dry, without a special smell of dampness, and only it can be used as a full-fledged additional floor. It is equipped with various storage facilities and full-fledged rooms - a boiler room, a laundry room, a bathhouse, a wine cellar, a billiard room, etc.
Phased basement construction
1. Before starting construction, it is important to find out how close the groundwater is to the cellars. If there is no special need, then it is enough to cover the foundation walls with clay from the outside, and provide the foundation with waterproofing. Building materials for the construction of a basement in the foundation are selected according to the construction site and the characteristics of the soil.
2. The basement in the house does not have to be high, just a little higher than human height, that is, up to 2 meters, is enough. Excavation is best done with an excavator. It is important to plan the usable area in advance - where the boiler room, communications, storerooms and other premises will be located.
3. The temperature in the basement or in the cellar is always low, it approaches the temperature of the adjacent soil, that is, in summer it is about half the average air temperature, and in winter it is usually above 0 ° C. With high-quality thermal insulation, it will be dry and cool there all the time, and in a residential basement, it is important to consider heating. Wall insulation is done both outside (clay) and inside (styrofoam) - this way less condensate is formed from temperature changes.
4. An important event is the waterproofing of the foundation and basement walls, which must be carried out in accordance with all the rules. But it is best to start these works with the arrangement of drainage (described above). There is external and internal waterproofing, as well as between the basement and the floors under the first floor, be sure to pay attention to this part of the work. With high soil moisture, it makes sense to waterproof the walls with roofing material or polyethylene.
5. Soil moisture determines what the basement floors will be made of - compacted gravel with sand is enough to base on dry ground. Soil with a high moisture content requires waterproofing with greasy clay or crushed stone impregnated with bitumen, a concrete slab is laid on top of it. You can use wooden shields made of softwood or tiles (ceramic, paving).

7. The main stage of work is completed with the equipment of the stairs and the entrance to the basement. Next comes the interior finishing work and the formation of the functional premises of the basement floor.