The essence and principles of organizing the placement of goods on the trading floor. Placement and display of goods on the trading floor: rules and principles for the placement of goods Drawing up a layout for the placement of an assortment of goods of homogeneous groups
Presentations and novelties placed in a showcase immediately opposite the entrance to attract the attention of the buyer, to arouse the desire to walk around the store.
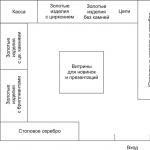
Product groups are placed on the trading floor in ascending order of price: the customer flow starts from the very cheap goods- products made of silver, then mass and inexpensive chains are placed, products without stones, then products with zirconium. These groups occupy the best places on the trading floor, as they are the most popular among the buyers of this store.
Expensive jewelry with semi-precious and precious stones are placed on the last counter, away from the entrance.
At the end of the shopping flow zone there is a showcase with silverware, which serves both as a showcase and a successful ending, since it is a separate product group.
An example of product category zoning for a jewelry store targeting middle-income shoppers is shown in Figure 3. 12.
Children's goods store.
The zoning of the product categories of a children's goods store depends on its format: it can be only goods for newborns, only children's clothes and shoes, baby food and toys, or a full range - clothes, shoes, food, toys, accessories, furniture, school supplies, goods for children. mothers Consider the option of the most complete range of children's products - a children's supermarket.

Fig 3 12 An example of product category zoning for a jewelry store.
entrance area traditionally reserved for seasonal and impulse demand goods - New Year's toys and carnival costumes, school supplies, seasonal clothes, seasonal entertainment (bicycles, skis, sleds, roller skates).
Center and left side The trading floor is usually allocated for toys, as these are mainly goods of impulsive demand, which should be located at the beginning of the customer flow. Clothing and footwear occupy the far part of the trading floor, as these are goods of target demand and the buyer will definitely reach them.
Goods for newborns should be allocated to a separate group and also zoned in the far part of the trading floor, since these are goods of target demand.
Nutrition, hygiene items, care products and products for mothers are also located in the far parts and on the right side of the trading floor. These are also groups of goods for targeted demand.
Furniture, strollers and bedding can be placed on the left side of the trading floor, and the strollers are closer to the checkout area. Furniture can also be located in a separate area - a "pocket", if any, since this is a product of periodic target demand.
On pallets throughout the trading floor there are such hot goods as baby diapers, inexpensive toys, baby juices.
An example is shown in Figure 3. 13.

Fig 3. 13. An example of product category zoning for a children's goods store.
Home goods store.
A home goods store usually has a fairly large area from 2-3 to 15-20 thousand square meters. m. (hypermarkets of goods for the home, construction and summer cottages).
entrance area traditionally reserved for seasonal and impulse goods, such as heating equipment, heaters, air conditioners and fans, lawn mowers, cleaning equipment around the house, rugs at the entrance, seedlings, Christmas goods, etc.
Shopping room divided into several functional zones.
1. Tools, hardware and hardware, electrical goods located in front of the trading floor behind the checkout area, as these goods are in high demand.
2. Repair Items located in the middle part of the trading floor, with each subgroup zoned separately, for example, paints, varnishes, rollers and brushes are presented together in one zone. Goods for repairs include:
Dry mixes;
Tiles and glue;
Floor coverings and accessories to them;
Paints and accessories to them;
Wallpaper and glue.
3. Bathroom Products combine:
plumbing;
Faucets;
Furniture and bathroom accessories.
4. Kitchen goods can be placed in the far part of the trading floor, to the right and left of the central aisle. For both groups, it is important to use an integrated approach to the presentation of goods, i.e. not separately sink, faucet and mirror, but all together. Kitchen products include:
kitchen furniture;
sinks;
Kitchen accessories.
5. doors and wood building materials can be placed along the back wall of the trading floor, since these are goods of target demand.
6. Home decoration products can be placed to the left of the central part of the sales area to the entrance area, then buyers can look at these goods on their way back after tiles, wallpaper and flooring. Home decor items include:
Fixtures;
Frames and baguettes.
7. Garden supplies should be placed separately, perhaps on the right side of the trading floor closer to the checkout area. Goods for the garden include:
Seedling;
Garden tools;
garden sculpture. An example is shown in Figure 3. 14.
IMPORTANT: in such a store, especially with a large area (about 10 thousand square meters), it is desirable to place information stands where customers can find out about the availability of goods and their location.

Fig 3. 14. An example of product category zoning for a home goods store.
Book store
AT the first part of the trading floor, just outside the entrance area, there are the most popular types of fiction (fiction, detective stories, romance novels, etc.), cookbooks, books on home economics and interior design, business literature of mass demand, since their purchase is often not planned.
In the entrance area and in the cash desk area they place deluxe editions, bestsellers (on display) and new popular fiction (additional points of sale) - all products with a high share of impulse purchases.
In the central part of the trading floor they have albums and literature on art, classical fiction, in depth - business literature, educational literature, books on branches of science, on technology, memoirs, books in foreign languages.
Children's literature zoned primarily by age: preschool literature, literature for elementary school students, middle grades, high school students Within the framework of age - by type of literature: fiction, educational, entertainment, technical, etc. In addition to books, you can place small toys and educational games ( puzzles, mini-constructors). It is important to organize the display so that children can also participate in the selection of goods.
In the checkout area they place postcards, posters, small souvenirs. Stationery can also be placed there (Fig. 3. 15).

Fig 3. 15. An example of product category zoning for a bookstore.
Despite the individual approach to stores of different profiles, as a conclusion we formulate general rules for the layout of the trading floor.
1. The main principle of the layout of the trading floor of the store is simplicity. The trading floor should be complete, convenient and understandable for the search for a particular product. Intricate architectural elements and ornate passages distract the buyer's attention, prevent him from navigating in space and choosing the trajectory of movement. As a result, he thinks not about buying.
2. The location of the entrance and the placement of commercial equipment should not violate the natural course of the movement of buyers - counterclockwise.
3. It is necessary to plan and allocate a highway for the main flow of buyers.
4. The buyer needs to take a breath - immediately after entering the store there should be an unoccupied area so that he can slow down, look around and get used to the new premises.
5. The buyer must say "Ah!" - what he sees right in front of the entrance should cause positive emotions.
6. In small stores and in one department of a large store, it is important to ensure the visibility of the trading floor - for better orientation and comfort of customers, as well as for all product groups to be in sight.
7. Anchor products - attractive (or frequently purchased) products - should be located at the top of the "golden triangles" as far as possible from the entrance in order to force the buyer to walk through the entire store.
8. When planning, it is necessary to take into account ergonomic requirements.
It is necessary to present the goods to the buyer not chaotically, but in accordance with a carefully developed scheme - a planogram. On it, each product from the laid out assortment is depicted in detail, indicating the exact location. The planogram is intended for the rational management of the retail space in which products are sold. The scheme will help increase the impact of the item being sold on the visitor, sales volumes, and form a closer relationship between the product and the buyer. Advertising and PR manager at Agro-Invest LLC Oleg Vlasov spoke about the principles and rules of leaving a planogram.
A planogram is a scheme for displaying goods on shelves and shop windows, which is compiled on the basis of an analysis of the requirements of the supplier of the goods, the capabilities of the retailer and the behavior of customers. It is carried out manually or with the help of computer programs in the form of images, drawings, photographs. The goal is to manage the perception and behavior of potential buyers. This is one of the effective tools and sales management on the trading floor.
Planogram Goals
With the help of a planogram, you can increase the turnover in the store and earn money by selling profitable places to suppliers. Sometimes an agreement is made between the supplier and the outlet, fixing the place of the product on the counter.
Planogram helps:
- Adjust the display of products in retail outlets
- Control the availability of a range of a particular brand
- Adjust the occupied area for a specific product
The number of potential buyers, their distribution over the trading area determines the coefficient of importance of trading places. Products that are in high demand occupy the most prominent positions. Display of goods should demonstrate products, facilitate their search and selection, and also create consumer preferences. Rational placement of selling positions stimulates the flow of buyers.
Read also:
Principles of drawing up a planogram
When developing a planogram, the following principles are followed:
- Visibility, visual appeal, neatness, aesthetics. The product should be available for review: the visitor will spend less time searching for the desired product
- Reasonable use of retail space and equipment. For each type of product, an area is allocated that corresponds to the volume of sales of products. The maximum area is intended for advertised and fast-selling products
- Consistency. Grouping related products in one place (place tea near sweets, household goods - from a display case with dishes)
- Compatibility. It is necessary to exclude the negative impact of the commodity neighborhood: if coffee is placed next to spices, the product will acquire a foreign smell or give it to the surrounding goods.
- Not far from high-demand products are impulsively purchased items. The rational alternation of expensive and cheap goods increases the profit of the store, draws attention to things with opposite properties.
- Sufficiency - a complete demonstration of the store's products
- Products should be located at eye level and outstretched arms
The development of a planogram is carried out according to the rules:
- Build a scale of product popularity. Buyer preference rating can be derived after consumer demand analysis
- The number of racks and shelves that should be assigned to a group of products is determined
- The placement of the assortment is controlled in accordance with the developed planogram. Any errors can subsequently contribute to a drop in sales.
Merchandisers or sellers are responsible for the correct display. Heads of departments and managers regularly check the compliance of product placement on the trading floor with the planogram. If you do not comply with the requirements of the supplier, violate the layout scheme, the supplier has the right to refuse to pay the bonus reward and further supply of products to this store.
Spread goods vertically, horizontally, and also combine the location. With a vertical layout, homogeneous products are laid out on the shelves vertically. Example: one vertical strip is represented by yoghurts, the other by cottage cheese, then sour cream, ryazhenka. The buyer is better guided when choosing a position. Also, products are placed horizontally, along the entire length of the equipment. Example:
- One shelf is occupied by apple juices, the second - by other juices.
- Juices on one shelf, water on the second
Other units or price tags should not obscure the information on the packaging. The main goods are placed in the visibility zone from the entrance.
Step-by-step instructions for compiling a planogram
Shelf space can be divided into:
- own retail equipment provided for the network (branded refrigerators, sales racks, etc.)
- network shelf space
In the first case, you can do whatever and however you like, depending on your goals. If we consider the shelf space of the network, then there is a problem in the form of occupancy of this space by competitors, as well as the network itself, which ultimately decides where to put your product. Therefore, in this case, it is necessary to approach the solution of the location of the product in more detail.
To determine the best place for your product, you need to have an understanding of the existing planogram, what it looks like without your product. To do this, it is enough to request it from a representative of the distribution network (which is sometimes impossible) or simply take a picture of your product category in the nearest supermarket. Transfer this photo to a computer and open it in any simple graphic editor (for example, Power Point). Next, take a photo of your product and transfer it to the planogram. Try to put your product in different places, guided by visual perception (for example: there should not be a similar or merging product nearby, unless of course you specifically pursue this goal), pay attention to the main competitors, do not place the product on the edge of the shelf.
Video how to make a planogram:
Different companies may have different schemes, but all of them are united by a common principle of construction:
- To draw up an effective scheme, a developed concept of one shelf and the entire outlet is required. Determine the type of product display and its location (counters, stands, shelves, baskets and other places and methods). The product should be noticeable, attract attention, interest, simplify the search for the buyer
- After developing the key points, they begin to draw a diagram. It depicts commercial equipment (department and each shelf in it). Reflect products, given the size, color, shape. Detailed drawing will allow store employees to quickly and easily navigate the planogram
- Enter the symbols for each product to facilitate its calculation
- The planogram is approved by management
In some cases, the supplier provides his own planogram. If the assortment expands, consumer demand changes, and adjustments are made to the planogram.
Programs for creating planograms
There are many programs for drawing up product layout diagrams:
- Retail Shelf Planner
- Shelf Logic
- Planogram Online
- excel
- power point
- Any graphic editors
 An example of a planogram drawn up in Excel
An example of a planogram drawn up in Excel All these programs will help you create effective layouts, optimize layout and space, and reduce layout errors. They will form a reference book of commercial equipment, calculate the turnover of the shelf, and provide a visual layout of positions.
Planogram examples
Consider how to create a planogram for a grocery store.
- Compile a sales rating for products of one category (“grocery”, “dairy products”), break it down into groups: cottage cheese, kefir, salt, flour, yogurt and others
- Determine for each group of units the share in the turnover, take the category as 100%, while milk can be 40%, and the remaining categories (cottage cheese, butter, sour cream or sour-milk products) 10-20%
- Given these data, the products are distributed in accordance with the share in the turnover. For milk, it is necessary to allocate the most racks (4, if there are only 10 of them in the store). For the rest, 1-2.
The share of the most profitable products is increasing. There is more space for them. If burgers occupy a square meter of space and brought in twice as much profit this month as pancakes, which take up the same amount of space, then the area for pancakes is reduced in favor of patties. The place for cutlets is increased to 1.5 square meters. An increase in the area can contribute to an increase in the sale of cutlets.
By the same principle, schemes are drawn up for goods of other categories.
beer department
Take the example of beer and branded refrigerators. The planogram is quite simple and includes 3 main zones:
- On the lower shelves there is a product of a low price category.
- At or near eye level, these are mass-market brands. What generates the main sales. The product in this zone will leave as quickly as possible.
- Above eye level - premium segment.

Bakery
Bakery products are grouped by types, varieties: separately black, white, bread without yeast, with additives, whole grain, sandwich rolls, unsweetened, sweet pastries, desserts, pastries, cakes. Long-term storage products are placed separately.
Confectionery products are laid out by type and variety on the internal shelves. Candies are poured into boxes and cabinets near the walls. For cakes and pastries with cream allocate enough space in the refrigerator.
Products from the bottom and top shelves don't sell well. A shelf at eye level is the best option. Closer to the buyer is a product that has an expiration date.
Furniture salon
Furniture is placed so that visitors can see the headset and individual products. Large stores decorate the interiors of apartments with a demonstration of furniture sets. To attract attention and create coziness, kitchen furniture is decorated with a variety of decorative elements: glasses, plates and other items.
Cheap and expensive products are separated. Cheap ones are located closer to the entrance. At the entrance, the price is especially clearly visible; furniture can be bought faster. The brightest goods are put on display.
Furniture for living rooms, bedrooms, cabinet share. You can move products around the hall once every two weeks. Weakly sold furniture is placed in prominent places. If the buyer comes again, he may notice something that he did not notice before.
Hardware store
Products are divided into large-sized, medium-sized goods, small-piece products. Interconnected groups are located nearby (nails, screws near tools, extension cords).
Dry mixes are laid out on racks in vertical blocks. The heaviest packages are placed on the lower shelves. Fasteners are grouped by type (self-tapping screws, dowels), purpose (for windows), size. Also, information materials are not superfluous in the trading floors.
Equipment and tools are laid out from the waist and above. Piece goods are located in the checkout area on racks. Stands are intended for wallpaper. The buyer is given the opportunity to independently deploy the roll and inspect it. The scheme displays the color scheme of the wallpaper, their type, material.

Stock
The territory of the warehouse visually needs to be divided into zones. Racks, sections, shelves are equipped with plates. According to the detailed scheme, the employee will find the goods by name and address. Products are placed according to the principle "closer demand - closer to delivery".
The scheme marks the zones of long-term storage and short-term storage. Products that are in low demand are placed in long-term storage areas.
The strategy of a rationally placed product should be thought out to the smallest detail. The purpose of the planogram is to increase turnover, increase product sales, improve the flow of potential buyers, increase competitiveness for goods of the same category from other manufacturers. Thanks to a carefully designed planogram, sales will increase, and the time spent searching for the right product will be reduced.
I propose to share in the comments the planograms that you have obtained.
The system of placing goods on the sales area, other premises of the store or in certain areas of the seller’s workplace according to certain assortment characteristics inherent in individual goods (type, group, article, size, style, grade) is called product placement.
The operations, the implementation of which ensures the creation of such a system, are called the placement of goods on the trading floor. The general complex of works on the placement of goods on the trading floor includes two fundamentally imminent types of work:
1) determining the placement of goods of individual product groups (or consumer complexes) in the trading floor based on previously developed plans (maps, schemes for the technological layout of trading floors)) and distribution of trading space for individual groups (consumer complexes)
2) determination of the locations of individual subgroups and names of goods on commercial equipment based on the equipment deployment scheme and the implementation of direct teaching of goods
Consequently, operations with the placement of goods on the trading floor are directly related to further technological operations for teaching goods on trade and technological equipment. In stores that sell goods through the service counter, the placement of goods consists in their conclusion at the workplace of the seller in order to facilitate his working conditions, in self-service stores, the placement of goods creates the prerequisites for their further teaching in the trading and technological equipment of the trading floor.
Rational execution of operations from the placement of goods helps to reduce the labor costs of sales personnel for replenishing stocks of goods on the trading floor and the correct formation of customer flows, saves their time for inspecting and choosing goods and improves the culture of trade services, increases the throughput of the store and its efficiency. At the same time, it is important to correctly choose the zones, places and sequence of the location of goods of individual groups (types) on the area of the trading floor, the size of the area for organizing trade in goods of a certain purpose or product group.
The work on determining the placement of product groups and the size of the area allocated for them in the trading floor of a type store is closely related to the development of technological planning schemes for trading floors and is based on taking into account the specifics of the range of goods that should be sold in the store, the methods used to sell them, and features space-planning solutions of the trading floor and the location of individual structural elements (doors, windows, columns.
In the case of selling goods through a service counter, the location of the inventory from which the seller releases the selected goods is not important for the buyer, since he is offered to know only samples of goods that are behind the counter while using self-service, the location of the goods on the sales floor and the area allotted for their display and sale, acquires daily significance. With self-service, the buyer receives all the necessary information about the product not from the seller, but directly getting acquainted with the goods presented on the trading floor.
On the trading floor, goods are placed according to the commodity-industry principle or according to the complex principle (according to the principle of complexity of demand, interchangeability of goods or common purpose) placement of goods according to the commodity-industry principle provides for the allocation of one workplace, zone or sales department for products of one commodity group; the complex principle of placing goods is to combine at one workplace, in one section, department, on one floor of a store of goods of various groups that are interconnected in demand, or those that satisfy the needs of certain contingents of buyers (in this case, opportunities are created for buyers to purchase t n complex purchases and reducing the time spent in the store).
In the practice of domestic self-service stores, they traditionally follow the following sequence of locating areas for the sale of food products "bread and bakery products - groceries - confectionery products - gastronomic products", while separately placing departments (zones, workplaces) for the sale of meat, fish, fresh vegetables and fruits, that is, goods with special physical and chemical properties and special requirements for the methods of their sale, as well as related non-food products.
In shops selling non-food products located in multi-storey buildings, goods of increased and more frequent demand (perfumes, haberdashery, stationery), bulky and heavy goods are traditionally placed on the first floor, non-food products that require more time for storage are placed on the second and upper floors. inspection and selection by their customers (below - children's assortment, in the search - shoes, clothes, knitwear, fabrics), and in the basement or basement - they organize food sales * 6.
*6:. Technology and equipment of trade enterprises /. Ed. V. M. Rebitsky -. M.:. Kooposvita, 1996. P. 167
The placement of goods is influenced by tradition, the nature and attractive appearance of the goods, the convenience of the sales staff, profitability, the need to prevent theft, the convenience of customers and the personal tastes of the store management.
In the process of developing a product placement scheme:
1) determine the location of each product group or consumer complex;
2) taking into account the specific weight of the group in the turnover, the required area for the placement of goods is calculated;
3) develop a scheme for the technological planning of the trading floor, indicating on it the areas for accommodating and teaching specific groups and types of goods;
4) select the appropriate types of trade and technological equipment for teaching stocks of goods
In the course of this work, special attention is paid to determining the area of the zone for the placement of individual product groups (consumer complexes). To do this, it is recommended to determine the share of goods of each of the groups in the retail turnover and, accordingly, calculate the share of the product group in the area of the trading floor. At the same time, the result obtained must be adjusted taking into account the turnover of commodity stocks of the relevant goods, container dimensions, and thin packaging.
The main requirements for the placement of goods on the trading floor traditionally include:
Ensuring a wide selection of goods;
Compliance with the rules of the commodity neighborhood;
The sufficiency of the quantity of goods to ensure the continuity of trade;
Accounting for the movement of customer flows;
Ensuring good visibility and accessibility of goods for buyers;
Providing customers with the opportunity to navigate the placement of individual complexes or product groups and make a purchase with minimal time spent on searching and purchasing goods;
Fixing for each group of goods (complex) permanent locations, "rational use of the area of the trading floor for placement and teaching of goods
When developing schemes for the placement of goods, special attention is paid to compliance with the requirements related to the need to take into account the directions of movement of customer flows in the store, the physical and chemical properties of goods, and compliance with the rules of product neighborhood.
Foreign experts recommend placing goods with relatively low prices, which create an attractive impression of the price level in the store, near the entrance to the trading floor (at the beginning of the route in the movement of buyers). However, the locations of these products should alternate with the locations of the products that generate the most profit for the store.
It is also effective to place the main brands at the beginning of each assortment group, since at the beginning of the route the buyer is ready to take more items into the basket than at the end of the route, when the basket is almost full1
In particular, the movement of the flow of buyers, as a rule, is directed from the entrance to the trading floor along the trading furniture with the goods set out on them in the direction opposite to the clockwise direction. The volume of goods, in the sale of which a trading company is interested, should be placed in places close to the beginning of the buyer's route.
In the practice of trade, the effective placement of goods is achieved subject to the following principles for placing goods on the trading floor:
Uniform placement of the entire range of store products on the trading floor, use of all places in the trading floor for displaying goods;
Allotment of space for individual product groups, taking into account the share of these goods on sale and their turnover;
Predominantly concentrated placement of homogeneous goods (on the same side of the devices, although it is allowed to place homogeneous goods in different places of the trading floor, if these goods enter the composite time truly to different consumer complexes, or if their concentration leads to a delay in the flow of buyers
Special highlighting of new products;
Placement of related products next to the main ones;
Placement of bulky, heavy goods along with the settlement nodes and with the exit from the store;
Grouping food products, as a rule, according to the commodity-industry principle, and non-food products - by combining them into micro-complexes;
Placement of goods of frequent demand or long-term familiarization in the depth of the sales area, away from the entry and exit areas and in different places of the sales area;
Location of low-demand items along with corresponding high-demand items;
The location on the first floors of multi-storey buildings of shops of goods of more frequent demand, which do not require a long choice
It is also important to single out separate accommodation zones:
Goods, the preliminary preparation for sale of which is carried out directly in the store, next to the premises for their preparation;
Goods that require frequent restocking, along with storage facilities for related stocks;
Food products, in the process of sale, require cutting, weighing, packaging (meat, fish, dairy gastronomy, vegetables, etc.) at the workplace of the seller at the service counter;
Goods with specific physical and chemical properties and harmful effects on other goods from the point of view of the commodity neighborhood - at the ends of island slides or in baskets isolated from the bulk of the goods
Expensive goods and goods in small packages - near the booth of the controller-cashier (in the "zone of effective observation")
Goods on the trading floor, depending on their purpose, are classified as working, exhibition or reserve stock
Working stock refers to goods intended for release to customers. In stores that sell goods using the traditional method (through a service counter), a working stock of goods is placed on the equipment of the seller’s workplace, and most of it is hidden from buyers. In self-service stores, a working stock of goods is laid out on the equipment openly, and customers have free access to it. When trading on samples, the working stock, prepared for submission to the trading floor, is located in the storage rooms. A working stock of goods in the trading floor of the store on the shelves of true and island trade and technological equipment and in a container-bath
The exhibition stock is intended to inform buyers about the range of goods available for sale. It is placed in showcases, on special stands, on the upper shelves of wall-mounted equipment. When selling goods through the service counter, the exhibition stock is placed in showcases and on the upper shelves of wall-mounted equipment. In self-service stores, the working stock is also an exhibition stock. When selling goods according to samples, samples of goods are exhibited on the trading floor.
The reserve stock is used to replenish the working stock during the working day, as well as to replace the exhibition stock of goods. It is created for uninterrupted customer service and is stored in the warehouse of the store (pantries, cold rooms, etc.) and partially in the trading floor. When selling goods through the service counter, the reserve stock is stored at the sellers' workplaces in the lower drawers of the counters adjacent to the trading floor, or on the shelves located on the back side of the wall gyros.
As a result of the formation on this basis of a real scheme for the placement of goods in a store, a convenient system for placing goods in terms of conditions for the timely supply of their stocks to the trading floor should be created.
Quite often, coming home from a store (especially a supermarket) and critically evaluating a considerable amount of purchases (necessary and not very necessary), you think about the reasons that encourage you to make such rash spending. And there is a rather logical explanation for everything - merchandising, in accordance with which a competent display of goods on the trading floor was made.
Merchandising
A natural consequence of the improvement and oversaturation of the market is the intensification of competition not only between commodity producers, but also between trade organizations, on which the final result of the efficiency of all production often depends to a greater extent. It is merchandising, that is, a system of measures to increase sales in retail trade and create an atmosphere conducive to this, that contributes to the successful sale of goods. Literally translated from English, this term means the process of trading.
The basic principles of marketing strategies are formed as a result of a thorough analysis of the behavioral stereotypes of buyers. Thus, the basis of merchandising is to draw up clear, psychologically justified measures aimed at stimulating purchases. If we take into account that on average more than 70% of goods are purchased impulsively, without a balanced preliminary decision on the need for such a purchase, then the ever-increasing effectiveness of merchandising in modern conditions becomes clear.
Properly made display of goods on the trading floor - as the first step or the basis of merchandising - should ensure maximum availability of products, as well as visually affect a person, helping to attract his attention to the object of purchase.
Marketing strategy
Properly organized display of goods in the store is the most significant part. One of the most important conditions for the sale of goods is its visual visibility, attractiveness. Analyzing the actual turnover, marketers came to quite logical conclusions: goods placed on shelves at the level of human eyes have the highest sales figures. However, there are many other factors that have a significant impact on sales volumes.
Target areas
The display of goods is used to achieve various narrowly focused, often overlapping goals:
- Increasing sales volumes.
- Formation of consumer confidence in the product.
- Strengthening the impact of the brand on the consumer and the formation of persistent taste priorities.
- Increasing competitiveness among similar products.
- Acquisition of well-deserved recognition in the field of successful promotion of products.

Product presentation options
Various options for the presentation of goods are due to the specifics of individual sales offers, consumer needs and taste preferences.
Style or species grouping is carried out in grocery, hardware and manufactured goods stores, where this type of placement is traditionally used in relation to everyone. For example, sections with outerwear and summer collections, shoes, haberdashery and so on are located in various departments of the store.
The ideological grouping is most often based on a concept or simply the reputation and image of a trading facility. For example, salons that sell furniture according to samples exhibit the most attractive specimens for a complete visual perception. At the same time, the surrounding interior is reproduced in accordance with the most fashionable trends, emphasizing the advantages of the advertised products.
The color scheme when laying out goods is typical for shops and boutiques with high trade margins, designed for the most affluent category of consumers. Such a contingent is attracted by the brightness of the image, stimulating them to buy.
Price grouping allows buyers to evaluate the diversity of the assortment and choose products at the most suitable price, while a large-scale display gives buyers an idea of low prices for a huge number of similar products.
With a frontal presentation of a product in expanded form, the buyer is shown all its features, emphasizing their attractiveness as much as possible.

Placement of departments and groups of goods
The logical placement of certain types of products on the trading floor is the result of an adequate assessment of several fundamental factors:
- The number of purchases per unit of time of certain groups of goods, i.e. the frequency of their purchase.
- Dimensions and weight of products sold.
- The number of different product modifications.
- The time and spatial distance required for the buyer to inspect or review a potential purchase, as well as to select the most attractive item from the analogues presented on the shelf.
In addition to quantified factors, the display of goods directly depends on the quality and texture of the products offered, packaging, the image and layout of the store, and the profitability of certain groups of goods.

For example, in elite salons and boutiques, the presented products are often combined according to their stylistic and color similarity. In stores with a medium price level, goods are usually grouped by size, while in outlets with minimum prices, they can be placed simply in containers.
Traffic routes
To achieve maximum rationality in the use of available retail space, it is necessary to determine the sequence of location of departments in the store as a whole, and the choice of the most successful location for each section. After considering the established traffic path in a large store, experienced marketers place departments with insignificant, impulsive products on the way to sections with the most frequent purchases. This means that a person who seeks to purchase only certain things is forced to go through other departments in which a properly organized display of goods literally lures and forces to make a purchase.
The art of product display
The methods used for displaying goods traditionally depend on the placement of products sold in relation to homogeneous products and specialized equipment.
With a horizontal layout, homogeneous goods are evenly placed along the entire length of the shelf. At the same time, in one direction, the units are ranked as the volume decreases (or increases), according to the serial production, placing the largest and cheapest on the lower shelves. And products intended for quick sale should be as accessible as possible to the buyer and in a certain way attract attention.

With this placement, the least popular products located close to the more popular analogues will be in high demand, partially borrowing from them consumer sympathies.
With a vertical layout, homogeneous products are placed on racks in several rows: smaller and lighter ones are on the upper shelves, and their larger counterparts are on the lower ones. This method improves the quality of visual perception and is quite convenient for buyers, regardless of their height. Most often, this kind of display of goods is used in large trading floors of self-service stores.
The display way of laying out is carried out with the help of additional points of sale, i.e., goods are displayed at the most favorable angle on a stand-alone company stand or counter. The location of such a stand is in no way tied to the actual place of sale of a particular product.
Planogram
The presentation of goods to the buyer should not be carried out randomly, but in accordance with a scheme (drawing, drawing or photograph) that was previously thought out and made manually or on a computer, which is called a planogram. On it, each position of the laid out assortment list should be depicted in as much detail as possible, indicating the exact location for each trade unit. A planogram is drawn up for the display of goods, taking into account the wishes of suppliers and buyers, as well as the capabilities of the retailer. The time spent on its preparation, as a result, significantly reduces the time required to place products on the trading floor. In addition, many software products have been developed that significantly facilitate and speed up the process of such detailing.
The product display planogram must be approved by the head of the outlet, and all its subsequent changes are also subject to approval.

General principles
Depending on the specifics of the store and the products sold, a wide variety of positions are followed when developing a planogram. But the general principles of laying out goods are as follows:
- The principle of visibility - is implemented in the creation of visual appeal and accessibility for review.
- Achieving the highest efficiency at reasonably reasonable costs (rational use of retail equipment and space). For each type of product, areas are allocated that approximately correspond to the volume of their sales. Maximum areas - for fast-selling or advertised goods; the latter, in turn, should be located in the most viewed places of the trading floor. Do not forget about ensuring free passage to the laid out products.
- Consistency. The placement and display of goods is carried out in complex blocks, i.e. things that are interconnected according to some attribute are grouped in one place. For example, household goods, and nearby - a showcase with dishes, etc.
- Compatibility of nearby goods in relation to each other, i.e., the negative influence of commodity neighbors must be excluded. The laid out coffee products should not be located near spices or wet products. Such a neighborhood will negatively affect the consumer properties of the goods sold (coffee can itself acquire a foreign smell, or it can give it to surrounding objects).
- Impulse-purchased items should be close to high-demand products. For example, the correct alternation of expensive and cheap goods allows you to increase the profitability of the store, drawing attention to units that are diametrically opposed in their properties. At the same time, the aesthetics and safety of the laid out products should be ensured.
- It is very important to monitor the sufficiency of the display, i.e., the most complete representation of the available assortment, depending on the retail space, the specifics of the outlet and the demand for the proposed list of goods, as well as the entire range of marketing policies.
- To create an enticing image of the store, quite often (especially when it is opened) they resort to reducing trade allowances, promotions and discounts. This is provided for the formation of stable sympathy of buyers for a shopping facility.
The specifics of the display of food products
The display of food products is designed to ensure not only accessibility, but also maximum safety. Depending on the storage conditions, the packaging used and other factors, various methods of their sale are used. Liquid products in bottles are conveniently arranged in several rows on the shelves, occasionally right in the boxes. Meat, fish and sausage products - in exposing the buyer to the cut goods in the most attractive form. Packaged products (or in packs) are neatly laid out in rows or stacks on shelves, grouping units by type.

For bakery products, near-wall and island slides are used, as well as special equipment that ensures compliance with sanitary storage standards. Such a display of goods (the photo is presented above) is the most rational for its safety.
Features of the display of industrial goods
Industrial goods are characterized by their maximum differentiation into groups in accordance with types, articles and purpose. Clothing, for example, can be distributed around the trading floor depending on styles, seasonality, gender, age, and other characteristics. Hats are placed on special consoles, as well as designs of various configurations, which make it possible to show this or that thing in the most advantageous way. The display of goods in the store allows you to plan an effective direction of consumer flows that contribute to the profitability of the trading business.
It is very important when planning the display to ensure that the product is not blocked by a queue that limits its visibility and accessibility. At the same time, its front side should be best presented to the consumer's gaze. It is believed that the most advantageous arrangement of racks is on the left side of the direction of movement of the main customer flow. With a uniform loading of goods on the shelves, that part of it, on which maximum marketing efforts are directed, should be approximately at eye level, and in addition, it should be located close to the checkout area. Strengthening the impact on consumer sympathy can be achieved using a variety of advertising media. The increase in turnover also occurs when the same product is displayed in several zones of the shopping facility at once.

Product placement options
Thoughtful placement of goods in the store significantly increases sales. To most effectively attract the attention of the buyer, quite a variety of types of display of goods are used with the involvement of special equipment:
- Shelves and racks.
- Counters and special exhibitions.
- Wire baskets and floor pallets.
- Separate stands.
- Dispensing machines.
- Advertised packages, beautiful boxes, etc.
Exhibitions of goods in promotional packages look very impressive. High-quality and expensive printing, competently provided by the manufacturer, is of particular interest to store visitors, drawing attention primarily to themselves.
Features of merchandising in a pharmacy
The use of a competent marketing strategy in the pharmacy chain has some features in relation to other trading facilities. Pharmacy merchandising is a complex activity of increasing through promotional activities aimed at drawing consumer attention to over-the-counter drugs. One of the most important features of a pharmacy outlet is the specifics of consumer psychology, often expressed in rather shy behavior: the client tries to get as much information as possible on the windows before asking questions, for example, about medicines for fungal or sexually transmitted diseases, as well as other rather intimate medicines . Pharmacies are developing a certain system of rubricators that facilitate the search for the necessary information on therapeutic groups of medications.

In addition, looking for a medicine, a potential buyer inspects the trading floor and involuntarily becomes interested in other medications that he needed earlier (but it was not possible to purchase them) or those that he will buy today or in the future.
Pharmacy display zoning
Traditionally, the display of goods in a pharmacy is carried out taking into account zoning, which makes it as easy as possible to find medicines. Almost every pharmacy kiosk has the following zones:
Products sold without a prescription. These are rather voluminous calculations in which drugs are placed according to their areas of application.
A separate place is given to medicinal plants and dietary supplements, various homeopathic preparations.
Many vitamin complexes, products for diabetics and people seeking to lose weight are located in a separate area. Also here you can find a variety of modifications of drugs for people leading a healthy lifestyle.
Various variations of natural and decorative cosmetics (from toothpastes and creams to lipsticks and pads).
Medical equipment and patient care products, orthopedic products and compression hosiery.
Products for young children, newborns, their mothers and pregnant women. On the shelves are lined with specialized cosmetics, baby food and various devices for the development of the child.
In separate zones, drugs are usually allocated that help increase efficiency and prevent stressful effects on the human body. The showcases display medicines against motion sickness, which strengthen eyesight and protect against the harmful effects of technical equipment in the workplace.
The checkout area contains special offers, advertised products and seasonal equipment, as well as printed materials dedicated to the problems of maintaining and restoring health.

Adequate visualization of the presented drugs provides for their location not lower than 0.8 m from the floor, but not higher than 1.6-1.7 m, i.e. not higher than the head of an average person.
The highest sign of the effectiveness of the marketing policy, which takes into account all the rules for laying out goods, is the growth in sales volumes, as well as the reduction in time spent on finding the necessary products by buyers. Competent marketing not only facilitates the buying process by reducing the time to find the right product, but also draws too much attention to not the most necessary things.
The placement of each product group in store No. 39 occurs in accordance with the location of a particular department that sells the goods of this product group, and certain types of goods are located within the group.
The placement of goods is based on the traditional approach. This approach assumes that the area allocated for a product should be proportional to the volume of its sales. It also takes into account: profit received from the sale of goods; stock of goods on the trading floor; the need to maintain the desired direction of movement of consumer flows; locations of entrances and exits.
The placement of goods is presented on the scheme of the trading floor (Appendix I).
Of great importance in the organization of customer service is the display of goods, which in modern conditions is not only a part of the technological process, but also acts as an effective means of stimulating sales, can be an element of the image of the enterprise and a permanent component of the culture of service. Under the display of goods, one should understand certain ways of laying and displaying goods on the demonstration area of the trading floor.
Store No. 39 sells goods mainly through the traditional service method, with the exception of bakery products and groceries, which are sold using the self-service method.
In departments with a traditional method of service, both product and decorative display are used, it is used for window dressing and allows you to attract a buyer.
In the department where the goods are sold by the self-service method, the product display is used in a vertical and horizontal way. The vertical layout provides good visibility of goods, which allows customers to quickly navigate the assortment and make a purchase. With the horizontal method, a certain product occupies one or two shelves that are in the field of view of buyers.
An analysis of the display of goods on commercial equipment is shown in Table 3.6.
Table 3.6 - Analysis of the display of goods on commercial equipment in store No. 39
|
Name of product |
Display type |
The equipment on which the goods are laid out |
Laying method |
The criterion underlying the calculation |
Benefits of laying out |
Calculation disadvantages |
|
1 Juice, canned fruit and vegetables |
Commodity |
Wall slides |
Vertical |
1 manufacturer 2 pack size |
Good product visibility | |
|
2 alcoholic beverages, beer, drinks |
Commodity |
Wall slides |
Vertical |
1 manufacturer 2 pack size |
Good product visibility |
It is not easy to compare the price, may lead to the exhaustion of goods |
|
3 groceries |
Commodity |
Wall slides |
Vertical |
1 manufacturer 2 pack size |
Good product visibility |
It is not easy to compare the price, may lead to the exhaustion of goods |
|
4 Sausages |
Decorative |
Refrigeration showcase |
1 Manufacturer 2Assortment | |||
|
5 Bakery products |
Commodity |
Wall slides |
horizontal |
1 Manufacturer 2 Assortment 3 availability of packaging |
1 Ease of selection 2 effective use of shop equipment |
For successful work, it is advisable to plan the placement and layout in advance, this allows you to save time for buyers when choosing goods. To do this, in store No. 39, a display place is “fixed” for certain goods. Figure 3 shows the planogram of dairy products.
A planogram is a diagram (drawing, photograph) that determines the place, location and method of presentation of each commodity unit on commercial equipment.
Figure 3 - Planogram of dairy products
It is also important to correctly and correctly place price tags. The price tag should be well read, its location should not raise doubts about which product it refers to. At the same time, it is necessary that the size of the price tag corresponds to the dimensions of the product and does not cover it. These simple principles can significantly increase sales. The store administration and sellers control whether the price tags are set correctly, however, due to the wide range of some products, it is not possible to place price tags under each type, which complicates the selection process and causes dissatisfaction among customers.
However, due to the lack, in my opinion, of specialists in this field, the insufficient number of employees, the display of goods is not always satisfactory.
But still, the main thing in the store is the product: its assortment, and then the placement and well-placed accents. If the product is uninteresting, of poor quality, does not have its own "face", then all your efforts to design the trading floor, alas, will be in vain.