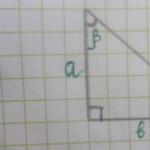
What is the area of a rectangle triangle? How to find the area of a triangle (formulas)
In elementary geometry, a right triangle is a figure consisting of three segments connected at points, with angles two of which are acute and one straight (that is, equal to 90°). Right triangle is characterized by a number of important properties, many of which form the basis of trigonometry (for example, the relationship between its sides and angles). Since school, we all know how to calculate area of a right triangle, and in everyday life we encounter this geometric figure quite often, sometimes without even noticing it. It finds quite wide application in technology and therefore engineers, designers and architects often have to solve such a problem.
Architects need to determine this value when they design buildings with pediments, which are the completion of the facades and have triangular shape bounded by a cornice and on the sides by roof slopes. Often the angle between the slopes is straight, and in such cases the pediment has the shape of a right triangle. It is necessary to determine its area for the simple reason that it is necessary to know exactly the amount of building material required for its arrangement. It should be noted that gables are mandatory elements of low-rise buildings (country houses, cottages, dachas).
Finding the area of a right triangle
| S | ab |
a- leg
b- leg
S- area of a right triangle
Form right triangle have many of the details from which modern furniture is made. As you know, in order to make the most efficient use of room space, all elements of the furnishings must be placed in it in an optimal way. You can make good use of areas such as corners using triangular-shaped tables, the tops of which in most cases are right-angled triangles with legs adjacent to the walls. When designing and calculating these elements, furniture production designers use the formula according to which finding the area of a right triangle is carried out based on the length of its sides. In addition, they often have to develop designs for tables attached directly to the walls, which include supporting elements, which also represent right triangles.
Builders engaged in facing work often in their professional activities have to use ceramic tiles in the shape of a right triangle with legs of the same or different lengths. They also have to determine the area of these elements in order to find out the required number.
Form right triangle It also has such an important and necessary measuring tool as a square. It is used to construct and control right angles, and it is used very widely and by many: from ordinary schoolchildren in geometry lessons to designers of cutting-edge technology.
A right triangle is found in reality on almost every corner. Knowledge of the properties of a given figure, as well as the ability to calculate its area, will undoubtedly be useful to you not only for solving geometry problems, but also in life situations.
Triangle geometry
In elementary geometry, a right triangle is a figure that consists of three connected segments that form three angles (two acute and one straight). The right triangle is an original figure characterized by a number of important properties that form the foundation of trigonometry. Unlike a regular triangle, the sides of a rectangular figure have their own names:
- The hypotenuse is the longest side of a triangle, opposite the right angle.
- Legs are segments that form a right angle. Depending on the angle under consideration, the leg can be adjacent to it (forming this angle with the hypotenuse) or opposite (lying opposite the angle). There are no legs for non-right triangles.
It is the ratio of the legs and hypotenuse that forms the basis of trigonometry: sines, tangents and secants are defined as the ratio of the sides of a right triangle.
Right triangle in reality
This figure has become widespread in reality. Triangles are used in design and technology, so calculating the area of a figure has to be done by engineers, architects and designers. The bases of tetrahedrons or prisms - three-dimensional figures that are easy to meet in everyday life - have the shape of a triangle. Additionally, a square is the simplest representation of a "flat" right triangle in reality. A square is a metalworking, drawing, construction and carpentry tool that is used to construct angles by both schoolchildren and engineers.
Area of a triangle
The area of a geometric figure is a quantitative estimate of how much of the plane is bounded by the sides of the triangle. The area of an ordinary triangle can be found in five ways, using Heron's formula or using such variables as the base, side, angle and radius of the inscribed or circumscribed circle. The simplest formula for area is expressed as:
where a is the side of the triangle, h is its height.
The formula for calculating the area of a right triangle is even simpler:
where a and b are legs.
Working with our online calculator, you can calculate the area of a triangle using three pairs of parameters:
- two legs;
- leg and adjacent angle;
- leg and opposite angle.
In problems or everyday situations you will be given different combinations of variables, so this form of the calculator allows you to calculate the area of a triangle in several ways. Let's look at a couple of examples.
Real life examples
Ceramic tile
Let's say you want to cover the kitchen walls with ceramic tiles, which have the shape of a right triangle. In order to determine the consumption of tiles, you must find out the area of one cladding element and the total area of the surface being treated. Let's say you need to process 7 square meters. The length of the legs of one element is 19 cm, then the area of the tile will be equal to:
This means that the area of one element is 24.5 square centimeters or 0.01805 square meters. Knowing these parameters, you can calculate that to finish 7 square meters of wall you will need 7/0.01805 = 387 elements of facing tiles.
School task
Let's say in a school geometry problem you need to find the area of a right triangle, knowing only that the side of one leg is 5 cm, and the opposite angle is 30 degrees. Our online calculator comes with an illustration showing the sides and angles of a right triangle. If side a = 5 cm, then its opposite angle is angle alpha, equal to 30 degrees. Enter this data into the calculator form and get the result:
Thus, the calculator not only calculates the area of a given triangle, but also determines the length of the adjacent leg and hypotenuse, as well as the value of the second angle.
Conclusion
Right triangles are found in our lives literally on every corner. Determining the area of such figures will be useful to you not only when solving school assignments in geometry, but also in everyday and professional activities.
Depending on the type of triangle, there are several options for finding its area. For example, to calculate the area of a right triangle, use the formula S= a * b / 2, where a and b are its legs. If you want to find out the area of an isosceles triangle, then you need to divide the product of its base and height by two. That is, S= b*h / 2, where b is the base of the triangle, and h is its height.
Next, you may need to calculate the area of an isosceles right triangle. Here the following formula comes to the rescue: S = a* a / 2, where the legs “a” and “a” must necessarily have the same values.
Also, we often have to calculate the area of an equilateral triangle. It is found by the formula: S= a * h/ 2, where a is the side of the triangle, and h is its height. Or according to this formula: S= √3/ 4 *a^2, where a is the side.
How to find the area of a right triangle
Do you need to find the area of a right triangle, but the problem statement does not indicate the dimensions of two of its legs at once? Then we cannot use this formula (S= a * b / 2) directly.
Let's consider several possible solutions:
- If you do not know the length of one leg, but the dimensions of the hypotenuse and the second leg are given, then we turn to the great Pythagoras and, using his theorem (a^2+b^2=c^2), we calculate the length of the unknown leg, then use it to calculate the area of the triangle.
- If the length of one leg and the degree slope of the angle opposite it are given: we find the length of the second leg using the formula - a=b*ctg(C).
- Given: the length of one leg and the degree slope of the angle adjacent to it: to find the length of the second leg, we use the formula - a=b*tg(C).
- And lastly, given: the angle and length of the hypotenuse: we calculate the length of both of its legs using the following formulas - b=c*sin(C) and a=c*cos(C).
How to find the area of an isosceles triangle
The area of an isosceles triangle can be very easily and quickly found using the formula S= b*h / 2, but if one of the indicators is missing, the task becomes much more complicated. After all, it is necessary to perform additional actions.
Possible task options:
- Given: the length of one of the sides and the length of the base. Using the Pythagorean theorem, we find the height, that is, the length of the second leg. Provided that the length of the base divided by two is the leg, and the initially known side is the hypotenuse.
- Given: the base and the angle between the side and the base. We calculate the height using the formula h=c*ctg(B)/2 (do not forget to divide side “c” by two).
- Given: the height and the angle that was formed by the base and side: we use the formula c=h*tg(B)*2 to find the height, and multiply the result by two. Next we calculate the area.
- Known: the length of the side and the angle formed between it and the height. Solution: we use the formulas - c=a*sin(C)*2 and h=a*cos(C) to find the base and height, after which we calculate the area.
How to find the area of an isosceles right triangle
If all the data is known, then using the standard formula S= a* a / 2 we calculate the area of an isosceles right triangle, but if some indicators are not indicated in the problem, then additional actions are performed.
For example: we do not know the lengths of both sides (we remember that in an isosceles right triangle they are equal), but the length of the hypotenuse is given. Let's apply the Pythagorean theorem to find the same sides "a" and "a". Pythagorean formula: a^2+b^2=c^2. In the case of an isosceles right triangle, it transforms into this: 2a^2 = c^2. It turns out that to find leg “a”, you need to divide the length of the hypotenuse by the root of 2. The result of the solution will be the length of both legs of an isosceles right triangle. Next we find the area.
How to find the area of an equilateral triangle
Using the formula S= √3/ 4*a^2 you can easily calculate the area of an equilateral triangle. If the radius of the triangle's circumscribed circle is known, then the area can be found using the formula: S= 3√3/ 4*R^2, where R is the radius of the circle.
As you may remember from your school geometry curriculum, a triangle is a figure formed from three segments connected by three points that do not lie on the same straight line. A triangle forms three angles, hence the name of the figure. The definition may be different. A triangle can also be called a polygon with three angles, the answer will also be correct. Triangles are divided according to the number of equal sides and the size of the angles in the figures. Thus, triangles are distinguished as isosceles, equilateral and scalene, as well as rectangular, acute and obtuse, respectively.
There are a lot of formulas for calculating the area of a triangle. Choose how to find the area of a triangle, i.e. Which formula to use is up to you. But it is worth noting only some of the notations that are used in many formulas for calculating the area of a triangle. So, remember:
S is the area of the triangle,
a, b, c are the sides of the triangle,
h is the height of the triangle,
R is the radius of the circumscribed circle,
p is the semi-perimeter.
Here are the basic notations that may be useful to you if you completely forgot your geometry course. Below are the most understandable and uncomplicated options for calculating the unknown and mysterious area of a triangle. It is not difficult and will be useful both for your household needs and for helping your children. Let's remember how to calculate the area of a triangle as easily as possible:
In our case, the area of the triangle is: S = ½ * 2.2 cm * 2.5 cm = 2.75 sq. cm. Remember that area is measured in square centimeters (sqcm).
Right triangle and its area.
A right triangle is a triangle in which one angle is equal to 90 degrees (hence called right). A right angle is formed by two perpendicular lines (in the case of a triangle, two perpendicular segments). In a right triangle there can only be one right angle, because... the sum of all angles of any one triangle is equal to 180 degrees. It turns out that 2 other angles should divide the remaining 90 degrees, for example 70 and 20, 45 and 45, etc. So, you remember the main thing, all that remains is to find out how to find the area of a right triangle. Let's imagine that we have such a right triangle in front of us, and we need to find its area S.

1. The simplest way to determine the area of a right triangle is calculated using the following formula:

In our case, the area of the right triangle is: S = 2.5 cm * 3 cm / 2 = 3.75 sq. cm.
In principle, there is no longer any need to verify the area of the triangle in other ways, because Only this one will be useful and will help in everyday life. But there are also options for measuring the area of a triangle through acute angles.
2. For other calculation methods, you must have a table of cosines, sines and tangents. Judge for yourself, here are some options for calculating the area of a right triangle that can still be used:

We decided to use the first formula and with some minor blots (we drew it in a notebook and used an old ruler and protractor), but we got the correct calculation:
S = (2.5*2.5)/(2*0.9)=(3*3)/(2*1.2). We got the following results: 3.6=3.7, but taking into account the shift of cells, we can forgive this nuance.
Isosceles triangle and its area.
If you are faced with the task of calculating the formula for an isosceles triangle, then the easiest way is to use the main and what is considered to be the classical formula for the area of a triangle.

But first, before finding the area of an isosceles triangle, let’s find out what kind of figure it is. An isosceles triangle is a triangle in which two sides have the same length. These two sides are called lateral, the third side is called the base. Do not confuse an isosceles triangle with an equilateral triangle, i.e. a regular triangle with all three sides equal. In such a triangle there are no special tendencies to the angles, or rather to their size. However, the angles at the base in an isosceles triangle are equal, but different from the angle between equal sides. So, you already know the first and main formula; it remains to find out what other formulas for determining the area of an isosceles triangle are known.
A right triangle is a triangle in which one of the angles is 90°. Its area can be found if two sides are known. You can, of course, take the long route - find the hypotenuse and calculate the area using , but in most cases this will only take extra time. That is why the formula for the area of a right triangle looks like this:
![]()
The area of a right triangle is equal to half the product of the legs.
An example of calculating the area of a right triangle.
Given a right triangle with legs a= 8 cm, b= 6 cm.
We calculate the area: ![]()
Area is: 24 cm 2
The Pythagorean theorem also applies to a right triangle. – the sum of the squares of the two legs is equal to the square of the hypotenuse.
The formula for the area of an isosceles right triangle is calculated in the same way as for a regular right triangle.
An example of calculating the area of an isosceles right triangle:
Given a triangle with legs a= 4 cm, b= 4 cm. Calculate the area:
Calculate the area: = 8 cm 2
The formula for the area of a right triangle by the hypotenuse can be used if the condition is given one leg. From the Pythagorean theorem we find the length of the unknown leg. For example, given the hypotenuse c and leg a, leg b will be equal to:
Next, calculate the area using the usual formula. An example of calculating the formula for the area of a right triangle based on the hypotenuse is identical to that described above.
Let's consider an interesting problem that will help consolidate knowledge of formulas for solving a triangle.
Task: The area of a right triangle is 180 square meters. see, find the smaller leg of the triangle if it is 31 cm less than the second.
Solution: let's designate the legs a And b. Now let’s substitute the data into the area formula: we also know that one leg is smaller than the other a – b= 31 cm
From the first condition we obtain that
We substitute this condition into the second equation: ![]()
Since we found the sides, we remove the minus sign.
It turns out that the leg a= 40 cm, a b= 9 cm.