Offer - what is it in simple words?
Offer, offer... What is it? Many people, listening to the radio or reading magazines, come across this word. But not everyone understands its meaning. And therefore, your attention is invited to an article that tells in detail about the nature of the offer, its types, proper execution, as well as what happens for non-fulfillment of the points specified in this document.
Offer - what kind of "beast" is this? In simple words
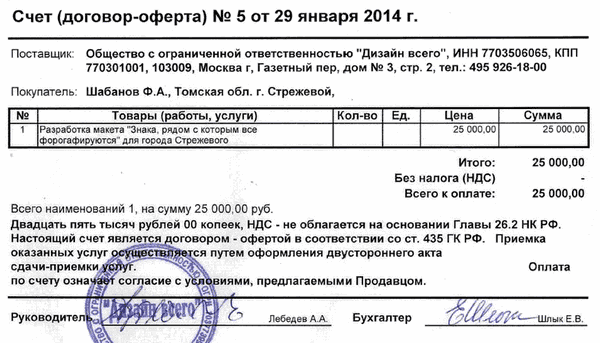
Simply put, an offer is a contract of sale. But the contract is not quite ordinary. In an offer, unlike a contract, only the most essential conditions for its conclusion are unilaterally prescribed. Whereas the contract contains very complete information about the services provided or the goods offered and is concluded by both parties.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to solve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to know how solve exactly your problem- contact a consultant:
+7 (499) 350-63-18
(Moscow)
+7 (812) 627-14-92
(St. Petersburg)
It's fast and for free!
However, if in Russia and European countries the essential terms of the offer are prescribed without fail, then Anglo-American law says that if the consumer has a clear understanding of the terms of the transaction, then these conditions may not be reflected on paper.
Another feature of such an agreement is that it enters into force immediately after the consent of the consumer, his acceptance, is received. In the same Anglo-American law, the unspoken "rule of the mailbox" operates. It consists in the following: an offer can be considered concluded when the consent to it is dropped directly into the mailbox of the person who submitted this offer.
By the way, silence, which is considered to be a sign of consent, is not considered consent in the case of an offer. That is, if the document itself is presented in writing, then the consent must be drawn up accordingly. However, due to the fact that different countries have slightly different traditions and laws, most often the offer clearly indicates the period during which an agreement of this type can be concluded.
How to make an offer?
Naturally, there are generally accepted rules for drawing up an offer, prescribed in the legislative framework. They are guided by all individuals and legal entities constituting an agreement of this type.
- Immediately before drawing up an offer, you need to thoroughly consider all the conditions. It is better to start with a draft, put the necessary marks on it, and then just proceed.
- In general, according to the type of preparation of the offer, there is a written and oral one. When using the first option, the offer can be presented both on the letterhead of the company, and in any form. Very often this is done: a blank sheet of paper / form is taken, the addressee is indicated in the upper right corner, and at the very bottom of the sheet, in the center, write “Offer”.
- Next is written, in fact, the commercial offer itself.
- Then, which is a very important point, the terms of the contract are indicated. It is on them that the final result depends. If this is some kind of service, then you need to describe its merits and why it is needed by the person who is offered the offer. If this is a product, then its name must be indicated (preferably according to GOST) and the main characteristics.
- After everything written in the document, the conditions for the provision of the service / delivery of the goods and the methods of payment are prescribed - non-cash or cash.
Main types of offers
Many believe that the offer is only public. This comes from the very frequent use in the media of the phrase "is not a public offer." This type of contract will be discussed later. People close to business and sales distinguish three more types of offers:
I would like to say a few words about the irrevocable offer, or rather about how the issuing companies use it. This is done in order to enable the shareholder to redeem the value of the security he has acquired.
With the help of irrevocable offers, by the way, both the issuer and the shareholder can control the value of shares and possible risks - interest and credit, respectively. The date of the bond offer is negotiated at the initial stage and then does not change. The cost of the bond and the procedure for its redemption are determined by the investor and the issuer.
Public offer rules
The public offer differs significantly from the previous ones. It can be distinguished from the flow of documents according to three main features:
- in an offer of this type, all essential conditions are included without fail;
- persons interested in concluding such an agreement must understand what responsibility they take;
- the person signing the offer fully agrees with all its conditions, without discussing them.
What does not apply to a public offer?
In the laws of almost all countries, advertising of any products and services is not considered a public offer, as it does not contain specific proposals. If there are any, then such advertising is recognized as an offer and, according to the law, is valid for two months from the date of its creation (however, the advertiser himself can set any period of validity of the offer). With such a formulation of the question, an agreement of this type can be concluded, but all responsibility for its execution lies with the advertiser / seller.
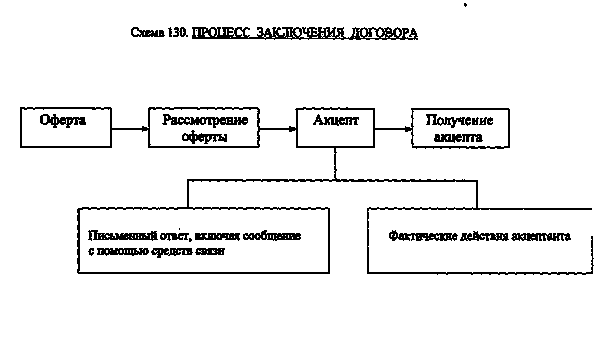
Once again about acceptance
As already mentioned, acceptance is the consent of a potential buyer of a product / service. Acceptance can be presented both on paper and orally. Also, acceptance is any action on the part of the buyer of the goods/services that partially meets the terms of the offer.
But legally, an offer can be concluded if the parties fulfill all the clauses of the offer in full. As for any seals and stamps, they are affixed only at the request of the parties.
What are violations of a public offer?
In general, any offer, including a public offer, is interpreted by the laws of different countries as a legal document. And therefore, for violation or any non-compliance with the conditions specified in the public offer, it is subject to rather severe sanctions.
Violation of the offer may be a banal overestimation of the cost of goods. That is, if goods are taken at the retail premises at the same price, and a check with a completely different price breaks through at the checkout, then the buyer has the right to contact the store administration in order to resolve the situation.
In this case, the probability of selling the goods at the original cost is very high.
If it “didn’t grow together” with the management of the store, then there is an option to report a violation by making an appropriate entry in the Book of Complaints and Suggestions. In principle, you can go even further: take a photo of the price tag with the declared price, attach a cashier's check to it with the very statement about the violation of the Rules of Trade and send it all to Rospotrebnadzor.
But, as a rule, such drastic measures do not reach: the administration meets halfway, and the goods are sold at the original price. With expensive goods, the situation is a little more complicated. This is where the case could go to court. In most cases, representatives of Themis take the side of the consumer and satisfy the claim. Here the deceived buyer wins doubly: not only is he returned the cost difference of the goods, they also compensate for moral damage in material terms.
Conclusion
So, with knowledge of the signs and rules of a public offer, you can always defend your rights in any organization. By the way, it also happens that persons who have violated the contract of a public offer begin to "swing rights" and threaten. If such things happen, it is only from impotence: the offending side understands that it is not right, and indulges in "everything bad". There is no need to be afraid of this: the law will be on your side in any case, because the main rule of trade and the provision of services is that the client is always right.
Except, of course, in cases where any conditions in favor of the seller of goods / services are clearly and very clearly spelled out in the offer agreement.
In contact with